
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The R and S should be designated to below substrates as well as products of the bimolecular reaction and products with optical activity should be identified.
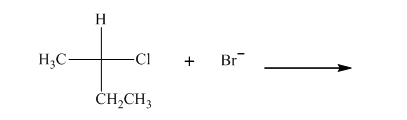
Concept introduction: In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order with the
The Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority. If the groups are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter, if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(b)
Interpretation: The R and S should be designated to belowsubstrates as well as products of the bimolecular reaction and products that are optically active should be identified.
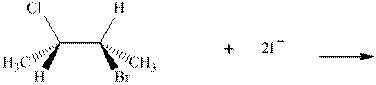
Concept introduction:In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order with the atomic number as the fundamental property. The one with the highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as “a” and so on.
The Fischer projection is written along with the priorities assigned and groups are interchanged between adjacent places so as to obtain the lowest priority group at the bottom or lowest priority. If the groups are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion then R is assigned to the stereocenter, if the rotation is anticlockwise then S is assigned at the configuration.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(c)
Interpretation: The R and S should be designated to below substrates as well as products of the bimolecular reaction and products that are optically active should be identified.
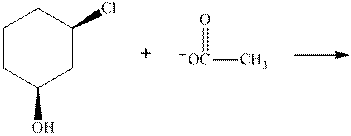
Concept introduction: In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of the atomic number. The one with the highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as “a” and so on.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion the R is assigned to the stereocenter, provided the hydrogen is present below the plane. If hydrogen or least priority group is not below the plane the same molecule is designated as S.
If the rotation is anticlockwise the S is assigned at the configuration provided the hydrogen is present below the plane. If hydrogen or least priority group is not below the plane the same molecule is designated as R.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
(d)
Interpretation: The R and S should be designated to below substrates as well as products of the bimolecular reaction and products that are optically active should be identified.
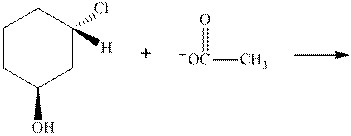
Concept introduction: In order to assign absolute configuration of R and S Cahn − Ingold − Prelog rules are used and the first step is to assign the priority order on the basis of the atomic number. The one with the highest atomic number gest highest priority and is designated as “a” and so on.
If the groups now are arranged are read from highest towards least in clockwise fashion the R is assigned to the stereocenter, provided the hydrogen is present below the plane. If hydrogen or least priority group is not below the plane the same molecule is designated as S.
If the rotation is anticlockwise the S is assigned at the configuration provided the hydrogen is present below the plane. If hydrogen or least priority group is not below the plane the same molecule is designated as R.
Any organic compound must have no plane of symmetry in order to be optically active. The compounds with any plane of symmetry are achiral and optically inactive.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-PACKAGE
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
