
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781118921876
Author: Pritchard, Philip J.; Leylegian, John C.; Bhaskaran, Rajesh
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 80P
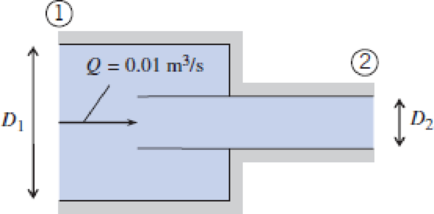
Water flows from a larger pipe, diameter D1 = 100 mm, into a smaller one, diameter D2 = 50 mm, by way of a reentrant device. Find the head loss between points ① and ②.
P8.80
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
:+B
العنوان
I need a actanicu urawing with Car nation
The guide vane angle of a reaction turbine (Francis type
make 20° with the tangent. The moving blade angle at entry is
120° The external diameter of runner is 450 mm and the internal
diameter is 300 mm. Runner width at entry is 62.5mm and at exit
100mm. Calculate the blade angle at exit for radial discharge.
The guide vane angle of a reaction turbine (Francis type
make 20° with the tangent. The moving blade angle at entry is
120°. The external diameter of runner is 450 mm and the internal
diameter is 300 mm. Runner width at entry is 62.5mm and at exit
100mm. Calculate the blade angle at exit for radial discharge.
answer this as soon as possible, please.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
Ch. 8 - Consider incompressible flow in a circular...Ch. 8 - What is the maximum flow rate of air that may...Ch. 8 - For flow in circular tubes, transition to...Ch. 8 - An incompressible fluid flows between two infinite...Ch. 8 - Oil is confined in a 4-in.-diameter cylinder by a...Ch. 8 - Viscous oil flows steadily between parallel...Ch. 8 - Calculate for the flow in this two-dimensional...Ch. 8 - The velocity profile in a two-dimensional open...Ch. 8 - A large mass is supported by a piston of diameter...Ch. 8 - A hydraulic jack supports a load of 9000 kg. The...
Ch. 8 - The basic component of a pressure gage tester...Ch. 8 - When a horizontal laminar flow occurs between two...Ch. 8 - In a laminar flow of water of 0:007 m3/s between...Ch. 8 - Consider the simple power-law model for a...Ch. 8 - A sealed journal bearing is formed from concentric...Ch. 8 - Using the profile of Problem 8.15, show that the...Ch. 8 - In a laminar flow between parallel plates spaced...Ch. 8 - A fluid of specific gravity 0.90 flows at a...Ch. 8 - Two immiscible fluids are contained between...Ch. 8 - The record-read head for a computer disk-drive...Ch. 8 - Consider steady, incompressible, and fully...Ch. 8 - In a flow of air between parallel plates spaced...Ch. 8 - Consider fully developed flow between parallel...Ch. 8 - Free-surface waves begin to form on a laminar...Ch. 8 - A viscous-shear pump is made from a stationary...Ch. 8 - The efficiency of the viscous-shear pump of Fig....Ch. 8 - An inventor proposes to make a viscous timer by...Ch. 8 - A continuous belt, passing upward through a...Ch. 8 - A wet paint film of uniform thickness, , is...Ch. 8 - Consider first water and then SAE 10W lubricating...Ch. 8 - Using Eq. A.3 in Appendix A for the viscosity of...Ch. 8 - Consider fully developed laminar flow in the...Ch. 8 - Carbon dioxide flows in a 50-mm-diameter pipe at a...Ch. 8 - Consider fully developed laminar flow in a...Ch. 8 - What is the largest diameter of pipeline that may...Ch. 8 - Consider fully developed laminar flow in the...Ch. 8 - Consider fully developed pressure-driven flow in a...Ch. 8 - In the laminar flow of an oil of viscosity 1 Pa_s,...Ch. 8 - In a laminar flow of 0.007 m3/s in a...Ch. 8 - Consider blood flow in an artery. Blood is...Ch. 8 - The classic Poiseuille flow (Eq. 8.12), is for...Ch. 8 - For pressure-driven, steady, fully developed...Ch. 8 - In a laminar flow in a 12-in.-diameter pipe the...Ch. 8 - A fluid of specific gravity 0.90 flows at a...Ch. 8 - In a food industry plant, two immiscible fluids...Ch. 8 - A horizontal pipe carries fluid in fully developed...Ch. 8 - Kerosene is pumped through a smooth tube with...Ch. 8 - In a flow of water in a 0.3-m-diameter pipe, the...Ch. 8 - A liquid drug, with the viscosity and density of...Ch. 8 - Laufer [5] measured the following data for mean...Ch. 8 - Equation 8.23 gives the power-law velocity profile...Ch. 8 - Consider fully developed laminar flow of water...Ch. 8 - Consider fully developed laminar flow in a...Ch. 8 - If the turbulent velocity profile in a pipe 0.6 m...Ch. 8 - Water flows in a horizontal constant-area pipe;...Ch. 8 - For a given volume flow rate and piping system,...Ch. 8 - Consider the pipe flow from the water tower of...Ch. 8 - At the inlet to a constant-diameter section of the...Ch. 8 - When oil (kinematic viscosity 1 104 m2/s,...Ch. 8 - When fluid of specific weight 50 lb/ft3 flows in a...Ch. 8 - If the head lost in 30-m-diameter of...Ch. 8 - Water flows at 10 L/min through a horizontal...Ch. 8 - Laufer [5] measured the following data for mean...Ch. 8 - Water is pumped at the rate of 0.075 m3/s from a...Ch. 8 - Just downstream from the nozzle tip the velocity...Ch. 8 - A horizontal nozzle having a cylindrical tip of 75...Ch. 8 - When 0.3 m3/s of water flows through a...Ch. 8 - Water flows through a 2-in.-diameter tube that...Ch. 8 - A 50-mm-diameter nozzle terminates a vertical...Ch. 8 - A 12-in.-diameter pipe leaves a reservoir of...Ch. 8 - A water pipe gradually changes from 6-in.-diameter...Ch. 8 - Air at standard conditions flows through a sudden...Ch. 8 - Water flows from a larger pipe, diameter D1 = 100...Ch. 8 - Flow through a sudden contraction is shown. The...Ch. 8 - A flow rate of 1.01/min of oil of specific gravity...Ch. 8 - Water flows in a smooth pipeline at a Reynolds...Ch. 8 - Air flows out of a clean room test chamber through...Ch. 8 - A conical diffuser is used to expand a pipe flow...Ch. 8 - By applying the basic equations to a control...Ch. 8 - Water at 45C enters a shower head through a...Ch. 8 - Water discharges to atmosphere from a large...Ch. 8 - A laboratory experiment is set up to measure...Ch. 8 - Oil with kinematic viscosity = 7.5 104 ft2/s...Ch. 8 - Water from a pump flows through a 9-in.-diameter...Ch. 8 - A 5-cm-diameter potable water line is to be run...Ch. 8 - A system for testing variable-output pumps...Ch. 8 - Two reservoirs are connected by three clean...Ch. 8 - Water, at volume flow rate Q = 0.75 ft3/s, is...Ch. 8 - When you drink a beverage with a straw, you need...Ch. 8 - What flow rate (gpm) will be produced in a...Ch. 8 - Gasoline flows in a long, underground pipeline at...Ch. 8 - An 18-in.-diameter new riveted steel pipeline 1000...Ch. 8 - What diameter of smooth masonry pipe is needed to...Ch. 8 - Water flows steadily in a 125-mm-diameter...Ch. 8 - Two galvanized iron pipes of diameter D are...Ch. 8 - A mining engineer plans to do hydraulic mining...Ch. 8 - The flow of water through a 150-mm-diameter...Ch. 8 - The fluid flowing has specific gravity 0.90; V75=6...Ch. 8 - Water is flowing. Calculate the direction and...Ch. 8 - Investigate the effect of tube roughness on flow...Ch. 8 - Investigate the effect of tube length on water...Ch. 8 - For the pipe flow into a reservoir of Example 8.5...Ch. 8 - Calculate the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 8 - Experimental determination of local losses and...Ch. 8 - Water is flowing. Calculate the gage reading when...Ch. 8 - The siphon shown is fabricated from 50-mm-i.d....Ch. 8 - A large open water tank has a horizontal cast iron...Ch. 8 - A tank containing 30 m3 of kerosene is to be...Ch. 8 - A 90 screwed elbow is installed in a...Ch. 8 - Calculate the total tension in the bolts. Neglect...Ch. 8 - A horizontal 50-mm-diameter PVC pipeline leaves...Ch. 8 - You are watering your lawn with an old hose....Ch. 8 - Your boss claims that for pipe flow the flow rate,...Ch. 8 - A hydraulic press is powered by a remote...Ch. 8 - One-quarter of a cubic meter per second of liquid...Ch. 8 - Calculate the flow rate from this water tank if...Ch. 8 - A 6-ft-diameter pipeline 4 miles long between two...Ch. 8 - A new industrial plant requires a water flow rate...Ch. 8 - What diameter water pipe is required to handle...Ch. 8 - A pipe friction experiment for air consists of a...Ch. 8 - Oil has been flowing from a large tank on a hill...Ch. 8 - The pressure rise across a water pump is 35 psi...Ch. 8 - Cooling water is pumped from a reservoir to rock...Ch. 8 - You are asked to size a pump for installation in...Ch. 8 - Heavy crude oil (SG = 0.925 and = 1.0 104 m2/s)...Ch. 8 - Petroleum products are transported over long...Ch. 8 - The head versus capacity curve for a certain fan...Ch. 8 - A swimming pool has a partial-flow filtration...Ch. 8 - Water at 65C flows through a 75-mm-diameter...Ch. 8 - A 12 in. 6 in. Venturi meter is installed in a...Ch. 8 - A 1-in.-diameter nozzle is attached to a...Ch. 8 - A sharp-edged orifice with conventional pressure...Ch. 8 - A venturi meter with a 3-in.-diameter throat is...Ch. 8 - Air flows through a venturi meter with a...Ch. 8 - Water at 10C flows steadily through a venturi. The...Ch. 8 - Drinking straws are to be used to improve the air...Ch. 8 - In some western states, water for mining and...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1‘21 Same as Problem 1.20, excepi the anicle should be
on safety as related to su rveying-
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Assume the following variables are defined: int age; double pay; char section; Write a single cin statement tha...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
In the following exercises, write a program to carry out the task. The program should use variables for each of...
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Modify the Product_T table by adding an attribute QtyOnHand that can be used to track the finished goods invent...
Modern Database Management
Explain the meaning of the term object persistence.
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A piston–cylinder device contains 50 kg of water at 250 kPa and 25°C. The cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.1 m2. Heat is now transferred to the water, causing part of it to evaporate and expand. When the volume reaches 0.26 m3, the piston reaches a linear spring whose spring constant is 100 kN/m. More heat is transferred to the water until the piston rises 20 cm more. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the work done during this process. The work done during this process is kJ.arrow_forwardA 4-m × 5-m × 7-m room is heated by the radiator of a steam-heating system. The steam radiator transfers heat at a rate of 10,000 kJ/h, and a 100-W fan is used to distribute the warm air in the room. The rate of heat loss from the room is estimated to be about 5000 kJ/h. If the initial temperature of the room air is 10°C, determine how long it will take for the air temperature to rise to 25°C. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. The gas constant of air is R = 0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K (Table A-1). Also, cv = 0.718 kJ/kg·K for air at room temperature (Table A-2). Steam enters the radiator system through an inlet outside the room and leaves the system through an outlet on the same side of the room. The fan is labeled as W sub p w. The heat is given off by the whole system consisting of room, radiator and fan at the rate of 5000 kilojoules per hour. It will take 831 Numeric ResponseEdit Unavailable. 831 incorrect.s for the air temperature to rise to 25°C.arrow_forwardA piston–cylinder device contains 50 kg of water at 250 kPa and 25°C. The cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.1 m2. Heat is now transferred to the water, causing part of it to evaporate and expand. When the volume reaches 0.26 m3, the piston reaches a linear spring whose spring constant is 100 kN/m. More heat is transferred to the water until the piston rises 20 cm more. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the final pressure and temperature. The final pressure is kPa. The final temperature is ºC. Find the work done during the processarrow_forward
- A garden hose attached with a nozzle is used to fill a 20-gal bucket. The inner diameter of the hose is 1 in and it reduces to 0.53 in at the nozzle exit. The average velocity in the hose is 8 ft/s and the density of water is 62.4 lbm/ft3. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the volume and mass flow rates of water through the hose. The volume flow rate of water through the hose is ft3/s. The mass flow rate of water through the hose is lbm/s. The change in time? What is the exit velocity?arrow_forwardA 23-ft3 rigid tank initially contains saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 160 psia. As a result of heat transfer from the refrigerant, the pressure drops to 50 psia. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the final temperature. Use data from refrigerant tables. The final temperature is ºF.arrow_forwardA 23-ft3 rigid tank initially contains saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 160 psia. As a result of heat transfer from the refrigerant, the pressure drops to 50 psia. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the heat transfer. The heat transfer is Btu.arrow_forward
- The shaft shown in the figure below is subjected to axial loads as illustrated. The diameters of segments AB, BC, and CD are 20mm, 25mm, and 15mm, respectively. If the modulus of elasticity of the material is 610 MPa. Determine the change of A to D lengtharrow_forwardDetermine the final pressure and temperature. The final pressure is kPa. The final temperature is ºC.arrow_forwardAir enters the 1-m2 inlet of an aircraft engine at 100 kPa and 20°C with a velocity of 184 m/s. Determine the volume flow rate, in m3/s, at the engine’s inlet and the mass flow rate, in kg/s, at the engine’s exit. The gas constant of air is R = 0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K. The volume flow rate at the engine’s inlet m3/s. The mass flow rate at the engine’s exit is kg/s.arrow_forward
- The ventilating fan of the bathroom of a building has a volume flow rate of 33 L/s and runs continuously. If the density of air inside is 1.20 kg/m3, determine the mass of air vented out in one day. The mass of air is kg.arrow_forwardA steady-flow compressor is used to compress helium from 15 psia and 70°F at the inlet to 200 psia and 600°F at the outlet. The outlet area and velocity are 0.01 ft2 and 100 ft/s, respectively, and the inlet velocity is 53 ft/s. Determine the mass flow rate and the inlet area. The gas constant of helium is R = 2.6809 psia·ft3/lbm·R. The mass flow rate is lbm/s. The inlet area is ft2.arrow_forward1. The maximum and minimum stresses as well as the shear stress seen subjected the piece in plane A-A. Assume it is a cylinder with a diameter of 12.7mm 2. Draw the Mohr circle for the stress state using software. 3. Selection of the material for the prosthesis, which must be analyzed from the point of safety and cost view.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Physics 33 - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mzjlAla3H1Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY