
Testing the Difference Between Two Means In Exercises 9–20, (a) identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) calculate
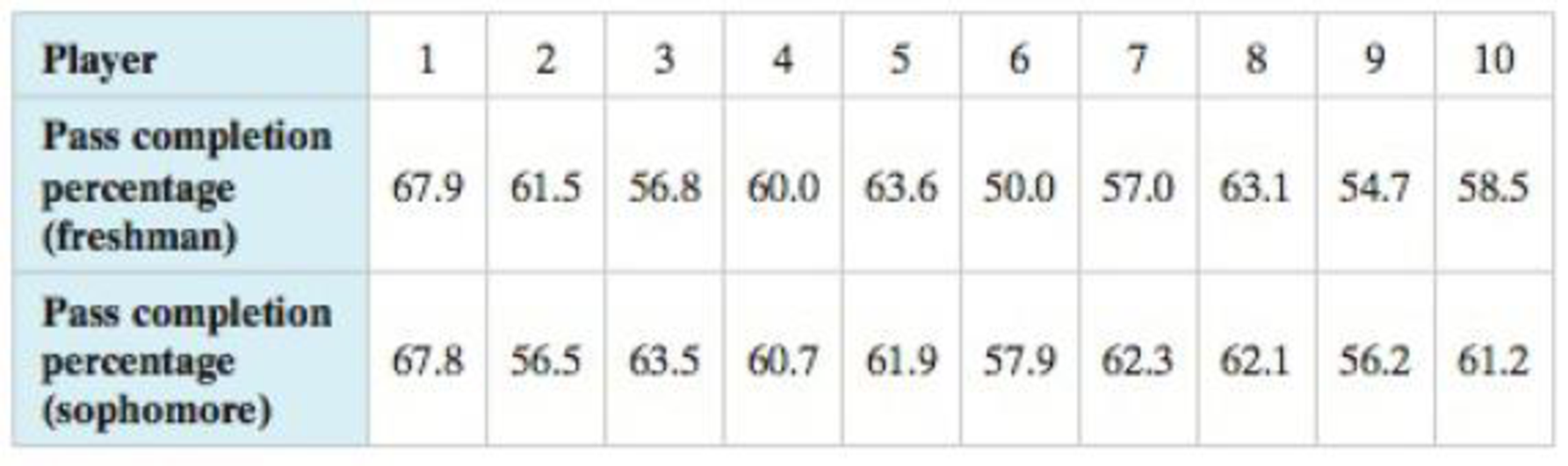
18. Pass Completion Percentages The pass completion percentages of 10 college football quarterbacks for their freshman and sophomore seasons are shown in the table below. At α = 0.10, is there enough evidence to support the claim that the pass completion percentages have changed? (Source: Sports Reference, LLC)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- T1.4: Let ẞ(G) be the minimum size of a vertex cover, a(G) be the maximum size of an independent set and m(G) = |E(G)|. (i) Prove that if G is triangle free (no induced K3) then m(G) ≤ a(G)B(G). Hints - The neighborhood of a vertex in a triangle free graph must be independent; all edges have at least one end in a vertex cover. (ii) Show that all graphs of order n ≥ 3 and size m> [n2/4] contain a triangle. Hints - you may need to use either elementary calculus or the arithmetic-geometric mean inequality.arrow_forwardWe consider the one-period model studied in class as an example. Namely, we assumethat the current stock price is S0 = 10. At time T, the stock has either moved up toSt = 12 (with probability p = 0.6) or down towards St = 8 (with probability 1−p = 0.4).We consider a call option on this stock with maturity T and strike price K = 10. Theinterest rate on the money market is zero.As in class, we assume that you, as a customer, are willing to buy the call option on100 shares of stock for $120. The investor, who sold you the option, can adopt one of thefollowing strategies: Strategy 1: (seen in class) Buy 50 shares of stock and borrow $380. Strategy 2: Buy 55 shares of stock and borrow $430. Strategy 3: Buy 60 shares of stock and borrow $480. Strategy 4: Buy 40 shares of stock and borrow $280.(a) For each of strategies 2-4, describe the value of the investor’s portfolio at time 0,and at time T for each possible movement of the stock.(b) For each of strategies 2-4, does the investor have…arrow_forwardNegate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forward
- Negate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forwardQuestion 6: Negate the following compound statements, using De Morgan's laws. A) If Alberta was under water entirely then there should be no fossil of mammals.arrow_forwardNegate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forward
- Characterize (with proof) all connected graphs that contain no even cycles in terms oftheir blocks.arrow_forwardLet G be a connected graph that does not have P4 or C3 as an induced subgraph (i.e.,G is P4, C3 free). Prove that G is a complete bipartite grapharrow_forwardProve sufficiency of the condition for a graph to be bipartite that is, prove that if G hasno odd cycles then G is bipartite as follows:Assume that the statement is false and that G is an edge minimal counterexample. That is, Gsatisfies the conditions and is not bipartite but G − e is bipartite for any edge e. (Note thatthis is essentially induction, just using different terminology.) What does minimality say aboutconnectivity of G? Can G − e be disconnected? Explain why if there is an edge between twovertices in the same part of a bipartition of G − e then there is an odd cyclearrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





