
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780321885326
Author: Jane B. Reece, Martha R. Taylor, Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, Kelly A. Hogan
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 13TYK
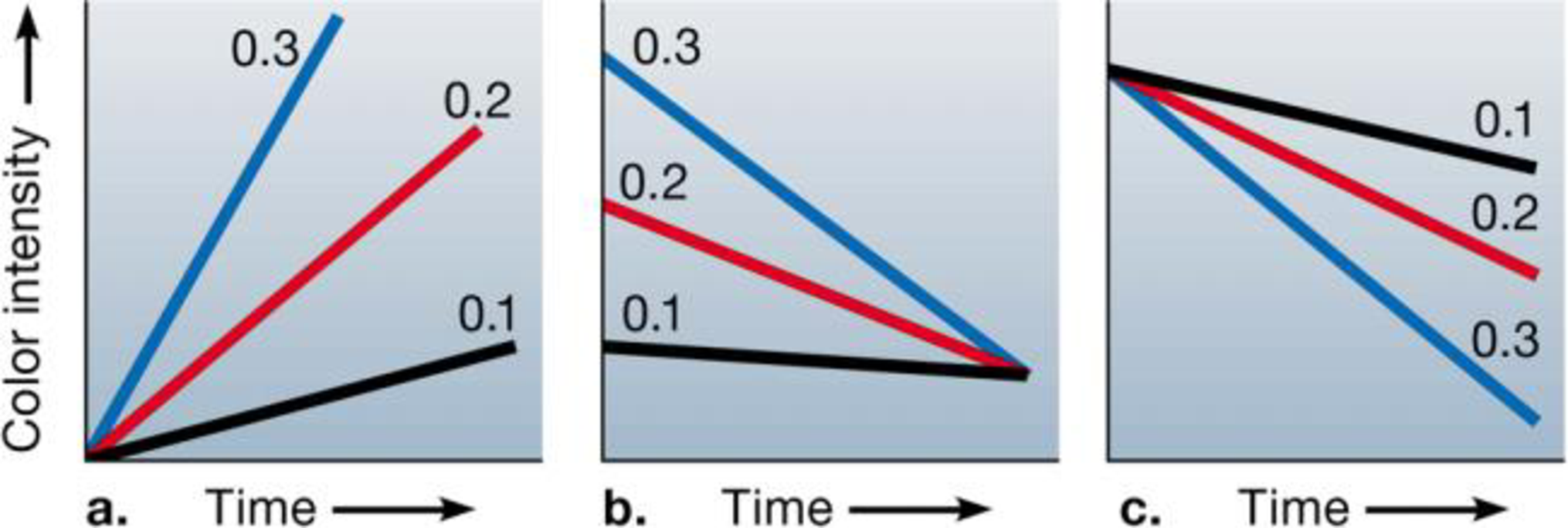
In the citric acid cycle, an enzyme oxidizes malate to oxaloacetate, with the production of NADH and the release of H+. You are studying this reaction using a suspension of bean cell mitochondria and a blue dye that loses its color as it takes up H+. You set up reaction mixtures with mitochondria, dye, and three different concentrations of malate (0.1 mg/L, 0.2 mg/L, and 0.3 mg/L). Which of the following graphs represents the results you would expect, and why?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
HAND DRAW
There should be two pro
Molecular Biology Question. Please help solve. Thanks.
Please draw how two nucleotide triphosphates are linked together to form a dinucleotide, and label the 5' and 3' ends of the resulting dinucleotide.
What is a reversion in molecular biology?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
Ch. 6 - Fill in the blanks in this summary map to help you...Ch. 6 - A biochemist wanted to study how various...Ch. 6 - In glycolysis, _____ is oxidized and _____ is...Ch. 6 - Which of the following is the most immediate...Ch. 6 - Which of the following is a true distinction...Ch. 6 - The poison cyanide binds to an electron carrier...Ch. 6 - In which of the following is the first molecule...Ch. 6 - Which of the three stages of cellular respiration...Ch. 6 - Compare and contrast fermentation as it occurs in...Ch. 6 - Prob. 10TYK
Ch. 6 - Prob. 11TYKCh. 6 - Prob. 12TYKCh. 6 - In the citric acid cycle, an enzyme oxidizes...Ch. 6 - ATP synthase enzymes are found in the prokaryotic...Ch. 6 - 15. SCIENTIFIC THINKING Several studies have found...Ch. 6 - For a short time in the 1930s, some physicians...Ch. 6 - Explain how the mechanism of brown fat metabolism...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is a gain of function mutation?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question: Please help. Thank you Is Southern hybridization's purpose detecting specific nucleotide sequences? How so?arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the question(s) below. Martin Wikelski and L. Michael Romero (Body size, performance and fitness in Galápagos marine iguanas, Integrative and Comparative Biology 43 [2003]:376-86) measured the snout-to-vent (anus) length of Galápagos marine iguanas and observed the percent survival of different-sized animals, all of the same age. The graph shows the log snout-vent length (SVL, a measure of overall body size) plotted against the percent survival of these different size classes for males and females. Survival (%) 100- 80- 60- 40- 20- 0+ 1.9 T 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Log SVL (mm) 19) Examine the figure above. What type of selection for body size appears to be occurring in these marine iguanas? A) directional selection B) stabilizing selection C) disruptive selection D) You cannot determine the type of selection from the above information. 3arrow_forward
- 24) Use the following information to answer the question below. Researchers studying a small milkweed population note that some plants produce a toxin and other plants do not. They identify the gene responsible for toxin production. The dominant allele (T) codes for an enzyme that makes the toxin, and the recessive allele (t) codes for a nonfunctional enzyme that cannot produce the toxin. Heterozygotes produce an intermediate amount of toxin. The genotypes of all individuals in the population are determined (see table) and used to determine the actual allele frequencies in the population. TT 0.49 Tt 0.42 tt 0.09 Refer to the table above. Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) Yes. C) No; there are more homozygotes than expected. B) No; there are more heterozygotes than expected. D) It is impossible to tell.arrow_forward30) A B CDEFG Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following forms a monophyletic group? A) A, B, C, and D B) C and D C) D, E, and F D) E, F, and Garrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question. Please help with step solution and explanation. Thank you: The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) reaction consists of three steps denaturation, hybridization, and elongation. Please describe what occurs in the annealing step of the PCR reaction. (I think annealing step is hybridization). What are the other two steps of PCR, and what are their functions? Next, suppose the Tm for the two primers being used are 54C for Primer A and 67C for Primer B. Regarding annealing step temperature, I have the following choices for the temperature used during the annealing step:(a) 43C (b) 49C (c) 62C (d) 73C Which temperature/temperatures should I choose? What is the corresponding correct explanation, and why would I not use the other temperatures? Have a good day!arrow_forward
- Using the data provided on the mean body mass and horn size of 4-year-old male sheep, draw a scatterplot graph to examine how body mass and horn size changed over time.arrow_forwardPlease write a 500-word report about the intake of saturated fat, sodium, alcoholic beverages, or added sugar in America. Choose ONE of these and write about what is recommended by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans (guideline #4) and why Americans exceed the intake of that nutrient. Explain what we could do as a society and/or individuals to reduce our intake of your chosen nutrient.arrow_forwardWrite a 500-word report indicating how you can change the quantity or quality of TWO nutrients where your intake was LOWER than what is recommended by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and/or the DRIs. Indicate how the lack of the nutrient may affect your health. For full credit, all of the following points must be addressed and elaborated on in more detail for each nutrient: The name of the nutrient At least 2 main functions of the nutrient (example: “Vitamin D regulates calcium levels in the blood and calcification of bones.”) Your percent intake compared to the RDA/DRI (example “I consumed 50% of the RDA for vitamin D”) Indicate why your intake was below the recommendations (example: “I only had one serving of dairy products and that was why I was below the recommendations for vitamin D”) How would you change your dietary pattern to meet the recommendations? – be sure to list specific foods (example: “I would add a yogurt and a glass of milk to each day in order to increase my…arrow_forward
- Why are nutrient absorption and dosage levels important when taking multivitamins and vitamin and mineral supplements?arrow_forwardI'm struggling with this topic and would really appreciate your help. I need to hand-draw a diagram and explain the process of sexual differentiation in humans, including structures, hormones, enzymes, and other details. Could you also make sure to include these terms in the explanation? . Gonads . Wolffian ducts • Müllerian ducts . ⚫ Testes . Testosterone • Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) . Epididymis • Vas deferens ⚫ Seminal vesicles ⚫ 5-alpha reductase ⚫ DHT - Penis . Scrotum . Ovaries • Uterus ⚫ Fallopian tubes - Vagina - Clitoris . Labia Thank you so much for your help!arrow_forwardRequisition Exercise A phlebotomist goes to a patient’s room with the following requisition. Hometown Hospital USA 125 Goodcare Avenue Small Town, USAarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Intro to Food Microbiology; Author: A professor pressing record;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vg8fSmk0dVU;License: Standard youtube license