
Concept explainers
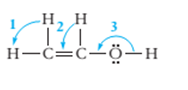
7.68 Give approximate values for the indicated bond angles. (a) Cl—S—Cl in SCl2, (b) N—N—O in N2O, (c) bond angles marked as 1, 2, and 3 in the following structure for vinyl alcohol:
(a)
Interpretation:
The approximate value for the indicated bond angle of the following molecule should be determined:
Concept Introduction
A bond angleis the angle formed between three atoms across at least two bonds. We can predict the angle of a molecule by the knowledge of their bond pairs, lone pairs and VSPER theory.According to this theory, the atoms take such a position in which there is a minimum possible repulsion between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electrons, if any, where the lone pair is the pair of electrons occupying the orbital but not taking part in the bonding.
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a shape to their molecule.
Here, the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. The repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair changes the position of atom as well as bond angles. The order of repulsion is as follows:
It means the lone pair-lone pair repulsion is more than lone pair- bond pair repulsion and bond pair- bond pair repulsion is least among all.
Answer to Problem 7.68PAE
Solution:
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of sulphur (S) is
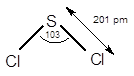
(b)
Interpretation: The approximate value for the indicated bond angle of the following molecule should be determined:
Concept Introduction
A bond angle is the angle formed between three atoms across at least two bonds. We can predict the angle of a molecule by the knowledge of their bond pairs, lone pairs and VSPER theory. According to this theory, the atoms take such a position in which there is a minimum possible repulsion between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electrons, if any, where the lone pair is the pair of electrons occupying the orbital but not taking part in the bonding.
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a shape to their molecule.
Here, the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. The repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair changes the position of atom as well as bond angles. The order of repulsion is as follows:
It means the lone pair-lone pair repulsion is more than lone pair- bond pair repulsion and bond pair- bond pair repulsion is least among all.
Answer to Problem 7.68PAE
Solution:
The bond angle of
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of N is
Structure of
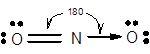
(c)
Interpretation: The approximate value for the indicated bond angle of the following molecule should be determined:
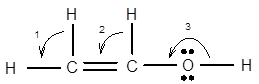
Concept Introduction
A bond angle is the angle formed between three atoms across at least two bonds. We can predict the angle of a molecule by the knowledge of their bond pairs, lone pairs and VSPER theory. According to this theory, the atoms take such a position in which there is a minimum possible repulsion between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electrons, if any, where the lone pair is the pair of electrons occupying the orbital but not taking part in the bonding.
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a shape to their molecule.
Here, the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. The repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair changes the position of atom as well as bond angles. The order of repulsion is as follows:
It means the lone pair-lone pair repulsion is more than lone pair- bond pair repulsion and bond pair- bond pair repulsion is least among all.
Answer to Problem 7.68PAE
Solution:
The bond angle of vinyl alcoholare listed as under according to the marking: 1.
2.
3.
Explanation of Solution
In the first angle
Structure of
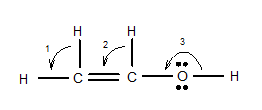
The bond angles of vinyl alcohol for their respective bonds are as follows:
1.
2.
3.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry for Engineering Students
- Briefly explain chemical potential.arrow_forwardReason whether it is possible to determine changes in the Galvani potential difference at the metal-solution interface.arrow_forwardObtain the standard potential at 25°C of the Cu* I Cu | Pt electrode from the standard potentials E° Cu²+/Cu = 0.341 V and E Cu²+ /Cu+ = 0.153 V.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

