
a.
To define: The variables to represent the cost of a taco and the cost of a burrito.
a.
Answer to Problem 13MCQ
The algebraic quantities x and y are variables that represent cost of one taco and cost of one burrito respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
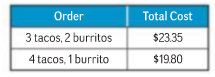
The cost of two orders at a restaurant is shown in table given below.
Concept used:
The variables are independent quantities.
Definition:
Suppose the cost of one taco is x and cost of one burrito is y . The algebraic quantities x and y are variables.
b.
To write: A system of equations to find the cost of a single taco and a single burrito.
b.
Answer to Problem 13MCQ
A system of equations to find the cost of a single taco and a single burrito is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The data table in part (a)
Concept used:
According to the given conditions we connect the variables and given quantities.
Calculations:
Conclusion:
In order-1, the total cost of 3 tacos and 2 burritos is $23.35. The cost of one taco is x and that of burrito is y . So cost of 3 tacos is $ 3x and of 2 burritos is $ 2y . Therefore, the equation that connect the variable and given quantities is
… (1)
In order-2, the total cost of 4 tacos and 1burritos is $19.80. The cost of one taco is x and that of burrito is y . So cost of 3 tacos is $ 4x and of 2 burritos is $ y . Therefore, the equation that connect the variable and given quantities is
… (2)
Conclusion:
A system of equations to find the cost of a single taco and a single burrito is
c.
To solve: The system of equations in obtained in part (a).
c.
Answer to Problem 13MCQ
The solution of system of equations is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given system of equations is
Method used:
We solve equations using graphing calculator.
Graph:
The graph of given system of equations
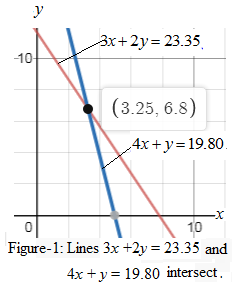
We see that lines
The solution means that cost of one taco is $ 3.35 and the cost of one burrito is $6.80.
Conclusion:
The solution of system of equations is
d.
To find: The amount to be paid by a customer to buy 2 taco and 2 burrito.
d.
Answer to Problem 13MCQ
The amount to be paid by a customer to buy 2 taco and 2 burrito is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The cost of one taco is $ 3.35 and the cost of one burrito is $6.80.
Formula used:
Cost of n items C = n × cost of one item.
Calculations:
The amount paid by customer to buy 2 tacos
The amount paid by customer to buy 2burritos
Therefore, the amount to be paid by a customer to buy 2 taco and 2 burrito is
Conclusion:
The amount to be paid by a customer to buy 2 taco and 2 burrito is
Chapter 6 Solutions
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
- 2) If Mand N be two water hyper Plane ofx Show that MUN and MN is hy Per Plane ofx with prove and Examplame. or 3) IS AUB is convex set and affine set or blensed set or symmetre setorsubsie.... Show that A and B is convex or affine or Hensedsed or symmetivce or subspace. 4) 18 MUN is independence show that Prove or ExPlane Mand Nave independend. or not. 5) Jet X be Vector Pace over I show that is xty tnx st Xty 3 fix→ F s-t f(x) (9) Jet Mand N be two blanced set of Xbe Vector space show tha MUNIS ansed setarrow_forwardFind a polynomial with integer coefficients that satisfies the given conditions. T(x) has degree 4, zeros i and 1 + i, and constant term 12.arrow_forwardHow to solve 2542000/64132 without a calculator?arrow_forward
- How much is the circumference of a circle whose diameter is 7 feet?C =π darrow_forwardHow to solve 2542/64.132arrow_forwardAssume that you fancy polynomial splines, while you actually need ƒ(t) = e²/3 – 1 for t€ [−1, 1]. See the figure for a plot of f(t). Your goal is to approximate f(t) with an inter- polating polynomial spline of degree d that is given as sa(t) = • Σk=0 Pd,k bd,k(t) so that sd(tk) = = Pd,k for tk = −1 + 2 (given d > 0) with basis functions bd,k(t) = Σi±0 Cd,k,i = • The special case of d 0 is trivial: the only basis function b0,0 (t) is constant 1 and so(t) is thus constant po,0 for all t = [−1, 1]. ...9 The d+1 basis functions bd,k (t) form a ba- sis Bd {ba,o(t), ba,1(t), bd,d(t)} of the function space of all possible sα (t) functions. Clearly, you wish to find out, which of them given a particular maximal degree d is the best-possible approximation of f(t) in the least- squares sense. _ 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.3 -0.4 -0.5 -0.6 -0.7 -0.8 -0.9 -1 function f(t) = exp((2t)/3) - 1 to project -1 -0.9 -0.8 -0.7 -0.6 -0.5 -0.4 -0.3 -0.2 -0.1 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5…arrow_forward
- An image processor considered a 750×750 pixels large subset of an image and converted it into gray-scale, resulting in matrix gIn - a false-color visualization of gIn is shown in the top-left below. He prepared a two-dim. box filter f1 as a 25×25 matrix with only the 5×5 values in the middle being non-zero – this filter is shown in the top-middle position below. He then convolved £1 with itself to get £2, before convolving £2 with itself to get f3. In both of the steps, he maintained the 25×25 size. Next, he convolved gIn with £3 to get gl. Which of the six panels below shows g1? Argue by explaining all the steps, so far: What did the image processor do when preparing ₤3? What image processing operation (from gin to g1) did he prepare and what's the effect that can be seen? Next, he convolved the rows of f3 with filter 1/2 (-1, 8, 0, -8, 1) to get f4 - you find a visualization of filter f 4 below. He then convolved gIn with f4 to get g2 and you can find the result shown below. What…arrow_forward3ur Colors are enchanting and elusive. A multitude of color systems has been proposed over a three-digits number of years - maybe more than the number of purposes that they serve... - Everyone knows the additive RGB color system – we usually serve light-emitting IT components like monitors with colors in that system. Here, we use c = (r, g, b) RGB with r, g, bЄ [0,1] to describe a color c. = T For printing, however, we usually use the subtractive CMY color system. The same color c becomes c = (c, m, y) CMY (1-c, 1-m, 1-y) RGB Note how we use subscripts to indicate with coordinate system the coordinates correspond to. Explain, why it is not possible to find a linear transformation between RGB and CMY coordinates. Farbenlehr c von Goethe Erster Band. Roſt einen Defte mit fergen up Tübingen, is et 3. Cotta'fden Babarblung. ISIO Homogeneous coordinates give us a work-around: If we specify colors in 4D, instead, with the 4th coordinate being the homogeneous coordinate h so that every actual…arrow_forwardCan someone provide an answer & detailed explanation please? Thank you kindly!arrow_forward
- Given the cubic function f(x) = x^3-6x^2 + 11x- 6, do the following: Plot the graph of the function. Find the critical points and determine whether each is a local minimum, local maximum, or a saddle point. Find the inflection point(s) (if any).Identify the intervals where the function is increasing and decreasing. Determine the end behavior of the graph.arrow_forwardGiven the quadratic function f(x) = x^2-4x+3, plot the graph of the function and find the following: The vertex of the parabola .The x-intercepts (if any). The y-intercept. Create graph also before solve.arrow_forwardwhat model best fits this dataarrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





