
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The major elimination product obtained when the given alcohol is heated in the presence of sulphuric acid has to be has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction of alcohol with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
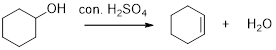
E1 dehydration reaction of secondary and tertiary alcohols:
The alcohols react with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding stable carbocation intermediate. The elimination of hydrogen from the beta carbon results in the
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
(b)
Interpretation:
The major elimination product obtained when the given alcohol is heated in the presence of sulphuric acid has to be has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction of alcohol with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
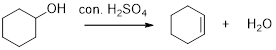
E1 dehydration reaction of secondary and tertiary alcohols:
The alcohols react with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding stable carbocation intermediate. The elimination of hydrogen from the beta carbon results in the alkene product. Thus the removal of water molecule occurs in the dehydration process and the major product of the acid-catalysed dehydration reaction will be the more substituted product.
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
(c)
Interpretation:
The major elimination product obtained when the given alcohol is heated in the presence of sulphuric acid has to be has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction of alcohol with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
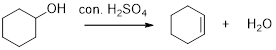
E2 dehydration of primary alcohols:
Due to the unstability of the primary carbocation, the dehydration of primary alcohol is an E2 reaction.
In the E2 reaction, protonation of the most basic atom occurs and then base will remove a proton from the beta carbon.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major elimination product obtained when the given alcohol is heated in the presence of sulphuric acid has to be has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction of alcohol with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
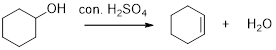
E1 dehydration reaction of secondary and tertiary alcohols:
The alcohols react with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding stable carbocation intermediate. The elimination of hydrogen from the beta carbon results in the alkene product. Thus the removal of water molecule occurs in the dehydration process and the major product of the acid-catalysed dehydration reaction will be the more substituted product.
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- 4. True or false: This skeletal structure represents a saturated fatty acid. Ini to 0 fale) me OH faistong starrow_forwardBy malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 5-Methyl-2-hexanone (with the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the first photo attached*arrow_forward
- Draw the formula for 3-chlorobenzoic acetic anhydride.arrow_forwardBy malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 2-methylbutanoic acid (indicate the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forwardObtain 2-methylbutanoic acid by malonic or acetylacetic synthesis (indicate the formulas of the compounds involved).arrow_forward
- EFFICIENTS SAMPLE READINGS CONCENTRATIONS Pigiadient) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) 58 6.274 3.898 301.7 151.2 14150 5.277 3.865 348.9 254.8 B 5.136 3.639 193.7 85.9 605 4.655 3.041 308.6 199.6 05 5.135 3.664 339.5 241.4 0139 4.676 3.662 160.6 87.6 90148 5.086 3.677 337.7 242.5 0092 6.348 3.775 464.7 186.4 PART3 5.081 3.908 223.5 155.8 5.558 3.861 370.5 257.1 4.922 3.66 326.6 242.9 4.752 3.641 327.5 253.3 50 5.018 3.815 336.1 256.0 84 4.959 3.605 317.9 216.6 38 4.96 3.652 203.8 108.7 $3 5.052 3.664 329.8 239.0 17 5.043 3.767 221.9 149.7 052 5.058 3.614 331.7 236.4 5.051 4.005 211.7 152.1 62 5.047 3.637 309.6 222.7 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 995 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 04 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 16 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 0.011 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 AVERAGE STDEV COUNT 95% CI Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH₃COCH₃) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH), applying heat to them produces an aldol condensation of the two compounds. If this is correct, draw the formula for the final product.arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH3COCH3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH); if we apply heat (A), what product(s) are obtained?arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardYou need to make a buffer by dissolving benzoic acid and sodium benzoate in water. What is the mass of benzoic acid that you would weigh out, in mg, to create 50 mL of a buffer at pH = 4.7 that will change pH no more than 0.10 units with the addition of 0.001 moles of acid or base? Enter just the answer without the units (mg) - just the number will do!arrow_forwardDraw the formula for 3-isopropylcyclopentane-1-carbonyl chloride.arrow_forward
