
Concept explainers
( Appendix 6B) Inventory Costing Methods
Grencia Company uses a periodic inventory system. For 2018 and 2019, Grencia has the following data (assume all purchases and sales are for cash):
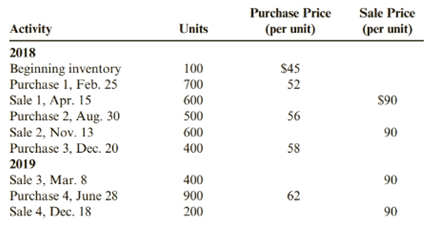
Required:
1. Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using FIFO.
2. Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using LIFO.
3. Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using the average cost method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.)
4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method would result in the lowest amount paid for taxes?
5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method produces the most realistic amount for income? For inventory? Explain your answer.
6. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION What is the effect of purchases made later in the year on the gross margin when LIFO is employed? When FIFO is employed? Be sure to explain why any differences occur.
7. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION If you worked Problem 6-68B, compare your answers. What are the differences? Be sure to explain why any differences occurred.
(a)
Introduction:
In this system, inventory not updated day to day basis.
A real counting of goods which is remaining in the hand calculating at the end of accounting period.
It always maintain a specific accounting period for determine a periodic financial statement. This may use gross method of net method, but always shows a single momentary value for each journal.
Cost of goods sold (COGS) = Beginning inventory + Purchases − Ending inventory
To choose:
Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using FIFO.
Answer to Problem 73BPSB
For 2018
Cost of goods sold=$63300
Cost of ending inventory = $28800
Gross margin =$44700
For 2019
Cost of goods sold=$35000
Cost of ending inventory =$49600
Gross margin = $19000.
Explanation of Solution
Closing stock for 2018
| Date | Units | Rate | Total |
| 2018 2 august |
100 | 56 | 5600 |
| 3 dec | 400 | 58 | 23200 |
| Total | 500 | 28800 |
Calculate cost of goods sold
| Date | Purchase unit | Rate | Total |
| 1 feb | 700 | 52 | 36400 |
| 2 august | 500 | 56 | 28000 |
| 3 dec | 400 | 58 | 23200 |
| Total | 1600 | 87600 |
Cost of goods sold = Cost of units in beginning inventory + Cost of units purchased during the period − Cost of units in ending inventory
=
Gross margin = Total sale − cost of goods sold
=
For 2019
Closing stock for 2019
| Date | Units | Rate | Total |
| Total | 800 | 62 | 49600 |
Calculate cost of goods sold
| Date | Purchase unit | Rate | Total |
| 4 june | 900 | 62 | 55800 |
| Total | 900 | 62 | 55800 |
Cost of goods sold = Cost of units in beginning inventory + Cost of units purchased during the period − Cost of units in ending inventory
Gross margin = Total sale − cost of goods sold
= $
(b)
Introduction:
In last in first out method, the company sold those types of goods which purchase at the end of last day purchase and sold firstly.
Calculation of cost of goods sold and ending value according to this method.
The last in, first out (LIFO) method is used to place an accounting value on inventory. The LIFO method operates under the assumption that the last item of inventory purchased is the first one sold.
To compute:
Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using LIFO.
Answer to Problem 73BPSB
For 2018
Cost of goods sold=$25300
Cost of ending inventory = $66800
Gross margin =$41200
For 2019
Cost of goods sold=$33200
Cost of ending inventory =$47900
Gross margin = $20800.
Explanation of Solution
Closing stock for 2018
| Date | Units | Rate | Total |
| 100 | 45 | 4500 | |
| 400 | 52 | 20800 | |
| Total | 500 | 25300 |
Calculate total purchase sold
| Date | Purchase unit | Rate | Total |
| 1 feb | 700 | 52 | 36400 |
| 2 august | 500 | 56 | 28000 |
| 3 dec | 400 | 58 | 23200 |
| Total | 1600 | 87600 |
Cost of goods sold = Cost of units in beginning inventory + Cost of units purchased during the period − Cost of units in ending inventory
=
Gross margin = Total sale − cost of goods sold
=
Closing stock for 2019
Opening stock
| Units | Rate | Total | |
| 100 | 45 | 4500 | |
| 400 | 52 | 20800 | |
| Total | 500 | 25300 |
Closing stock
| Date | Units | Rate | Total |
| 100 | 45 | 4500 | |
| 700 | 62 | 43400 | |
| Total | 800 | 47900 |
Calculate purchaseunits
| Date | Purchase unit | Rate | Total |
| 4 june | 900 | 62 | 55800 |
| Total | 900 | 55800 |
Cost of goods sold = Cost of units in beginning inventory + Cost of units purchased during the period − Cost of units in ending inventory
= $33200
Gross margin = Total sale − cost of goods sold
=
= $20800.
(c)
Introduction:
In average cost method, the company calculating the goods value on the average basis of all similar goods purchase by the company. The average cost method is calculated by dividing the cost dof goods purchase in inventory divided by the total number of item available for sale.
The average cost method is an inventory costing method in which the cost of every thing in an inventory is determined on the basis of the average cost of every comparative great in the inventory.
To compute:
Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using Average cost method.
Answer to Problem 73BPSB
| Particular | ||
| Cost of goods sold | ||
| Closing inventory value |
For 2018
Cost of goods sold=$65011
Cost of ending inventory = $27088.2
Gross margin = $42988.24
For 2019
Cost of goods sold =$35523
Cost of ending inventory = $47364
Gross margin = $18477.
Explanation of Solution
Total purchase during 2018
| Date | Purchase unit | Rate | Total |
| 1 feb | 700 | 52 | 36400 |
| 2 aug | 500 | 56 | 28000 |
| 3 dec | 400 | 58 | 23200 |
| Total | 1600 | 87600 |
Total unit = 100+1600=1700
Total cost = 4500+87600 = 92100
Weight average cost
Cost of goods sold = 1200
Ending inventory = total units − sold unit
=1700 − 1200 = 500
Cost of ending inventory = 500
= 27088.2
Gross margin = Total sale − cost of goods sold
=1200 units
= $42988.24
For 2019
Total purchase during 2018
| Date | Purchase unit | Rate | Total |
| 4 June | 900 | $62 | $55800 |
Total unit = 500+900=1400
Total cost = $27088.2+$55800 = $82888
Weight average cost
Cost of goods sold = 600
Ending inventory = total units − sold unit
=1400 − 600 = 800
Cost of ending inventory = 800
= $47364
Gross margin = Total sale − cost of goods sold
=600 units
= $18477.
(d)
Introduction:
A periodic inventory system is an accounting system, in this system calculating the value of goods at the end of the accounting period or in fixed period. In this system, cost of goods sold is calculated at the end the period and all entry makes in a single day. In this system account not updated day to day transactions.
Cost of goods sold (COGS) = Beginning inventory + Purchases − Ending inventory
To discuss:
Which method produces the most realistic amount paid for taxes.
Answer to Problem 73BPSB
As per the comparison of two methods the lowest profit to be taken for the purpose the tax paid.
Profit as per FIFO = 63700
Profit as LIFO = 62000
Company should adopt the LILO because profit is lowest.
Explanation of Solution
As per FIFO method
For 2018
Cost of goods sold=$63300
Cost of ending inventory = $28800
Gross margin =$44700
For 2019
Cost of goods sold=$35000
Cost of ending inventory =$49600
Gross margin = $19000
Total profit = 44700+19000=63700
As per LIFO method
For 2018
Cost of goods sold=$25300
Cost of ending inventory = $66800
Gross margin =$41200
For 2019
Cost of goods sold=$33200
Cost of ending inventory =$47900
Gross margin = $20800
Total profit = 41200+20800=62000
As per the comparison of two methods the lowest profit to be taken for the purpose the tax paid.
Profit as per FIFO = 63700
Profit as LIFO = 62000
Company should adopt the LILO because profit is lowest.
(e)
Introduction:
A periodic inventory system is an accounting system, in this system calculating the value of goods at the end of the accounting period or in fixed period. In this system, cost of goods sold is calculated at the end the period and all entry makes in a single day. In this system account not updated day to day transactions.
Cost of goods sold (COGS) = Beginning inventory + Purchases − Ending inventory
In last in first out method, the company sold those types of goods which purchase at the end of last day purchase and sold firstly.
Calculation of cost of goods sold and ending value according to this method.
To discuss:
Which method produces the most realistic amount for income? For inventory? Explain your answer.
Answer to Problem 73BPSB
LIFO gives the most sensible generally speaking increase regard since it facilitates the most current costs to the most present earnings. Since costs usually rise after some time, LIFOs can result in the most diminished in general increase and charges.
Explanation of Solution
LIFO gives the most reasonable overall gain esteem since it coordinates the most current expenses to the most present incomes. Since expenses ordinarily ascend after some time, LIFOs can result in the most reduced overall gain and charges.
(f)
Introduction:
In this system, inventory not updated day to day basis. A real counting of goods which is remaining in the hand calculating at the end of accounting period. It always maintain a specific accounting period for determine a periodic financial statement. This may use gross method of net method, but always shows a single momentary value for each journal.
Cost of goods sold (COGS) = Beginning inventory + Purchases − Ending inventory
In last in first out method, the company sold those types of goods which purchase at the end of last day purchase and sold firstly.
Calculation of cost of goods sold and ending value according to this method.
The last in, first out (LIFO) method is used to place an accounting value on inventory. The LIFO method operates under the assumption that the last item of inventory purchased is the first one sold.
To discuss:
What effect of purchase made later in the year on the gross margin when LIFO is employed? When FIFO is employed? Be sure to explain why any differences occur.
Answer to Problem 73BPSB
Under the LIFO method, the gross profit and ending balance amounts are lower under the Last in first out method. While, when price reduces are falling the Last-in first-out method is likely to generate higher income.
A company chooses to value its inventory effect on its gross profit.
According to the FIFO method, FIFO gives a correct valuation for ending inventory on the income statement. While FIFO increases net income and increased net incomes can increase taxes owned.
In the LIFO method, assumes the last item entering inventory is the first sold.
Explanation of Solution
A company can choose the method of inventory according to own goods.
As per FIFO, the company calculates the ending inventory, and gets effect on the gross margin. The company earns high gross earning.
Disadvantages of using LIFO, if the company uses the warehouse faculty, then LIFO is more difficult to maintain than FIFO.
LIFO is results more complex record the accounting recording.
For this purpose, most of the company maintain the inventory record using the FIFO.
(g)
The periodic framework depends upon an intermittent physical check of the stock to decide the closure stock parity and the expense of products sold, while the perpetual framework monitors stock adjusts.
To discuss:
Find the difference and compare the result with all method.
Answer to Problem 73BPSB
As per LIFO
As per Perpetual
| Particular | ||
| Cost of goods sold | ||
| Closing inventory value |
As per periodical
| Particular | ||
| Cost of goods sold | 66800 | 33200 |
| Closing inventory value | 25300 | 47900 |
As per Weight average method
As per Perpetual
| Particular | ||
| Cost of goods sold | ||
| Closing inventory value |
As per Periodic
| Particular | ||
| Cost of goods sold | $65011 | $35523 |
| Closing inventory value | $27088.2 | $47364 |
Explanation of Solution
Under a periodic stock framework
In this system, inventory not updated day to day basis.
A real counting of goods which is remaining in the hand calculating at the end of accounting period.
It always maintain a specific accounting period for determine a periodic financial statement.
This may use gross method of net method, but always shows a single momentary value for each journal.
Under a perpetual stock framework,
In this system, each transaction will be recorded in detail and updated on daily basis.
During the accounting period, sale and sale return recorded are recorded in the inventory system.
In this method, each journal entry records the financial events within continuous process.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
- Can you help me with accounting questionsarrow_forwardCariveh Co sells automotive supplies from 25 different locations in one country. Each branch has up to 30 staff working there, although most of the accounting systems are designed and implemented from the company's head office. All accounting systems, apart from petty cash, are computerised, with the internal audit department frequently advising and implementing controls within those systems. Cariveh has an internal audit department of six staff, all of whom have been employed at Cariveh for a minimum of five years and some for as long as 15 years. In the past, the chief internal auditor appoints staff within the internal audit department, although the chief executive officer (CEO) is responsible for appointing the chief internal auditor. The chief internal auditor reports directly to the finance director. The finance director also assists the chief internal auditor in deciding on the scope of work of the internal audit department. You are an audit manager in the internal audit…arrow_forwardCariveh Co sells automotive supplies from 25 different locations in one country. Each branch has up to 30 staff working there, although most of the accounting systems are designed and implemented from the company's head office. All accounting systems, apart from petty cash, are computerised, with the internal audit department frequently advising and implementing controls within those systems. Cariveh has an internal audit department of six staff, all of whom have been employed at Cariveh for a minimum of five years and some for as long as 15 years. In the past, the chief internal auditor appoints staff within the internal audit department, although the chief executive officer (CEO) is responsible for appointing the chief internal auditor. The chief internal auditor reports directly to the finance director. The finance director also assists the chief internal auditor in deciding on the scope of work of the internal audit department. You are an audit manager in the internal audit…arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





