
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The parent name in each chemical name given below should be underlined.
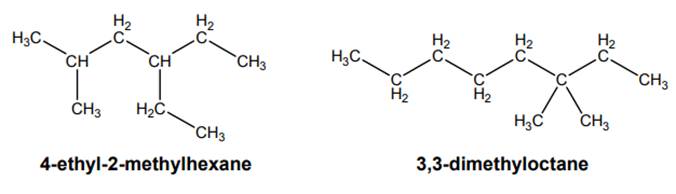
Concept introduction: Systematic way to name different organic compounds is
Rules for nomenclature of
1 The longest continuous carbon chain is identified first and named in accordance with number of carbon atoms present in it. For example, hydrocarbon with one carbon atom has prefix “meth”, that with two carbon atoms has prefix “eth”, that with three carbon atoms has prefix “prop” and so on. Suffix used for alkanes is “ane.”
2. Substituents attached to parent carbon chain are to be identified. These are named by removal of single hydrogen atom from carbon chain end and named by replacement of suffix “ane” by “yl.” For example if
3. Carbons of parent chain are named in such way that substituents acquire the lowest numbers.
4. If same substituent is present more than one time in molecule, it is represented by prefix “di”, “tri” and so on. It depends on number of times substituent occurs in molecule.
5. If two or more substituents are present in molecule, these are named in alphabetical order.
6. If carbon chains of same length exist in same molecule, chain with the largest number of side chains, followed by lowest number to substituents, chain with the greatest number of carbon atoms in smaller chain and chain with the least branched side chains are preferred over other ones.
7. Prefix “cyclo” is used if cyclic alkane is present in molecule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter NW1 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- The following equations represent the formation of compound MX. What is the AH for the electron affinity of X (g)? X₂ (g) → 2X (g) M (s) → M (g) M (g) M (g) + e- AH = 60 kJ/mol AH = 22 kJ/mol X (g) + e-X (g) M* (g) +X (g) → MX (s) AH = 118 kJ/mol AH = ? AH = -190 kJ/mol AH = -100 kJ/mol a) -80 kJ b) -30 kJ c) -20 kJ d) 20 kJ e) 156 kJarrow_forwardA covalent bond is the result of the a) b) c) d) e) overlap of two half-filled s orbitals overlap of a half-filled s orbital and a half-filled p orbital overlap of two half-filled p orbitals along their axes parallel overlap of two half-filled parallel p orbitals all of the abovearrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forward
- Which one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forwardAll of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forwardA student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forward
- Ppplllleeeaaasssseeee helllppp wiithhh thisss Organic chemistryyyyyy I talked like this because AI is very annoyingarrow_forwardName the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH₂ || CH3-C-NH2 0 ။ CH3-C-CH₂ CH=O–CH=CH, CH₂ HO CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 family amine Darrow_forward1b. Br LOHarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
