
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds, the compound with high regioselective ability towards addition of
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as
The product of electrophilic addition reaction obtained by addition of electrophile to
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
Chemical reaction involves bond making and breaking of two or more reactants in order to attain products from the reactants.
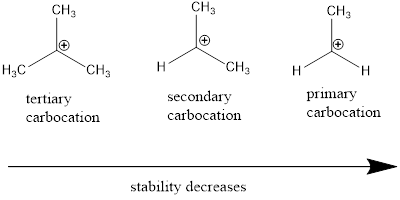
Cation: The positively charged chemical species is referred as cation.
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
(b)
Interpretation:
From the given compounds, the compound with high regioselective ability towards addition of
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
The product of electrophilic addition reaction obtained by addition of electrophile to
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves substrate with a pair of electrons via heterolytic bond cleavage.
Chemical reaction involves bond making and breaking of two or more reactants in order to attain products from the reactants.
Cation: The positively charged chemical species is referred as cation.
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- What alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. and two equivalents of CH2=O draw structure ...arrow_forwardH-Br Energy 1) Draw the step-by-step mechanism by which 3-methylbut-1-ene is converted into 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. 2) Sketch a reaction coordinate diagram that shows how the internal energy (Y- axis) of the reacting species change from reactants to intermediate(s) to product. Brarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 H-CI CH2Cl2 CIarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. དའི་སྐད”“ H3C OH H3C CH CH3 KEq Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C NH2 NH2 KEq H3C-CH₂ 1. Product acid Product basearrow_forwardWhat alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward
