
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The total number of hydrogen atoms should be identified in ethane molecule.
Concept Introduction: The general formula of a hydrocarbon is 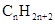 For hydrocarbons with 1 double bond the general formula is
For hydrocarbons with 1 double bond the general formula is 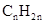 Similarly, for hydrocarbons with 1 triple bond the formula is
Similarly, for hydrocarbons with 1 triple bond the formula is 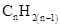 A hydrocarbon chain can be in cyclic or ring form, for that the general formula is
A hydrocarbon chain can be in cyclic or ring form, for that the general formula is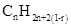 Here, r represents the number of rings.
Here, r represents the number of rings.
(b)
Interpretation: The total number of hydrogen atoms should be identified in 1-butyne
molecule.
Concept Introduction: The general formula of a hydrocarbon is 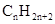 For hydrocarbons with 1 double bond the general formula is
For hydrocarbons with 1 double bond the general formula is 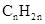 Similarly, for hydrocarbons with 1 triple bond the formula is
Similarly, for hydrocarbons with 1 triple bond the formula is 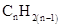 A hydrocarbon chain can be in cyclic or ring form, for that the general formula is
A hydrocarbon chain can be in cyclic or ring form, for that the general formula is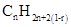 Here, r represents the number of rings.
Here, r represents the number of rings.
(c)
Interpretation: The total number of hydrogen atoms should be identified in propene
molecule.
Concept Introduction: The general formula of a hydrocarbon is 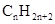 For hydrocarbons with 1 double bond the general formula is
For hydrocarbons with 1 double bond the general formula is 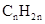 Similarly, for hydrocarbons with 1 triple bond the formula is
Similarly, for hydrocarbons with 1 triple bond the formula is 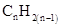 A hydrocarbon chain can be in cyclic or ring form, for that the general formula is
A hydrocarbon chain can be in cyclic or ring form, for that the general formula is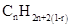 Here, r represents the number of rings.
Here, r represents the number of rings.
(d)
Interpretation: The total number of hydrogen atoms should be identified in cyclooctane
molecule.
Concept Introduction: The general formula of a hydrocarbon is 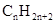 For hydrocarbons with 1 double bond the general formula is
For hydrocarbons with 1 double bond the general formula is 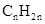 Similarly, for hydrocarbons with 1 triple bond the formula is
Similarly, for hydrocarbons with 1 triple bond the formula is 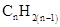 A hydrocarbon chain can be in cyclic or ring form, for that the general formula is
A hydrocarbon chain can be in cyclic or ring form, for that the general formula is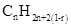 Here, r represents the number of rings.
Here, r represents the number of rings.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry for Changing Times
- Can the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? ? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C :0 T Add/Remove step Garrow_forwardThe following equations represent the formation of compound MX. What is the AH for the electron affinity of X (g)? X₂ (g) → 2X (g) M (s) → M (g) M (g) M (g) + e- AH = 60 kJ/mol AH = 22 kJ/mol X (g) + e-X (g) M* (g) +X (g) → MX (s) AH = 118 kJ/mol AH = ? AH = -190 kJ/mol AH = -100 kJ/mol a) -80 kJ b) -30 kJ c) -20 kJ d) 20 kJ e) 156 kJarrow_forwardA covalent bond is the result of the a) b) c) d) e) overlap of two half-filled s orbitals overlap of a half-filled s orbital and a half-filled p orbital overlap of two half-filled p orbitals along their axes parallel overlap of two half-filled parallel p orbitals all of the abovearrow_forward
- Can the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forwardWhich one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forwardAll of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forward
- A student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction:arrow_forwardCalculate the density of 21.12 g of an object that displaces 0.0250 L of water.arrow_forward
- Draw the expected reactant R28. Cu(II) CO₂Mearrow_forwardPpplllleeeaaasssseeee helllppp wiithhh thisss Organic chemistryyyyyy I talked like this because AI is very annoyingarrow_forwardName the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH₂ || CH3-C-NH2 0 ။ CH3-C-CH₂ CH=O–CH=CH, CH₂ HO CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 family amine Darrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





