
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal
alkane .
(a)
Answer to Problem 31P
1-chloroethane.
Explanation of Solution
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(b)
Answer to Problem 31P
1,2-dibromoethane.
Explanation of Solution
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following molecule should be determined.
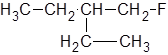
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(c)
Answer to Problem 31P
2-ethyl-1-fluorobutane.
Explanation of Solution
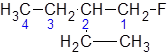
The longest carbon chain giving the halide atom the lowest number has four carbons. So, this is a butane. There is a fluorine atom attached at C-1 and an ethyl group at C-2. Alphabetically, ethyl substituent should be written before, fluoro-. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2-ethyl-1-fluorobutane.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(d)
Answer to Problem 31P
2,2-dimethyl-1-iodopropane.
Explanation of Solution
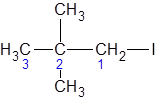
The longest carbon chain giving the halide atom the lowest number has three carbons. So, this is a propane. There is an iodine atom attached at C-1 and two methyl groups at C-2. Alphabetically, iodo- substituent should be written before, methyl. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2,2-dimethyl-1-iodopropane.
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following molecule should be determined.
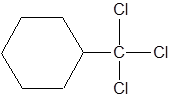
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(e)
Answer to Problem 31P
1-trichloromethylcyclohexane.
Explanation of Solution
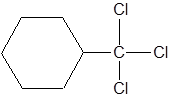
This is a substituted cycloalkane. The cycloalkane has six carbons, so, it is named as cyclohexane. There is a trichloromethyl group attached to C-1 of cyclohexane. So, IUPAC name of this molecule is 1-trichloromethylcyclohexane.
(f)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(f)
Answer to Problem 31P
Tribromomethane.
Explanation of Solution
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-PACKAGE
- 4. Read paragraph 4.15 from your textbook, use your calculated lattice energy values for CuO, CuCO3 and Cu(OH)2 an explain thermal decomposition reaction of malachite: Cu2CO3(OH)2 →2CuO + H2O + CO2 (3 points)arrow_forwardPlease sirrr soollveee these parts pleaseeee and thank youuuuuarrow_forwardIII O Organic Chemistry Using wedges and dashes in skeletal structures Draw a skeletal ("line") structure for each of the molecules below. Be sure your structures show the important difference between the molecules. key O O O O O CHON Cl jiii iiiiiiii You can drag the slider to rotate the molecules. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Q Search X G ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use F 3 W C 3/5arrow_forward
- 3. Use Kapustinskii's equation and data from Table 4.10 in your textbook to calculate lattice energies of Cu(OH)2 and CuCO3 (4 points)arrow_forward2. Copper (II) oxide crystalizes in monoclinic unit cell (included below; blue spheres 2+ represent Cu²+, red - O²-). Use Kapustinski's equation (4.5) to calculate lattice energy for CuO. You will need some data from Resource section of your textbook (p.901). (4 points) CuOarrow_forwardWhat is the IUPAC name of the following compound? OH (2S, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4R)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O (2R, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-ol O(2S, 4S)-4-chloropentan-2-olarrow_forward
- Use the reaction coordinate diagram to answer the below questions. Type your answers into the answer box for each question. (Watch your spelling) Energy A B C D Reaction coordinate E A) Is the reaction step going from D to F endothermic or exothermic? A F G B) Does point D represent a reactant, product, intermediate or transition state? A/ C) Which step (step 1 or step 2) is the rate determining step? Aarrow_forward1. Using radii from Resource section 1 (p.901) and Born-Lande equation, calculate the lattice energy for PbS, which crystallizes in the NaCl structure. Then, use the Born-Haber cycle to obtain the value of lattice energy for PbS. You will need the following data following data: AH Pb(g) = 196 kJ/mol; AHƒ PbS = −98 kJ/mol; electron affinities for S(g)→S¯(g) is -201 kJ/mol; S¯(g) (g) is 640kJ/mol. Ionization energies for Pb are listed in Resource section 2, p.903. Remember that enthalpies of formation are calculated beginning with the elements in their standard states (S8 for sulfur). The formation of S2, AHF: S2 (g) = 535 kJ/mol. Compare the two values, and explain the difference. (8 points)arrow_forwardIn the answer box, type the number of maximum stereoisomers possible for the following compound. A H H COH OH = H C Br H.C OH CHarrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





