
Concept explainers
Ten mL of pure liquid water in a cylinder with a movable piston is heated at a constant pressure of 1 atm from an initial temperature of 80°C. The temperature of the system is monitored, and the following behavior is observed:
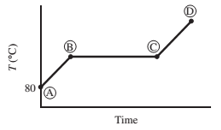
(a) What is happening in steps AB, BC, and CD? What is the temperature corresponding to the horizontal portion of the curve?
(b) Estimate the volume occupied by the water at points B and C. (Assume the vapor follows the ideal-gas equation of state.)
(a)
Interpretation:
Identify the process in AB, BC, CD areas and calculate horizontal zone temperature.
Concept introduction:
Energy is transferred into a system when it is heated. The system will change depending on the energy it receives. This can happen through increase in temperature. A heating curve is called a plot of the temperature versus time.
Answer to Problem 6.1P
- AB − Water liquid heating zone (temperature increase)
- BC − Vaporization of water (liquid to gas phase)
- CD − water vapor (gas phase) heating zone
Horizontal portion temperature = 100°C
Explanation of Solution
AB Step
As heat is absorbed, the temperature of the liquid begins to increase this is due to the increase in the kinetic energy of the molecules of liquid. For standard atmospheric pressure, the rise in temperature takes place until it reaches to 100°C. With increasing temperature, the volume of the liquid remains constant due to little expansion for liquids.
BC Step
At this point, the heat is consumed to begin vaporization of liquid. This temperature is known as the bubble point temperature. Due to change in the previous state, the temperature remains constant and water molecules are moving from liquid to vapor phase. At point C, the last drop of liquid gets evaporated.
CD Step
The temperature increases above 100 °C, when heating steam boils all the liquid into vapor. This cause increase in the volume. Step B shows transition of liquid to vapor. The boiling point of water is 100 °C (liquid here is water) and pressure is 1 atm.
(b)
Interpretation:
Volume occupied by water at point B and C should be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The ideal gas equation is represented as follows:
Here,
Answer to Problem 6.1P
At point B, the water is present as liquid only thus, the volume will be 10 mL
At point C
Explanation of Solution
At point B, the water is present as liquid only thus, the volume will be 10 mL
The number of moles in 10 mL of liquid water is calculated as follows:
The volume of vapor can be calculated using the ideal gas equation as follows:
Here, number of moles is 0.555 mol at 1 atm and
Putting the values,
Thus, at point C, the volume occupied by the water occupies is 17 L.
At point C,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Binder Ready Version
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
- Only focus on H(3), which the answer is minus 1.26 KJ/mol. This also has the ideal gas of nitrogen gas N2. Two enthalpies need to be calculated for this. The first enthalpy is H = (specific volume) times (pressure difference). For the specific volume of nitrogen, how was 12.089 x10^(-5) m^3/mol obtained? I understand the second enthalpy for the heat capacity for nitrogen gas.arrow_forwardchemical engineering. The answer for H(3) is minus 1.26 KJ/mol. Demonstrate the reference state to the process state for nitrogen gas. I know that is an ideal gas law for the nitrogen gas. I know how to calculate the heat capacity for this.arrow_forwardQ. VI: An equimolar liquid mixture of benzene and toluene is separated into two product streams by distillation. At each point in the column some of the liquid vaporizes and some of the vapor stream condenses. The vapor leaving the top of the column, which contains 97 mole% benzene, is completely condensed and split into two equal fractions: one is taken off as the overhead product stream, and the other (the reflux) is recycled to the top of the column. The overhead product stream contains 89.2% of the benzene fed to the column. The liquid leaving the bottom of the column is fed to a partial reboiler in which 45% of it is vaporized. The vapor generated in the reboiler (the boilup) is recycled to become the rising vapor stream in the column, and the residual reboiler liquid is taken off as the bottom product stream. The compositions of the streams leaving the reboiler are governed by the relation, YB/(1 - YB) XB/(1 - XB) = 2.25 where YB and XB are the mole fractions of benzene in the…arrow_forward
