
Concept explainers
Zingerone gives ginger its pungent taste.
a. What is the molecular formula of zingerone?
b. How many lone pairs are present?
c. Draw a skeletal structure.
d. How many
e. What orbitals are used to form each indicated bond
(a)
Interpretation: The molecular formula of zingerone is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
Answer to Problem 1.38P
The molecular formula of zingerone is
Explanation of Solution
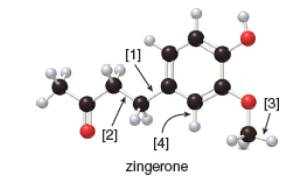
The given ball-and-stick model of zingerone is,
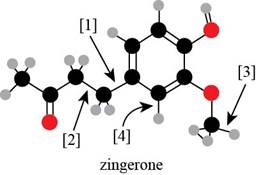
Figure 1
In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
In the above model,
• There are three red balls. Thus, there are three
• There are eleven black balls. Thus, there are eleven
• There are fourteen grey balls. Thus, there are fourteen
Hence, the molecular formula of zingerone is
The molecular formula of zingerone is
(b)
Interpretation: The number of lone pairs in zingerone is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In a compound or molecule, the lone pairs represent number of unshared electrons on atom. An atom may or may not have unshared electrons. For example, carbon and hydrogen atoms have no lone pair but each oxygen atom has two lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 1.38P
There are total
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of citric acid is
There are total
(c)
Interpretation: A skeletal structure of zingerone is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
Answer to Problem 1.38P
A skeletal structure of zingerone is,
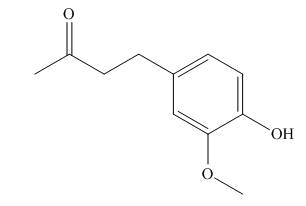
Explanation of Solution
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
A skeletal structure of zingerone is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond.
(d)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 1.38P
There are seven
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of zingerone is,
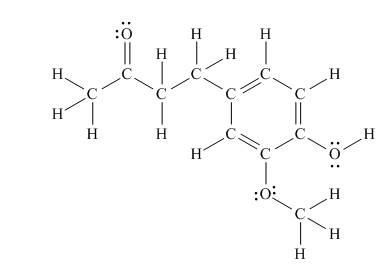
Figure 3
According to the rules of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
The
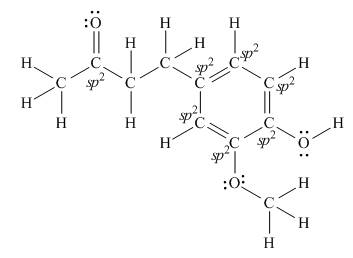
Figure 4
Thus, there are seven
There are seven
(e)
Interpretation: The orbitals that are used to form each indicated bond is to be stated.
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 1.38P
Bond
Explanation of Solution
Bond [1] represents bonding between the carbon atom of benzene
Thus,
Bond
Bond
Thus,
Bond
Thus, bond
The number of surrounded group around any atom predicts the hybridization of that atom, which is further helpful in predicting the orbitals involved in the bond formation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
HUMAN ANATOMY
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the cured electron-pushing arrows for thw following reaction or mechanistic steps. be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond making stepsarrow_forwardUsing the graphs could you help me explain the answers. I assumed that both graphs are proportional to the inverse of time, I think. Could you please help me.arrow_forwardSynthesis of Dibenzalacetone [References] Draw structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the enone below. Question 1 1 pt Question 2 1 pt Question 3 1 pt H Question 4 1 pt Question 5 1 pt Question 6 1 pt Question 7 1pt Question 8 1 pt Progress: 7/8 items Que Feb 24 at You do not have to consider stereochemistry. . Draw the enolate ion in its carbanion form. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. ⚫ Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu. ? 4arrow_forward
- Shown below is the mechanism presented for the formation of biasplatin in reference 1 from the Background and Experiment document. The amounts used of each reactant are shown. Either draw or describe a better alternative to this mechanism. (Note that the first step represents two steps combined and the proton loss is not even shown; fixing these is not the desired improvement.) (Hints: The first step is correct, the second step is not; and the amount of the anhydride is in large excess to serve a purpose.)arrow_forwardHi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forwardDraw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.025 M HCl is titrated with 0.035 M KOH. What volume of KOH is needed?arrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.025 M HCl is titrated with 0.035 M KOH. What volume of KOH is needed?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M HCl is titrated with 37.75 mL of NaOH. What is the molarity of the NaOH?arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning




