
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The reaction of alcohols with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergoes SN1 substitution reaction.
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
SN2 reaction:
The alcohols are reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding substitution product. Primary alcohol undergoes SN2 substitution reaction than secondary alcohol than tertiary alcohol because SN2 reaction is simultaneous reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction, the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
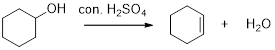
The stability of carbocation is given below,
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary and primary.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product should be identified.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohols is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergoes SN1 substitution reaction.
(e)
Interpretation:
The major product should be identified.
Concept introduction:
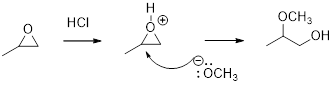
In the presence of acid catalyst, this reaction takes place through partial SN1 and partial SN2 pathway.
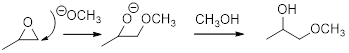
Epoxides are reactive, methoxide ion attacks the Epoxides in a less sterically hindered position which forms the alkoxide ion, and then it gets proton from alcohol which form the product.
(f)
Interpretation:
The major product should be identified.
Concept introduction:

In the presence of acid catalyst, this reaction takes place through partial SN1 and partial SN2 pathway. It is not a pure SN1 reaction because a carbocation is not formed fully and not a pure SN2 reaction because the leaving group begins to depart before the compound is attacked by the nucleophile. Epoxides are reactive; Epoxides get protonated followed by alcohol attacks to the stable carbocation and form the product.
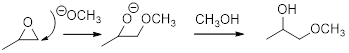
Epoxides are reactive, methoxide ion attacks the Epoxides in a less sterically hindered position which forms the alkoxide ion, and then it gets proton from alcohol which form the product. When a nucleophile attacks an unprotonated epoxide, the reaction is a pure SN2 reaction.
Note: Under acidic conditions, the nucleophile preferentially attacks the more substuituted ring carbon. Under Basic conditions, the nucleophile preferentially attacks the less substuituted ring carbon.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- Transmitance 3. Which one of the following compounds corresponds to this IR spectrum? Point out the absorption band(s) that helped you decide. OH H3C OH H₂C CH3 H3C CH3 H3C INFRARED SPECTRUM 0.8- 0.6 0.4- 0.2 3000 2000 1000 Wavenumber (cm-1) 4. Consider this compound: H3C On the structure above, label the different types of H's as A, B, C, etc. In table form, list the labeled signals, and for each one state the number of hydrogens, their shifts, and the splitting you would observe for these hydrogens in the ¹H NMR spectrum. Label # of hydrogens splitting Shift (2)arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure of C2H4Oarrow_forward
- a) 5. Circle all acidic (and anticoplanar to the Leaving group) protons in the following molecules, Solve these elimination reactions, and identify the major and minor products where appropriate: 20 points + NaOCH3 Br (2 productarrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardDr. Mendel asked his BIOL 260 class what their height was and what their parent's heights were. He plotted that data in the graph below to determine if height was a heritable trait. A. Is height a heritable trait? If yes, what is the heritability value? (2 pts) B. If the phenotypic variation is 30, what is the variation due to additive alleles? (2 pts) Offspring Height (Inches) 75 67.5 60 52.5 y = 0.9264x + 4.8519 55 60 65 MidParent Height (Inches) 70 75 12pt v V Paragraph B IUA > AT2 v Varrow_forward
- Experiment: Each team will be provided with 5g of a mixture of acetanilide and salicylic acid. You will divide it into three 1.5 g portions in separate 125 mL Erlenmeyer flasks savıng some for melting point analysis. Dissolve the mixture in each flask in ~60mL of DI water by heating to boiling on a hotplate. Take the flasks off the hotplate once you have a clear solution and let them stand on the bench top for 5 mins and then allow them to cool as described below. Sample A-Let the first sample cool slowly to room temperature by letting it stand on your lab bench, with occasional stirring to promote crystallization. Sample B-Cool the second sample 1n a tap-water bath to 10-15 °C Sample C-Cool the third sample in an ice-bath to 0-2 °C Results: weight after recrystalization and melting point temp. A=0.624g,102-115° B=0.765g, 80-105° C=1.135g, 77-108 What is the percent yield of A,B, and C.arrow_forwardRel. Intensity Q 1. Which one of the following is true of the compound whose mass spectrum is shown here? Explain how you decided. 100 a) It contains chlorine. b) It contains bromine. c) It contains neither chlorine nor bromine. 80- 60- 40- 20- 0.0 0.0 TT 40 80 120 160 m/z 2. Using the Table of IR Absorptions how could you distinguish between these two compounds in the IR? What absorbance would one compound have that the other compound does not? HO CIarrow_forwardIllustrate reaction mechanisms of alkenes with water in the presence of H2SO4, detailing each step of the process. Please show steps of processing. Please do both, I will thumb up for sure #1 #3arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





