
Organic Chemistry
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780073402772
Author: Janice G. Smith
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.63P
Draw in all the carbon and hydrogen atoms in each molecule.
a. 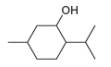 c.
c. 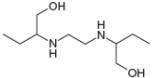
methanol ethambutol
(isolated from peppermint oil) (drug used to treat tuberculosis)
b. 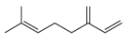 d.
d. 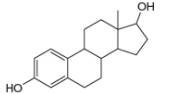
myrcene estradiol
(isolated from bayberry) (a female sex harmone)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4. True or false: This skeletal structure represents a saturated fatty acid. Ini to
0
fale) me
OH
faistong st
By malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 5-Methyl-2-hexanone (with the formulas of the compounds).
QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' by filling in all the empty green boxes
*The values are all provided in the first photo attached*
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 1 - While the most common isotope of nitrogen has a...Ch. 1 - Label each bond in the following compounds as...Ch. 1 - How many covalent bonds are predicted for each...Ch. 1 - Draw a valid Lewis structure for each species. a....Ch. 1 - Draw an acceptable Lewis structure for each...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.6PCh. 1 - Draw a Lewis structure for each ion. a. CH3Ob....Ch. 1 - Draw Lewis structures for each molecular formula....Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.9PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.10P
Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.11PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.12PCh. 1 - Draw a second resonance structure for each...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.14PCh. 1 - Draw a second resonance structure for nitrous...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.16PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.17PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.18PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.19PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.20PCh. 1 - Simplify each condensed structure by using...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.22PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.23PCh. 1 - Convert each skeletal structure to a complete...Ch. 1 - Draw in all hydrogens and lone pairs on the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.26PCh. 1 - What orbitals are used to form each of the CC, and...Ch. 1 - What orbitals are used to form each bond in the...Ch. 1 - Determine the hybridization around the highlighted...Ch. 1 - Classify each bond in the following molecules as ...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.31PCh. 1 - Rank the following atoms in order of increasing...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.33PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.34PCh. 1 - Provide the following information about...Ch. 1 - Use the ball-and-stick model to answer each...Ch. 1 - Citric acid is responsible for the tartness of...Ch. 1 - Zingerone gives ginger its pungent taste. a.What...Ch. 1 - Two radioactive isotopes of iodine used for the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.40PCh. 1 - Assign formal charges to each carbon atom in the...Ch. 1 - Assign formal charges to each N and O atom in the...Ch. 1 - Draw one valid Lewis structure for each compound....Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.44PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.45PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.46PCh. 1 - Draw all possible isomers for each molecular...Ch. 1 - 1.45 Draw Lewis structures for the nine isomers...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.49PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.50PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.51PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.52PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.53PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.54PCh. 1 - Draw all reasonable resonance structures for each...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.56PCh. 1 - Rank the resonance structures in each group in...Ch. 1 - 1.56 Consider the compounds and ions with curved...Ch. 1 - 1.57 Predict all bond angles in each...Ch. 1 - Predict the geometry around each indicated atom....Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.61PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.62PCh. 1 - Draw in all the carbon and hydrogen atoms in each...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.64PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.65PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.66PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.67PCh. 1 - Each of the following condensed or skeletal...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.69PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.70PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.71PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.72PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.73PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.74PCh. 1 - Two useful organic compounds that contain Cl atoms...Ch. 1 - Use the symbols + and to indicate the polarity of...Ch. 1 - Label the polar bonds in each molecule. Indicate...Ch. 1 - Answer the following questions about acetonitrile...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.79PCh. 1 - The principles of this chapter can be applied to...Ch. 1 -
a. What is the hybridization of each N atom in...Ch. 1 - 1.77 Stalevo is the trade name for a medication...Ch. 1 - 1.78 and are two highly reactive carbon...Ch. 1 - 1.79 The N atom in (acetamide) is hybridized,...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.85PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.86PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.87PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.88PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.89PCh. 1 - Prob. 1.90P
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How could you separate a mixture of the following compounds? The reagents available to you are water, either, 1...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
45. Calculate the mass of nitrogen dissolved at room temperature in an 80.0-L home aquarium. Assume a total pre...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
What process causes the Mediterranean intermediate Water MIW to become more dense than water in the adjacent At...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Why are mutants used as test organisms in the Ames test?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the formula for 3-chlorobenzoic acetic anhydride.arrow_forwardBy malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 2-methylbutanoic acid (indicate the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forwardObtain 2-methylbutanoic acid by malonic or acetylacetic synthesis (indicate the formulas of the compounds involved).arrow_forward
- EFFICIENTS SAMPLE READINGS CONCENTRATIONS Pigiadient) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) 58 6.274 3.898 301.7 151.2 14150 5.277 3.865 348.9 254.8 B 5.136 3.639 193.7 85.9 605 4.655 3.041 308.6 199.6 05 5.135 3.664 339.5 241.4 0139 4.676 3.662 160.6 87.6 90148 5.086 3.677 337.7 242.5 0092 6.348 3.775 464.7 186.4 PART3 5.081 3.908 223.5 155.8 5.558 3.861 370.5 257.1 4.922 3.66 326.6 242.9 4.752 3.641 327.5 253.3 50 5.018 3.815 336.1 256.0 84 4.959 3.605 317.9 216.6 38 4.96 3.652 203.8 108.7 $3 5.052 3.664 329.8 239.0 17 5.043 3.767 221.9 149.7 052 5.058 3.614 331.7 236.4 5.051 4.005 211.7 152.1 62 5.047 3.637 309.6 222.7 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 995 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 04 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 16 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 0.011 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 AVERAGE STDEV COUNT 95% CI Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH₃COCH₃) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH), applying heat to them produces an aldol condensation of the two compounds. If this is correct, draw the formula for the final product.arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH3COCH3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH); if we apply heat (A), what product(s) are obtained?arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardYou need to make a buffer by dissolving benzoic acid and sodium benzoate in water. What is the mass of benzoic acid that you would weigh out, in mg, to create 50 mL of a buffer at pH = 4.7 that will change pH no more than 0.10 units with the addition of 0.001 moles of acid or base? Enter just the answer without the units (mg) - just the number will do!arrow_forwardDraw the formula for 3-isopropylcyclopentane-1-carbonyl chloride.arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardComplete the following reactions- hand written pleasearrow_forwardGive the organic product: O A O B Ос ○ D -NH–CH3 + CH3 CH3 NEN C ? A CH3 CH3 NH- CH3 B CH3 CH3 N=N- C CH3 CH3 N=NNH CH3 D CH3 N=N CH3 NHCH3 LNH CHOarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY