
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781337398909
Author: Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 7.97PAE
7.97 Consider the structure shown below for 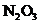 as well as any other important resonance structures.
as well as any other important resonance structures.
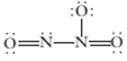
(a) What is the expected O—N—O bond angle in this structure? (b) The 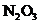 molecule contains N—O bonds of two different lengths. How many sborter N—O bonds would be present?
molecule contains N—O bonds of two different lengths. How many sborter N—O bonds would be present?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Can you please explain this problem to me and expand it so I can understand the full Lewis dot structure? Thanks!
Can you please explain this problem to me and expand it so I can understand the full Lewis dot structure? Thanks!
Can you please explain this problem to me and expand it so I can understand the full Lewis dot structure? Thanks!
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry for Engineering Students
Ch. 7 - List some factors influencing the biocompatibility...Ch. 7 - • use electron configurations to explain why...Ch. 7 - • describe die energy changes in the formation of...Ch. 7 - • define electronegativity and state how...Ch. 7 - • identify or predict polar, nonpolar, and ionic...Ch. 7 - • write Lewis electron structures for molecules or...Ch. 7 - • describe chemical bonding using a model based on...Ch. 7 - • explain how hybridization reconciles observed...Ch. 7 - • predict the geometry of a molecule from its,...Ch. 7 - • use models (real or software) to help visualize...
Ch. 7 - • explain the formation of multiple bonds in terms...Ch. 7 - • identify sigma and pi bonds in a molecule and...Ch. 7 - Define the term biocompatibility.Ch. 7 - List some properties associated with biomaterials...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.3PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.4PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.5PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.6PAECh. 7 - Why is the ion not found in nature?Ch. 7 - Why do nonmetals tend to form anions rather than...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.9PAECh. 7 - 7.10 Arrange the members of each of the following...Ch. 7 - 7.11 Arrange the following sets of anions in order...Ch. 7 - 7.12 Which pair will form a compound with the...Ch. 7 - 7.13 Figure 7-2 depicts the interactions of an ion...Ch. 7 - 7.14 Describe the difference between a covalent...Ch. 7 - 7.15 Covalently bonded compounds tend to have much...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.16PAECh. 7 - 7.17 Coulombic forces are often used to explain...Ch. 7 - 7.18 In terms of the strengths of the covalent...Ch. 7 - 7.19 If the formation of chemical bonds always...Ch. 7 - 7.20 Draw the Lewis dot symbol for each of the...Ch. 7 - 7.21 Theoretical models for the structure of...Ch. 7 - 7.22 Use Lewis dot symbols to explain why chlorine...Ch. 7 - 7.23 Define the term lone pair.Ch. 7 - 7.24 How many electrons are shared between two...Ch. 7 - 7.25 How does the bond energy of a double bond...Ch. 7 - 7.26 How is electronegativity defined?Ch. 7 - 7.27 Distinguish between electron affinity and...Ch. 7 - 7.28 Certain elements in the periodic table shown...Ch. 7 - 7.29 When two atoms with different...Ch. 7 - 7.30 The bond in HF is said to be polar, with the...Ch. 7 - 7.31 Why is a bond between two atoms with...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.32PAECh. 7 - 7.33 In each group of three bonds, which bond is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.34PAECh. 7 - 7.35 Which one of the following contains botb...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.36PAECh. 7 - 7.37 Draw the Lewis structure for each of the...Ch. 7 - 7.38 Draw a Lewis structure for each of the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.39PAECh. 7 - 7.40 Why is it impossible for hydrogen to be the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.41PAECh. 7 - 7.42 Draw resonance structure for (a) (b) and (c)Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.43PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.44PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.45PAECh. 7 - 7.46 Consider the nitrogen-oxygen bond lengths in...Ch. 7 - 7.47 Which of the species listed has a Lewis...Ch. 7 - 7.48 Identify what is incorrect in the Lewis...Ch. 7 - 7.49 Identify what is incorrect in the Lewis...Ch. 7 - 7.50 Chemical species are said to be isoelectronic...Ch. 7 - 7.51 Explain the concept of wave interference in...Ch. 7 - 7.52 How does orbital overlap explain the buildup...Ch. 7 - 7.53 How do sigma and pi bonds differ? How are...Ch. 7 - 7.54 CO , CO2 , CH3OH , and CO32 , all contain...Ch. 7 - 7.55 Draw the Lewis dot structure of the following...Ch. 7 - 7.56 Draw the Lewis dot structures of the...Ch. 7 - 7.57 What observation about molecules compels us...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.58PAECh. 7 - 7.59 What type of hybrid orbital is generated by...Ch. 7 - 7.60 What type of hybridization would be expected...Ch. 7 - 7.61 What hybrid orbitals would be expected for...Ch. 7 - 7.62 What type of hybridization would you expect...Ch. 7 - 7.63 What physical concept forms the premise of...Ch. 7 - 7.64 Predict the geometry of the following...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.65PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.66PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.67PAECh. 7 - 7.68 Give approximate values for the indicated...Ch. 7 - 7.69 Propene has the chemical formula Describe the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.70PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.71PAECh. 7 - 7.72 How does an MSN differ from amorphous silica...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.73PAECh. 7 - 7.74 In a lattice, a positive ion is often...Ch. 7 - 7.75 Use the concept of lattice energy to...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.76PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.77PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.78PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.79PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.80PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.81PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.82PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.83PAECh. 7 - 7.84 Which of the following molecules is least...Ch. 7 - 7.85 Consider the molecule whose structure is...Ch. 7 - 7.86 Nitrogen triiodide, NI3(s) , is unstable and...Ch. 7 - 7.87 Nitrogen is capable of forming single,...Ch. 7 - 7.88 The N5+ cation has been synthesized and...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.89PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.90PAECh. 7 - 7.91 A Lewis structure for the oxalate ion is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.92PAECh. 7 - 7.93 An unknown metal M forms a chloride with the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.94PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.95PAECh. 7 - 7.96 Consider the hydrocarbons whose structures...Ch. 7 - 7.97 Consider the structure shown below for as...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.98PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.99PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.100PAECh. 7 - 7.101 Lead selenide nanocrystals may provide a...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.102PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.103PAECh. 7 - 7.104 Hydrogen azide, HN3 , is a liquid that...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.105PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.106PAECh. 7 - 7.107 How do the Lewis symbols for C, Si, and Ge...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.108PAECh. 7 - Prob. 7.109PAE
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please answer the questions in the photos and please revise any wrong answers. Thank youarrow_forward(Please be sure that 7 carbons are available in the structure )Based on the 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT 135 NMR and DEPT 90 NMR, provide a reasoning step and arrive at the final structure of an unknown organic compound containing 7 carbons. Dept 135 shows peak to be positive at 128.62 and 13.63 Dept 135 shows peak to be negative at 130.28, 64.32, 30.62 and 19.10.arrow_forward-lease help me answer the questions in the photo.arrow_forward
- For the reaction below, the concentrations at equilibrium are [SO₂] = 0.50 M, [0] = 0.45 M, and [SO3] = 1.7 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K? 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g) Report your answer using two significant figures. Provide your answer below:arrow_forwardI need help with this question. Step by step solution, please!arrow_forwardZn(OH)2(s) Zn(OH)+ Ksp = 3 X 10-16 B₁ = 1 x 104 Zn(OH)2(aq) B₂ = 2 x 1010 Zn(OH)3 ẞ3-8 x 1013 Zn(OH) B4-3 x 1015arrow_forward
- Help me understand this by showing step by step solution.arrow_forwardscratch paper, and the integrated rate table provided in class. our scratch work for this test. Content attribution 3/40 FEEDBACK QUESTION 3 - 4 POINTS Complete the equation that relates the rate of consumption of H+ and the rate of formation of Br2 for the given reaction. 5Br (aq) + BrO3 (aq) + 6H (aq) →3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l) • Your answers should be whole numbers or fractions without any decimal places. Provide your answer below: Search 尚 5 fn 40 * 00 99+ 2 9 144 a [arrow_forward(a) Write down the structure of EDTA molecule and show the complex structure with Pb2+ . (b) When do you need to perform back titration? (c) Ni2+ can be analyzed by a back titration using standard Zn2+ at pH 5.5 with xylenol orange indicator. A solution containing 25.00 mL of Ni2+ in dilute HCl is treated with 25.00 mL of 0.05283 M Na2EDTA. The solution is neutralized with NaOH, and the pH is adjusted to 5.5 with acetate buffer. The solution turns yellow when a few drops of indicator are added. Titration with 0.02299 M Zn2+ requires 17.61 mL to reach the red end point. What is the molarity of Ni2+ in the unknown?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY