
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed when cis- and
Concept introduction:
Addition of hydrogen halides:
In the addition of hydrogen halides over
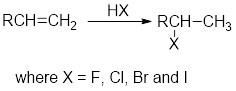
Carbocation: carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

Stereoisomers: Two compounds with same molecular formula but different in their orientation are considered as isomers.
The presence of atom with non-super impossible mirror image is defined as enantiomers which are given
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Chiral or Asymmetric carbon: Carbon bonded with four different substituents with it is termed as chiral or asymmetric carbon.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed when cis- and
Concept introduction:
Addition of
Catalytic hydrogenation in presence of
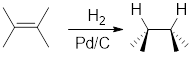
For cyclic reactants, the addition of
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed when cis- and
Concept introduction:
Acid Catalyzed addition of water: When water is added to alkene in the presence of an acid, the product formed will be an alcohol.
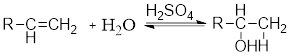
The electrophile
Nucleophile: It donates pair of electrons to positively charged chemical substrate resulting in the formation of
Electrophile: It is positively charged species which seeks for negative charge and hence accepts pair of electrons from negatively charged species (Nucleophiles) which results in the formation of chemical bond.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


