
Consider the circuit in Figure P7.49. Calculate the impedance seen by thesignalsource
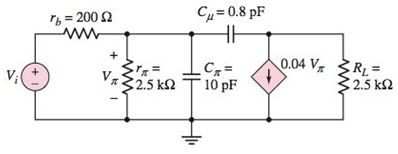
Figure P7.49
a.
The impedance seen by the signal source V1 at the given frequency.
Answer to Problem 7.49P
The impedance
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The circuit diagram is given as:
The given data:
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the capacitor
The value of the capacitor
The value of the trans-conductance
The frequency,
Evaluating the miller capacitance:
Substituting the known values:
Evaluating the value of the capacitance
Substituting the known values to the above equation:
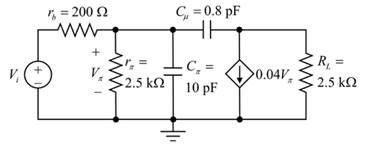
Redrawing the given diagram after some changes:
Evaluaating the impedance
Since,
Evaluating the impedance
Substitute
Hence, the impedance
b.
The impedance seen by the signal source V1 at the given frequency.
Answer to Problem 7.49P
The impedance
Explanation of Solution
Given:
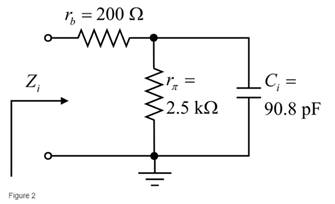
The circuit diagram is given as:
The given data:
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the capacitor
The value of the capacitor
The value of the trans-conductance
The frequency
Consider the following data
Calculate the impedance
Substitute
Therefore , the impedance
c.
The impedance seen by the signal source V1 at the given frequency.
Answer to Problem 7.49P
The impedance
Explanation of Solution
Given:
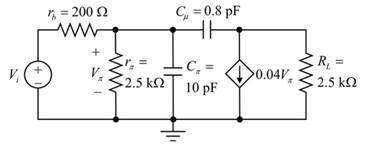
The circuit diagram is given as:
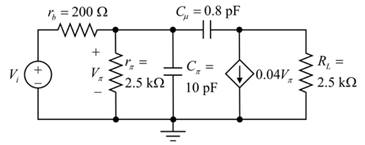
The given data:
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the capacitor
The value of the capacitor
The value of the trans-conductance
The frequency
Consider the following data:
Calculate the impedance
Substitute
Therefore, the impedance
c.
The impedance seen by the signal source V1 at the given frequency.
Answer to Problem 7.49P
the impedance
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The circuit diagram is given as:
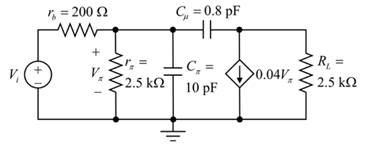
The given data:
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the resistor
The value of the capacitor
The value of the capacitor
The value of the trans-conductance
The frequency
Consider the following data:
Calculate the impedance
Substitute
Therefore, the impedance
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
- a) Three 30 2 resistors are arranged as shown in Figure 1 below. They are connected to a 480 V three-phase supply. The phase sequence is RYB anticlockwise. Calculate: i. The total power drawn by the circuit using the phase parameters. ii. The power read by each wattmeter. b) If Za, one of the 30 2 resistors, is now removed from the circuit, calculate: R- i. The line currents: IR, Iv, and la ii. The power read by each wattmeter. iii. The total power drawn by the two resistors. W₁ Be- W2 www 'R 22 12 B Figure 1arrow_forwardA certain magnetic circuit may be regarded as consisting of three parts, A, B and C in series, each one of which has a uniform cross-sectional area. Part A has a length of 300 mm and a cross- sectional area of 450 mm². Part B has a length of 120 mm and a cross-sectional area of 300 mm². Part C is an airgap 1.0 mm in length and of cross-sectional area 350 mm². The flux in the airgap is 0.35 mWb. Neglect magnetic leakage and fringing. The magnetic characteristic for parts A and B is given by: H (A/m) 400 560 800 1280 1800 B (T) 0.7 0.85 1.0 1.15 1.25 Calculate: i. The reluctance of each part, that is, of Part A, Part B, and Part C ii. The total reluctance of the magnetic circuit. iii. The total m.m.f.arrow_forwardHW_02.pdf EE 213-01 Assignments HW_#2 Toms are as muIcate uah.instructure.com b Answered: HW_#1 HW_01.pdf EE 213-01 Assignments P Pearson MyLab and Mastering uah.instructure.com P Course Home Watc... ✓ Download → Info × Close 1) (5 pts)For the circuit shown, find the value of Ia, Ib, Ic and Va: Ib 10 Ohms + Ic 40 Ohms 20 Ohms 70 Volts a Page 1 > of 2 - ZOOM + pui via Canvas Hint: use KCL to find Ic in terms of la and lb, use KVL around the right loop to find a relationship between la and lb, use KVL around the outer loop to solve for a current value (use ohms law for the voltage drops across the resistors) 2) (5 pts) – For problem 1, show that the power supplied (delivered) by the source equals the power absorbed by the resistors. 3) (5 pts) Determine the equivalent resistance looking into terminals a-b for the two circuits shown. Use series and parallel resistor combinations. Hint: work from the opposite end of terminals a-b towards terminals a-b a) 24 Ohms 10 Ohms 8 Ohms G a REQ b)…arrow_forward
- A three-phase load consists of three identical impedances connected in delta. The impedances have a value of (100 + j40) Q. The supply voltage is 440 V. The two- wattmeter method is used to determine the total power drawn by the load. One wattmeter, W₁, has its current coil connected in the blue line and its voltage coil connected between the yellow and blue lines. Calculate: a) The power measured by each wattmeter b) The power factor of the load using the wattmeter readings c) The apparent power supplied to the load d) The reactive power drawn by the load.arrow_forward4- A 75 KW, 250 V shunt generator has R₁ = 0.03 2 and RF =50 2. The generator has 6 poles and is lap wound with totally 400 conductors. The generator runs at 600 rpm on full load. The bore of the machine is 42 cm (in diameter), its axial length is 28 cm and each pole subtends an angle of 54 °. Field pole a) b) c) Find the airgap flux density. (10 pt) Find the induced voltage under full load. (10 pt) Find the average number of active conductors. (5 pts) 28 cm 21 cm 60° Armaturearrow_forwarda) The phase currents in a delta - connected three-phase load are as follows: between the red and yellow lines, 60 A at p.f. 0.9 leading; between the yellow and blue lines, 40 A at 0.95 p.f lagging; between the blue and red lines, 50 A at p.f. 0.8 lagging. The supply voltage is 240 V. Draw a labeled diagram of the circuit and calculate the line currents. Note: Use VRY as the reference phasor. b) The two-wattmeter method is used to measure the total power drawn by the load in 1 (a) above. Wattmeter one has its current coil connected in the yellow line and its voltage coil connected between the yellow and red lines. Calculate: i. The power measured by each wattmeter. ii. The power factor of the load.arrow_forward
- QUESTION NO. 1 a) State Lenz Law b) Explain Flux density c) A wire, 100 mm long, is moved at a uniform speed of 4 m/s at right angles to its length and to a uniform magnetic field. Calculate the density of the field if the e.m.f. generated in the wire is 0.15 V. If the wire forms part of a closed circuit having a total resistance of 0.04 2, calculate the force on the wire in newtons.arrow_forwardIn Figure (a) the drawing of the bipolar circuit was as shown in Figure 4. Draw me a unipolar circuit and how it will be in Figure (b). Please draw the circuit with the transistors.arrow_forwardSOLVE ON PAPER NOT BY CHATGPTarrow_forward
- Draw fabrication layer transistor MS (schottky diode)arrow_forwardNeed Handwritten solution not using chatgt or AIarrow_forward2. Suppose G₁(s) = (s+2) G₂(s) = (s-3) C(s) Find the transfer function G(s): for each of the following three configurations R(s) shown in Figure 1. Note (a) is a cascaded (series) system, (b) is a parallel system, and (c) is a feedback (closed-loop) system. € (c) C(s) R(s) G₁(s) G2(5) G₁(s) R(s) C(s) G2(s) C(s) R(s) G₁(s) G₂(s) Figure 1arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





