
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
A reactant W can undergo two separate reactions to yield either X or Y. From the free energy diagram given below, the product that would be in greater abundance at equilibrium is to be determined.
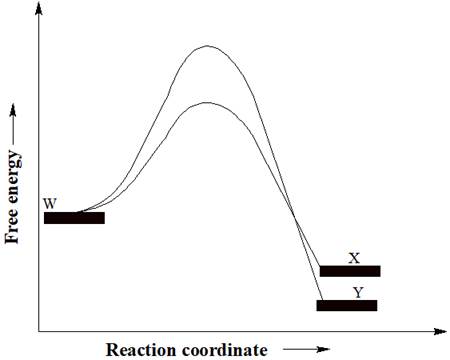
Concept introduction:
In a reaction free energy diagram, Gibbs free energy is plotted as a function of the reaction coordinate. As the reaction coordinate increases, the geometries of the species involved in the reaction increasingly resemble those of the products. The product having lower energy signifies that it is the most stable product. The most stable product would be in greater abundance at equilibrium.
(b)
Interpretation:
A reactant W can undergo two separate reactions to yield either X or Y. From the free energy diagram given below, the product that would be in greater abundance at equilibrium is to be determined.
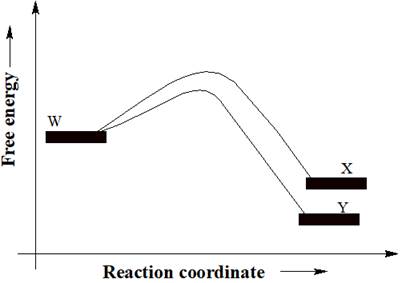
Concept introduction:
In a reaction free energy diagram, Gibbs free energy is plotted as a function of the reaction coordinate. As the reaction coordinate increases, the geometries of the species, involved in the reaction, increasingly resemble those of the products. The product having lower energy signifies that it is the most stable product. The most stable product would be in greater abundance at equilibrium.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms: Study Guide/solutions Manual (second)
- CH, CH CH₂ CH₂ Phytyl side chain 5. What is the expected order of elution of compounds A-D below from a chromatography column packed with silica gel, eluting with hexane/ethyl acetate? C D OHarrow_forwardPlease analze my gel electrophoresis column of the VRK1 kinase (MW: 39.71 kDa). Attached is the following image for the order of column wells and my gel.arrow_forward2.0arrow_forward
- Write the electron configuration of an atom of the element highlighted in this outline of the Periodic Table: 1 23 4 5 6 7 He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn Hint: you do not need to know the name or symbol of the highlighted element! ☐arrow_forwardCompare these chromatograms of three anti-psychotic drugs done by HPLC and SFC. Why is there the difference in separation time for SFC versus HPLC? Hint, use the Van Deemter plot as a guide in answering this question. Why, fundamentally, would you expect a faster separation for SFC than HPLC, in general?arrow_forwardA certain inorganic cation has an electrophoretic mobility of 5.27 x 10-4 cm2s-1V-1. The same ion has a diffusion coefficient of 9.5 x 10-6cm2s-1. If this ion is separated from cations by CZE with a 75cm capillary, what is the expected plate count, N, at an applied voltage of 15.0kV? Under these separation conditions, the electroosmotic flow rate was 0.85mm s-1 toward the cathode. If the detector was 50.0cm from the injection end of the capillary, how long would it take in minutes for the analyte cation to reach the detector after the field was applied?arrow_forward
- 2.arrow_forwardPlease solve for the following Electrochemistry that occursarrow_forwardCommercial bleach contains either chlorine or oxygen as an active ingredient. A commercial oxygenated bleach is much safer to handle and less likely to ruin your clothes. It is possible to determine the amount of active ingredient in an oxygenated bleach product by performing a redox titration. The balance reaction for such a titration is: 6H+ +5H2O2 +2MnO4- à 5O2 + 2Mn2+ + 8H2O If you performed the following procedure: “First, dilute the Seventh Generation Non-Chlorine Bleach by pipetting 10 mL of bleach in a 100 mL volumetric flask and filling the flask to the mark with distilled water. Next, pipet 10 mL of the diluted bleach solution into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask and add 20 mL of 1.0 M H2SO4 to the flask. This solution should be titrated with 0.0100 M KMnO4 solution.” It took 18.47mL of the KMnO4 to reach the endpoint on average. What was the concentration of H2O2 in the original bleach solution in weight % assuming the density of bleach is 1g/mL?arrow_forward
- 10.arrow_forwardProper care of pH electrodes: Why can you not store a pH electrode in distilled water? What must you instead store it in? Why?arrow_forwardWrite the electron configuration of an atom of the element highlighted in this outline of the Periodic Table: 1 23 4 569 7 He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn Hint: you do not need to know the name or symbol of the highlighted element! §arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning



