
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
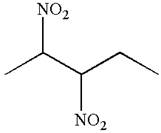
In this molecule, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has five carbon atoms. Hence, the root is pentane. The parent chain has two identical substituents; thus the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
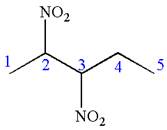
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
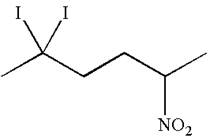
In this molecule, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has six carbon atoms. Hence, the root is hexane. The parent chain has three substituents; thus the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
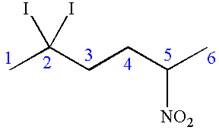
The substituents are arranged in an alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
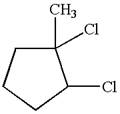
In this molecule, the five carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopentane. The ring has three substituents; thus, the ring is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
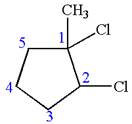
The substituents are arranged in alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms or the ring structure. The name of the substituent attached to the parent ring is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The parent ring is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
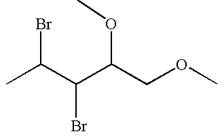
In this molecule, the five carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopentane. The parent chain has four substituents; thus, the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants according to alphabetical order.
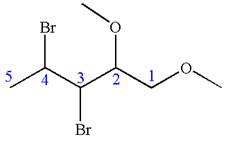
The substituents are arranged in alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
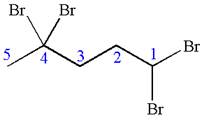
The given molecule is
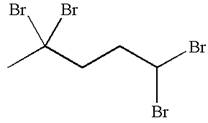
In this molecule, the five carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopentane. The parent chain has four identical substituents; thus, the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants according to alphabetical order.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(f)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms or the ring structure. The name of the substituent attached to the parent ring is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The parent ring is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents in a way to provide the lowest set of locants.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
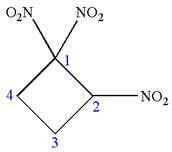
The given molecule is
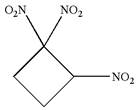
In this molecule, the four carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclobutane. The ring has three identical substituents; thus, the ring is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(g)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms or the ring structure. The name of the substituent attached to the parent ring is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The parent ring is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
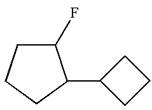
In this molecule, the five carbons ring is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopentane. The ring has two substituents; thus, the ring is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants according to alphabetical order.
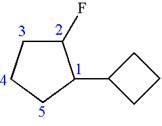
The substituents are arranged in alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(h)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
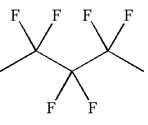
In this molecule, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has five carbon atoms. Hence, the root is pentane. The parent chain has six identical substituents; thus, the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
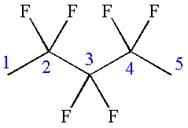
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(i)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
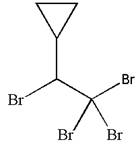
In this molecule, the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has two carbon atoms. Hence, the root is ethane. The parent chain has five substituents; thus, the chain is numbered so as to provide the lowest set of locants.
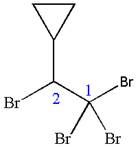
The substituents are arranged in alphabetical order with respective locant.
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
(j)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The root name of the molecule is the name of the alkane, which depends on the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. The name of the substituent attached to the parent chain is written as a prefix to the left side of the root. The chain is numbered such that the carbon atom to which the substituent is attached gets the lowest possible number. This number is written on the left side of the substituent and separated by a hyphen. If more than one substituent is present, then the numbering is determined by the alphabetical order of substituents.
Answer to Problem A.46P
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is
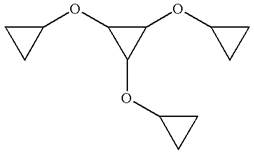
In this molecule, the middle ring of three carbons is a parent. Hence, the root is cyclopropane. The ring has three identical substituents.
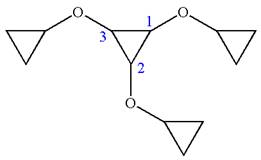
Hence, the IUPAC name is
The IUPAC name of the given molecule is written as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter A Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- The diagram shows two metals, A and B, which melt at 1000°C and 1400°C. State the weight percentage of the primary constituent (grains of C) that would be obtained by solidifying a 20% alloy of B. 1000°C a+L L+C 900°С 12 α a+C 45 1200 C L+y 140096 C+Y a+ß 800°C 700°C C+B 96 92 a+B 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 A % peso B Barrow_forward8. Choose the compound that will produce the spectrum below and assign the signals to the corresponding protons. 2 4 3 ō (ppm) OH 4 6 6 СОН 2 1 0arrow_forward7. Assign all of the protons on the spectrum below. A B 2 C E 2 1 3 6 4 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
- e. If (3R,4R)-3,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylhexane and (3R,4S)-3,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylhexane are in a solution at the same concentration, would this solution be expected to rotate plane polarized light (that is, be optically active)? Please provide your reasoning for your answer. [If you read this problem carefully, you will not need to draw out the structures to arrive at your answer...]arrow_forward1. How many neighbors does the proton that produces the multiplet below have? 2. 3. اللـ Draw a partial structure from the multiplet below. (The integration of the multiplet is 6) M Using the additivity constants found in appendix G of your lab manual, calculate the approximate chemical shifts of the protons indicated below. (Show your work!!!) B A Br SHarrow_forward1) Suppose 0.1 kg ice at 0°C (273K) is in 0.5kg water at 20°C (293K). What is the change in entropy of the ice as it melts at 0°? To produce the original "water gas" mixture, carbon (in a combustible form known as coke) is reacted with steam: 131.4 kJ + H20(g) + C(s) → CO(g) + H2(g) From this information and the equations in the previous problem, calculate the enthalpy for the combustion or carbon to form carbon dioxide. kindly show me how to solve this long problem. Thanksarrow_forward
- 4. An 'H-NMR of a compound is acquired. The integration for signal A is 5692 and the integration for signal B is 25614. What is the simplest whole number ratio of protons for signals A and B? (Show your work!!!) 5. Assign the carbons in the NMR below as either carbonyl, aromatic, or alkyl. 200 150 100 50 ō (ppm) 1arrow_forwardSpeaking of composite materials, indicate the correct option:(A). Composite materials can only be: metal-polymer or polymer-polymer.(B). Composite materials can be made up of particles, but not fibers or sheets.(C). When the reinforcing particles are uniformly distributed in a composite material, there may be a greater tendency for it to have isotropic properties.(D). None of the above is correct.arrow_forwardIf we are talking about viscoelastic modulus or viscoelastic relaxation modulus in polymers, indicate the correct option.(A). It reports the variation of elastic behavior as a function of time.(B). It is only useful for defining its glass transition temperature.(C). It only allows us to define the polymer degradation temperature.(D). Neither option is correct.arrow_forward
- When natural light falls perpendicularly on a material A, it has a reflectivity of 0.813%. Indicate the value of the refractive index.arrow_forwardIn piezoelectricity and piezoelectric ceramics, one of the following options is false:(A). Piezoelectricity allows an electrical signal to be transformed into a mechanical one.(B). PbZrO3 is a well-known piezoelectric ceramic.(C). Piezoelectricity and ferroelectricity in general have no relationship.(D). One of the applications of piezoelectricity is sonar.arrow_forward(30 MARKS) Give the major product(s ) formed including relevant stereochemistry or the complete reaction conditions for the following reactions. More than one step may be required for each reaction arrow, in which case the steps must be numbered 1), 2) etc. (2 marks each box) h) i) h) OH i) HO H3PO4, heat 2 Brarrow_forward

 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax



