
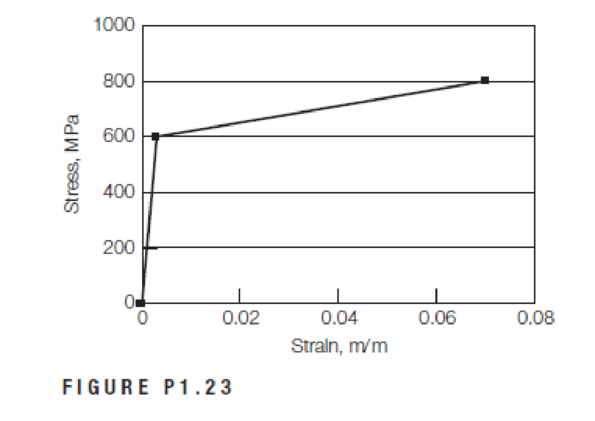
An elastoplastic material with strain hardening has the stress–strain relationship shown in Figure P1.23. The yield point corresponds to 600 MPa stress and 0.003 m/m strain.
a. If a bar made of this material is subjected to a stress of 650 MPa and then released, what is the permanent strain?
b. What is the percent increase in yield strength that is gained by the strain hardening shown in part (a)?
c. After strain hardening, if the material is subjected to a stress of 625 MPa, how much strain is obtained? Is this strain elastic, permanent, or a combination of both?
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 1 Solutions
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers (4th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
- The beam shown will be constructed from a standard steel W-shape using an allowable bending stress of 33.6 ksi. Assume P = 70 kips. L₁ = 2.2 ft, and L2 = 6.6 ft. (a) Determine the minimum section modulus required for this beam. (b) From the table below, select the lightest W shape that can be used for this beam. (c) What is the total weight of the steel beam itself (ie, not including the loads that are carried by the beam)? Lu B D L2 L₁ Wide-Flange Sections or W Shapes-U.S. Customary Units x x be Web Area Depth thickness Flange width Flange thickness Designation A d Tw by 4 S₁ و" in.² in. in. in. in. in,4 in.³ in. in.4 in,³ in. W24 x 94 27.7 24.3 0.515 9.07 0.875 2700 222 9.87 109 24.0 1.98 24 x 76 22.4 23.9 0.440 8.99 0.680 2100 176 9.69 82.5 18.4 1.92 24 x 68 20.1 23.7 0.415 8.97 0.585 1830 154 9.55 70.4 15.7 1.87 24 x 55 16.2 23.6 0.395 7.01 0.505 1350 114 9.11 29.1 8.30 1.34 W21 x 68 20.0 21.1 0.430 8.27 0.685 1480 140 8.60 64.7 15.7 1.80 21 x 62 18.3 21.0 0.400 8.24 0.615 1330 127…arrow_forwardA composite beam is made of two brass [E=114 GPa] bars bonded to two aluminum [E = 74 GPa] bars, as shown. The beam is subjected to a bending moment of 335 N-m acting about the z axis. Using a = 5 mm, b = 30 mm, c = 10 mm, and d = 20 mm, calculate (a) the maximum bending stress in the aluminum bars. (b) the maximum bending stress in the brass bars. N Aluminum C Brass Brass Aluminum b Answers: (a) σal= (b) Obr= a a MPa MPaarrow_forwardA standard steel pipe (D = 3.500 in.; d = 3.068 in.) supports a concentrated load of P = 630 lb as shown. The span length of the cantilever beam is L = 4 ft. Determine the magnitude of the maximum horizontal shear stress in the pipe. 720 psi 761 psi 508 psi 564 psi 667 psi L Pipe cross section.arrow_forward
- A beam is subjected to equal bending moments of M₂ = 59 kip-ft. The cross-sectional dimensions are b₁ = 7.5 in., d₁ = 1.4 in., b₂ = 0.55 in., d₂ = 5.0 in., b3 = 3.2 in., and d3 = 1.5 in. Determine: (a) the centroid location (measured with respect to the bottom of the cross-section), the moment of inertia about the z axis, and the controlling section modulus about the z axis. (b) the bending stress at point H. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. (c) the bending stress at point K. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. (d) the maximum bending stress produced in the cross section. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. M₂ Z M₂ Answer: (a) y= i Iz= in. in.4 S= i on,3 (b) σH= i ksi (c) OK = i ksi (d) σmax= ksi K b₁ d₁ H b₂ b3 d₂ d3arrow_forwardA cantilever timber beam with a span of L = 2.9 m supports a uniformly distributed load w. The beam width is b = 300 mm and the beam height is h = 160 mm. The allowable bending stress of the wood is 7 MPa. Determine the magnitude of the maximum load w that may be carried by the beam. Answer: w= I i kN/m.arrow_forwardAW18 × 40 standard steel shape is used to support the loads shown on the beam. Assume P = 24 kips, w = 4.4 kips/ft, LAB = 4.6 ft, LBC = 4.6 ft, and LCD = 15.0 ft. Determine the magnitude of the maximum bending stress in the beam. B C Answer: LAB ✓ LBC Omax i ksi W LCD xarrow_forward
- A simply supported timber beam carries a uniformly distributed load of w = 3 kN/m. Determine the magnitude of the largest horizontal shear stress at point H, which is 60 mm above the centroid, anywhere along the length of the beam. 293 kPa 234 kPa 252 kPa 321 kPa ○ 163 kPa พ 4 m 300 mm B 1 m 100 mm K 60 mm * 75 mmarrow_forwardThe "New Jersey" barrier is commonly used during highway construction. Determine its weight per foot of length if it is made from plain stone concrete. 4 in. 75°- 12 in. 55° 6 in. -24 inarrow_forwardThe "New Jersey" barrier is commonly used during highway construction. Determine its weight per foot of length if it is made from plain stone concrete. 4 in. 75°- 55° 12 in. 6 in. 24 inarrow_forward
- The prestressed concrete girder is made from plain stone concrete and four -in. cold form steel reinforcing rods. Determine the dead weight of the girder per foot of its length. 8 in. 6 in. 20 in. 6 in. 8 in. 4 in. 6 in. 4 in.arrow_forwardThe floor of a building, shown in Fig. (a), is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of 3.5 kPa over its surface area. Determine the loads acting on all the members of the floor system. AI Column Floor beam B Slab C D 3 at 4 m = 12 m Floor beam E F Girder GT -9 m. (a) Framing Planarrow_forwardCommercial trucks begin to arrive at a seaport entry plaza at 7:50 A.M., at the rate of λ(t) = 6.3 – 0.25t[λ(t) is in veh/min and t is in minutes]. The plaza opens at 8:00 A.M. For the first 10 minutes, one processing booth is open. After the first 10 minutes until the queue clears, two processing booths are open. Each booth processes trucks at a uniform rate of two per minute. What is the average delay per vehicle, the maximum queue length, and the average queue length?arrow_forward
 Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning



