
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.
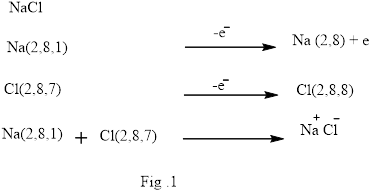
Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
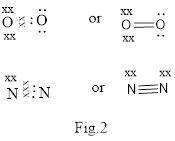
(b)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that contains various constituent particles (atoms, ions and molecules) in different chemical species. The chemical bond is off many types. Ionic or electrovalent bond, covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond.
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.

Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
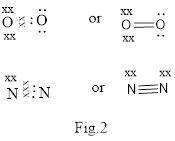
(c)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that contains various constituent particles (atoms, ions and molecules) in different chemical species. The chemical bond is off many types. Ionic or electrovalent bond, covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond.
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.

Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
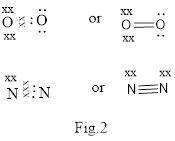
(d)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that contains various constituent particles (atoms, ions and molecules) in different chemical species. The chemical bond is off many types. Ionic or electrovalent bond, covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond.
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.

Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
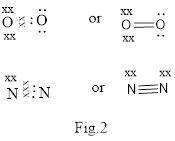
(d)
Interpretation:
To label each bond in the compounds as ionic or covalent.
Concept introduction:
In chemistry chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that contains various constituent particles (atoms, ions and molecules) in different chemical species. The chemical bond is off many types. Ionic or electrovalent bond, covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond.
Ionic bond is the bond that is formed when one or more electrons from the valence shell of an atom are completely transfer to another atom valence shell. Formation of ionic bond is shown below in Fig.1.

Covalent bond is formed between two atoms by mutual sharing of electrons pairs between them. By mutual sharing of electron pairs the atom attains the stable noble gas configuration. Thus in the covalent bonding the combining atom have equal claim of the shared electron pair. Illustration of covalent bond is shown below in Fig.2.
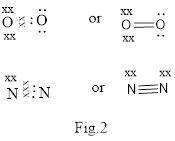
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Which of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forwardDraw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
- Draw the products of the hydrolysis reaction between the ester molecule and water. Determine the products of the following reaction.arrow_forwardWhat is the unsaturation number for compounds with the formula C₂H₁₂Cl₂? O õ õ o o 4 3arrow_forwardIndicate the product obtained (formula). F3C. CF3 Br NH2 NH OMe K2CO3, DABCO, DMFarrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





