
Concept explainers
Interpretation: Whether the answers in CTQ are in agreement with Memorization Task NW1.2 given below or not should be given.
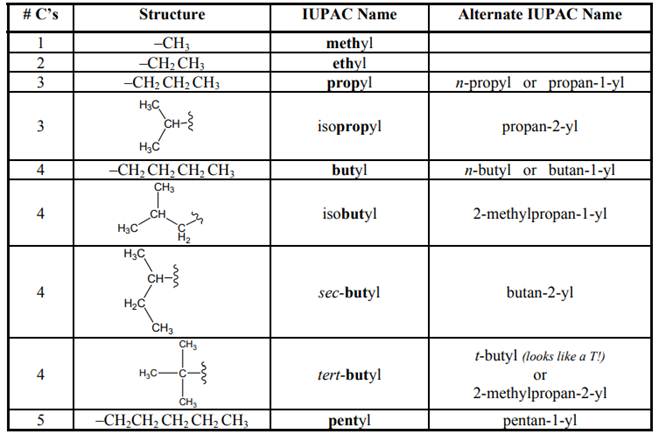
Concept introduction: Systematic way to name different organic compounds is
Rules for nomenclature of
1 The longest continuous carbon chain is identified first and named in accordance with number of carbon atoms present in it. For example, hydrocarbon with one carbon atom has prefix “meth”, that with two carbon atoms has prefix “eth”, that with three carbon atoms has prefix “prop” and so on. Suffix used for alkanes is “ane.”
2. Substituents attached to parent carbon chain are to be identified. These are named by removal of single hydrogen atom from carbon chain end and named by replacement of suffix “ane” by “yl.” For example if
3. Carbons of parent chain are named in such way that substituents acquire the lowest numbers.
4. If same substituent is present more than one time in molecule, it is represented by prefix “di”, “tri” and so on. It depends on number of times substituent occurs in molecule.
5. If two or more substituents are present in molecule, these are named in alphabetical order.
6. If carbon chains of same length exist in same molecule, chain with the largest number of side chains, followed by lowest number to substituents, chain with the greatest number of carbon atoms in smaller chain and chain with the least branched side chains are preferred over other ones.
7. Prefix “cyclo” is used if cyclic alkane is present in molecule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter NW1 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- Draw a Newman projection for the molecule below from the perspective indicated. Which of the groups (letters A-H) are methyl groups? CH3 H H H A H B ☑ >> H. ABCDEFG I H -H CH3 G D CH F E Numeric 4 points How many gauche interactions exist in the conformation shown in the previous problem? 1arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Would the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward13) When solid barium phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of barium ions to phosphate ions would be: a. 1:1 b. 2:3 c. 3:2 d. 2:1 14) The pH of a 0.05 M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is 15) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of KOH at 25°C isarrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