- Q. IV: Aqueous solutions of the amino-acid L-isoleucine (Ile) are prepared by putting 100.0 grams of pure water into each of six flasks and adding different precisely weighed quantities of lle to each flask. The densities of the solutions at 50.0±0.05°C are then measured with a precision densitometer, with the following results. r (g lle/100 g H2O) 0.000 p (g solution/cm³) 0.8821 0.98803 0.98984 1.7683 0.99148 2.6412 3.4093 0.99297 0.99439 4.2064 0.99580 (a) Plot a calibration curve showing the mass ratio, r, as a function of solution density, p, and fit a straight line to the data to obtain an equation of the form r = ap + b. (b) The volumetric flow rate of an aqueous lle solution at a temperature of 50°C is 150 L/h. The density of the sample of the stream is measured and found to be 0.9940 g/cm³. Use the calibration equation to estimate the mass flow rate of lle in the stream (in kg lle/h). (c) It has been later discovered that the thermocouple used to measure the stream temperature…arrow_forwardchemical engineering. The answer is minus 1.26 KJ/mol for H(3). Demonstrate the reference state to the process state and calculations. I only need help for determing that variable.arrow_forwardExhaust gas from a power plant passes through a 15-by-20-it rectangular duct at an average velocity of 50 ft/s. The total length of duct is 250 ft and there are two 90° bends.The gas is at 180°F and about 1 atm, and the properties are similar to those of air. Calculate the pressure drop in the duet and the power required to overcome pressure losses.arrow_forward
- Untuk sistem gas etilena (1)/propilena (2), estimasi (f^1, f^2, $^1, dan ^2 pada t = 150°C, P = 30 bar, dan y1 = 0,35; kij = 0. (a) Dengan menerapkan Persamaan (10.63). (b) Dengan asumsi bahwa campuran adalah lingkungan idealarrow_forwardOnly focus on H(3), which is the specific enthalpy for nitrogen gas. chemical engineeringarrow_forwardchemical engineering. Only focus on H(3), which is the nitrogen gas. Start with the reference state to the process state. Be thorough to the fullestarrow_forward
- acetone with these parameters: po:=101325; #Standard atmospheric pressure in PaTfo:=273.15-94.45; #Melting temperature in K Tvo:=273.15+56.15; #Boiling temperature in K Hv:=31270; #Enthalpy of vaporization in J/molR:=8.314; #Gas Constant in J/mol*KNLe:=1.76; #Lewis number for acetoneMw:= 0.05808 ; #kg/mol molecular weight of acetoneW0:= 0.15; Wsp:=0.005;Am:= 0.12; #m^2/kg dry solid for the exposed wet areah:= 11; #W/m^2K for heat transfer coefficienttau__min:= Hv*(W0-Wsp)/Mw/Am/h/(T8-TS); tau__min/60;arrow_forwardchemical engineering Material-energy balance. Only focus on the nitrogen gas, which is H(3)arrow_forward1. The settling chamber, shown schematically in Figure 2E1.1, is used as a primary separation device in the removal of dust particles of density 1500 kg/m³ from a gas of density 0:7 kg/m³ and viscosity 1.90 x 10-5 Pa s. Gas inlet Elevation Gas Gas exit exit H Collection surface -W Section X-X Dimensions: H=3m L = 10 m W=2m Figure 2E1.1 Schematic diagram of settling chamber Assuming Stokes' law applies, show that the efficiency of collection of particles of size x is given by the expression collection efficiency, x = x²8(pp - Pi)L 18μHU where U is the uniform gas velocity through the parallel-sided section of the chamber. State any other assumptions made. (b) What is the upper limit of particle size for which Stokes' law applies? (c) When the volumetric flow rate of gas is 0.9 m³/s, and the dimensions of the chamber are those shown in Figure 2E1.1, determine the collection efficiency for spherical particles of diameter 30 mm.arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





