
Concept explainers
Inventory Costing Methods
Crandall Distributors uses a perpetual inventory system and has the following data available for inventory, purchases, and sales for a recent year.
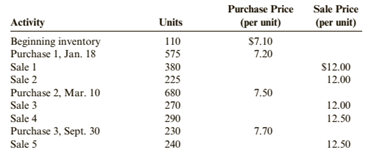
Required:
1. Compute the cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the specific identification method. Assume the ending inventory is made up of 40 units from beginning inventory, 30 units from Purchase 1, 80 units from Purchase 2, and 40 units from Purchase 3.
2. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the FIFO inventory costing method.
3. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the LIFO inventory costing method.
4. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the average cost inventory costing method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.)
5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compare the ending inventory and cost of goods sold computed under all four methods. What can you conclude about the effects of the inventory costing methods on the
(a)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the specific identification method.
Answer to Problem 50E
| Particular | |
| Cost of goods sold | |
| Closing inventory value |
Explanation of Solution
The given information is as follows:
Total available units are:
Calculation of Closing Inventory as per specific identification Method:
Under this method, closing inventory is provided to be valued.
| Closing inventory | Cost of Goods sold | |
| Total |
(b)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the FIFO.
Answer to Problem 50E
| Particular | |
| Cost of goods sold | |
| Closing inventory value |
Explanation of Solution
The given information is as follows:
Total available units are:
Calculation of Closing Inventory as per FIFO Method:
Under this method, which material purchased first, issued first for production. However closing inventory includes last purchased materials in stock. Due to latest purchase in closing inventory, higher value of latest purchase effects cost of goods sold as lower and profit margin will be high.
| Closing inventory | Cost of Goods sold | |
| Total |
(c)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the LIFO.
Answer to Problem 50E
| Particular | |
| Cost of goods sold | |
| Closing inventory value |
Explanation of Solution
The given information is as follows:
Total available units are:
Calculation of closing inventory as per LIFO Method:
Under this method, which material purchased last, issued first for production. However closing inventory includes earliest purchased material in stock. Due to earliest purchase material in stock, lower value of earliest purchased effects cost of goods sold as high and profit margin will be lower.
| Ending Inventory | Cost of Goods sold | |
| Total |
(d)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the average cost method.
Answer to Problem 50E
| Particular | |
| Cost of goods sold | |
| Closing inventory value |
Explanation of Solution
The given information is as follows:
Total available units are:
Calculation of closing inventory as per weighted average method:
Under this method, average cost per unit of inventory is calculated and closing inventory value is to be calculated on that basis. Average cost of inventory is changed on purchase high or low. However we follow indirect method of average cost to calculate closing inventory.
As the fist two sales are done only from two purchases and beginning inventory and the third sale is done including all purchases. Hence, there will requirement of two average cost for computing the cost of goods sold.
| Closing inventory | Cost of Goods sold | |
| Total |
(e)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The comparison of ending inventory and cost of goods sold and comment the effects of these on income statement and balance sheet.
Answer to Problem 50E
The lowest cost of goods sold and the highest closing inventory gives a higher gross profit which is in FIFO method. The highest cost of goods sold and the lowest closing inventory gives lower gross profit which is in LIFO method. This affects the net income and balance sheet also.
Explanation of Solution
The comparisons of the four methods are as follows:
| Ending inventory | Cost of goods sold | |
| Specific identification | ||
| FIFO | ||
| LIFO | ||
| Average Cost |
As per above calculated table, it can be concluded that the FIFO method will give higher gross profits as compared to other methods as it has highest ending inventory and lowest cost of goods sold which also reflect as higher net income and higher asset side of balance sheet.
Likewise, there is opposite scenario in LIFO method. In the LIFO method, there will be lower gross profits as compared to other methods as it has lowest ending inventory and highest cost of goods sold which also reflect as lower net income and lower asset side of balance sheet.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
- For 2014 moss corporation reported net income of solve this question correct answer general Accountingarrow_forwardExplain the concept of interim financial accounting reportingarrow_forwardThe contribution margin ratio is calculated as how? a) Gross margin divided by sales b) Operating income divided by sales c) Contribution margin divided by sales d) Net income divided by salesarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning





