
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781259977596
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.26P
Draw the products of homolysis or heterolysis of each indicated bond. Use electronegativity
differences to decide on the location of charges in the heterolysis reaction. Classify each
carbon reactive intermediate as a radical, carbocation, or carbanion.
a.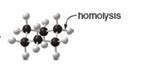 b.
b. 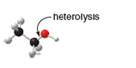
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
eks.com/aleksogi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS17Hd6m-HIl6n52njJN-TXdQA2X9yID-1SWQJTgnjARg30
111
States of Matter
Understanding conceptual components of the enthalpy of solution
0/5
Ge
A small amount of acetonitrile (CH, CN) is dissolved in a large amount of water. Imagine separating this process into the four stages sketched below. (These
sketches show only a portion of the substances, so you can see the density and distribution of atoms and molecules in them.)
CH,CN
H₂O
B
88
C
Use these sketches to answer the questions in the table below.
The enthalpy of solution AH is negative
soln
when CH3CN dissolves in water. Use this
information to list the stages in order of increasing
enthalpy.
Would heat be absorbed or released if the system
moved from Stage C to D?
What force would oppose or favor the system
moving from Stage C to D? Check all that apply.
1
absorbed
O released
neither absorbed nor released.
none
O ionic bonding force
covalent bonding force…
In a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of ŋ as a function of
the current density:
1. at low fields is linear 2. at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law
Find the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same
value as when calculated for cases 1 and 2 (maximum relative difference of
5% with respect to the behavior for higher fields). To which overpotential
range does this correspond?
Data: 10 = 1.5 mA cm², T = 300°C, ẞ = 0.64, R = 8.314 J K 1 mol¹ and F = 96485
C mol-1.
Indicate 10.6 with only one significant figure.
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 6 - Problem 6.1 Classify each transformation as...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.2PCh. 6 - Problem 6.3 By taking into account...Ch. 6 - Problem 6.4 Use curved arrows to show the movement...Ch. 6 - Problem 6.5 Follow the curved arrows and draw the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.6PCh. 6 - Problem 6.7 Use the values in Table 6.2 to...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.8PCh. 6 - aWhich Keq corresponds to a negative value of G,...Ch. 6 - Given each of the following values, is the...
Ch. 6 - Given each of the following values, is the...Ch. 6 - The equilibrium constant for the conversion of the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.13PCh. 6 - For a reaction with H=40kJ/mol, decide which of...Ch. 6 - For a reaction with H=20kJ/mol, decide which of...Ch. 6 - Draw an energy diagram for a reaction in which the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.17PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.18PCh. 6 - Problem 6.19 Consider the following energy...Ch. 6 - Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction,...Ch. 6 - Which value if any corresponds to a faster...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.22PCh. 6 - Problem 6.23 For each rate equation, what effect...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.24PCh. 6 - Identify the catalyst in each equation. a....Ch. 6 - Draw the products of homolysis or heterolysis of...Ch. 6 - Explain why the bond dissociation energy for bond...Ch. 6 - Classify each transformation as substitution,...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.29PCh. 6 - 6.30 Draw the products of each reaction by...Ch. 6 - 6.31 (a) Add curved arrows for each step to show...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.32PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.33PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.34PCh. 6 - Calculate H for each reaction. a HO+CH4CH3+H2O b...Ch. 6 - Homolysis of the indicated CH bond in propene...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.37PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.38PCh. 6 - 6.39. a. Which value corresponds to a negative...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.40PCh. 6 - For which of the following reaction is S a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.42PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.43PCh. 6 - 6.44 Consider the following reaction: .
Use curved...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.45PCh. 6 - Draw an energy diagram for the Bronsted-Lowry...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.47PCh. 6 - Indicate which factors affect the rate of a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.49PCh. 6 - 6.50 The conversion of acetyl chloride to methyl...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.51PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.52PCh. 6 - The conversion of (CH3)3Cl to (CH3)2C=CH2 can...Ch. 6 - 6.54 Explain why is more acidic than , even...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.55PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.56PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.57PCh. 6 - Although Keq of equation 1 in problem 6.57 does...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.59P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If I have 10 data points for variables x and y, when I represent y versus x I obtain a line with the equation y = mx + b. Is the slope m equal to dy/dx?arrow_forwardThe data for the potential difference of a battery and its temperature are given in the table. Calculate the entropy change in J mol-1 K-1 (indicate the formulas used).Data: F = 96485 C mol-1arrow_forwardIn a cell, the change in entropy (AS) can be calculated from the slope of the E° vs 1/T graph. The slope is equal to -AS/R, where R is the gas constant. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- Using the Arrhenius equation, it is possible to establish the relationship between the rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction and the temperature (T), in Kelvin (K), the universal gas constant (R), the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). This equation is widely applied in studies of chemical kinetics, and is also widely used to determine the activation energy of reactions. In this context, the following graph shows the variation of the rate constant with the inverse of the absolute temperature, for a given chemical reaction that obeys the Arrhenius equation. Based on the analysis of this graph and the concepts acquired about the kinetics of chemical reactions, analyze the following statements: I. The activation energy (Ea) varies with the temperature of the system. II. The activation energy (Ea) varies with the concentration of the reactants. III. The rate constant (K) varies proportionally with temperature. IV. The value of the…arrow_forwardIn an electrolytic cell, indicate the formula that relates E0 to the temperature T.arrow_forward-- 14:33 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 11. Compound A can transform into compound B through an organic reaction. From the structures below, mark the correct one: HO A تھے۔ די HO B ○ A) Compounds A and B are isomers. B) Both have the same number of chiral carbons. C) Compound A underwent an addition reaction of Cl2 and H2O to form compound B. D) Compound A underwent a substitution reaction forming the intermediate chlorohydrin to obtain compound B. E) Compound A underwent an addition reaction of Cl2 forming the chloronium ion and then added methanol to obtain compound B. 60arrow_forward
- -- 14:40 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 13. The compound 1-bromo-hex-2-ene reacts with methanol to form two products. About this reaction, mark the correct statement: OCH3 CH3OH Br OCH3 + + HBr A B A) The two products formed will have the same percentage of formation. B) Product B will be formed by SN1 substitution reaction with the formation of an allylic carbocation. C) Product A will be formed by SN1 substitution reaction with the formation of a more stable carbocation than product B. D) Product A will be formed by an SN2 substitution reaction occurring in two stages, the first with slow kinetics and the second with fast kinetics. E) The two compounds were obtained by addition reaction, with compound B having the highest percentage of formation. 57arrow_forward-- ☑ 14:30 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 10. Amoxicillin (figure X) is one of the most widely used antibiotics in the penicillin family. The discovery and synthesis of these antibiotics in the 20th century made the treatment of infections that were previously fatal routine. About amoxicillin, mark the correct one: HO NH2 H S -N. HO Figura X. Amoxicilina A) It has the organic functions amide, ester, phenol and amine. B) It has four chiral carbons and 8 stereoisomers. C) The substitution of the aromatic ring is of the ortho-meta type. D) If amoxicillin reacts with an alcohol it can form an ester. E) The structure has two tertiary amides. 62arrow_forwardThe environmental police of a Brazilian state received a report of contamination of a river by inorganic arsenic, due to the excessive use of pesticides on a plantation on the riverbanks. Arsenic (As) is extremely toxic in its many forms and oxidation states. In nature, especially in groundwater, it is found in the form of arsenate (AsO ₄ ³ ⁻ ), which can be electrochemically reduced to As ⁰ and collected at the cathode of a coulometric cell. In this case, Potentiostatic Coulometry (at 25°C) was performed in an alkaline medium (pH = 7.5 throughout the analysis) to quantify the species. What potential (E) should have been selected/applied to perform the analysis, considering that this is an exhaustive electrolysis technique (until 99.99% of all AsO ₄ ³ ⁻ has been reduced to As ⁰ at the electrode, or n( final) = 0.01% n( initial )) and that the concentration of AsO ₄ ³ ⁻ found in the initial sample was 0.15 mmol/L ? Data: AsO ₄ 3 ⁻ (aq) + 2 H ₂ O ( l ) + 2 e ⁻ → A s O ₂ ⁻ ( a…arrow_forward
- -- 14:17 15. Water-soluble proteins are denatured when there is a change in the pH of the environment in which they are found. This occurs due to the protonation and deprotonation of functional groups present in their structure. Choose the option that indicates the chemical bonds modified by pH in the protein represented in the following figure. E CH2 C-OH CH2 H₂C H₁C CH CH3 CH3 CH CH₂-S-S-CH₂- 910 H B -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH₂-NH3* −0—C—CH₂- ○ A) A, C e D. • В) Вес ○ C) DeE ○ D) B, De E ○ E) A, B e C 68arrow_forwardSuppose sodium sulfate has been gradually added to 100 mL of a solution containing calcium ions and strontium ions, both at 0.15 mol/L. Indicate the alternative that presents the percentage of strontium ions that will have precipitated when the calcium sulfate begins to precipitate. Data: Kps of calcium sulfate: 2.4x10 ⁻ ⁵; Kps of strontium sulfate: 3.2x10 ⁻ ⁷ A) 20,2 % B) 36,6 % C) 62,9 % D) 87,5 % E) 98.7%arrow_forward14:43 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 14. The following diagrams represent hypothetical membrane structures with their components numbered from 1 to 6. Based on the figures and your knowledge of biological membranes, select the correct alternative. | 3 5 || 人 2 500000 6 A) Structures 1, 3, 5, 2 and 4 are present in a constantly fluid arrangement that allows the selectivity of the movement ○ of molecules. Structure 4, present integrally or peripherally, is responsible for this selection, while the quantity of 6 regulates the fluidity. B) The membranes isolate the cell from the environment, but allow the passage of water-soluble molecules thanks to the presence of 2 and 3. The membrane in scheme is more fluid than that in 55arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Nomenclature: Crash Course Chemistry #44; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U7wavimfNFE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY