
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781292089034
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.9, Problem 19P
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the following reaction in which C is the most stable and B the least stable of the three species and the transition state going from A to B is more stable than the transition state going from B to C:
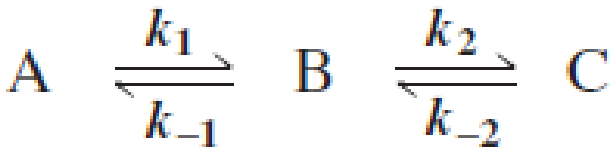
- a. How many intermediates are there?
- b. How many transition states are there?
- c. Which step has the greater rate constant in the forward direction?
- d. Which step has the greater rate constant in the reverse direction?
- e. Of the four steps, which has the greatest rate constant?
- f. Which is the rate-determining step in the forward direction?
- g. Which is the rate-determining step in the reverse direction?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Y= - 0.039 (14.01) + 0.7949
Suppose 1.76 g of magnesium acetate (Mg (CH3CO2)2) are dissolved in 140. mL of water. Find the composition of the resulting electrolyte solution.
In particular, list the chemical symbols (including any charge) of each dissolved ion in the table below. List only one ion per row.
mEq
Then, calculate the concentration of each ion in
dwrite the concentration in the second column of each row. Be sure you round your answers to the
L
correct number of significant digits.
ion
Add Row
mEq
L
x
5
A pdf file of your hand drawn, stepwise mechanisms for the reactions. For each reaction in the assignment, you must write each mechanism three times (there are 10 reactions, so 30 mechanisms). (A) do the work on a tablet and save as a pdf., it is expected to write each mechanism out and NOT copy and paste the mechanism after writing it just once. Everything should be drawn out stepwise and every bond that is formed and broken in the process of the reaction, and is expected to see all relevant lone pair electrons and curved arrows.
Chapter 5 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
Ch. 5.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 5.1 - Draw the structure for each of the following: a....Ch. 5.1 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 5.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 5.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 5.4 - a. For which reaction in each set below will S be...Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 9PCh. 5.6 - How many different alkenes can be hydrogenated to...Ch. 5.6 - The same alkane is obtained from the catalytic...
Ch. 5.6 - Prob. 12PCh. 5.6 - Rank the following compounds in order from most...Ch. 5.7 - The rate constant for a reaction can be increased...Ch. 5.7 - Prob. 15PCh. 5.7 - Prob. 16PCh. 5.9 - Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a two-step...Ch. 5.9 - Prob. 18PCh. 5.9 - Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the...Ch. 5.10 - Which of the following parameters would be...Ch. 5 - What is each compounds systematic name?Ch. 5 - Draw the structure of a hydrocarbon that has six...Ch. 5 - Which of the following compounds is the most...Ch. 5 - Prob. 24PCh. 5 - Prob. 25PCh. 5 - Prob. 26PCh. 5 - Prob. 27PCh. 5 - Name the following:Ch. 5 - Prob. 29PCh. 5 - Prob. 30PCh. 5 - Prob. 31PCh. 5 - Prob. 32PCh. 5 - Prob. 33PCh. 5 - Prob. 34PCh. 5 - Prob. 35PCh. 5 - Name each of the following:Ch. 5 - Prob. 38PCh. 5 - Given that the twist-boat conformer of cyclohexane...Ch. 5 - a. The G for conversion of axial fluorocyclohexane...Ch. 5 - Prob. 1PCh. 5 - Prob. 2PCh. 5 - Prob. 3PCh. 5 - Prob. 4PCh. 5 - Prob. 5PCh. 5 - Prob. 6PCh. 5 - Prob. 7PCh. 5 - Prob. 8PCh. 5 - Prob. 9PCh. 5 - Prob. 10P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part II. Identify whether the two protons in blue are homotopic, enantiopic, diasteriotopic, or heterotopic. a) HO b) Bri H HH c) d) H H H Br 0arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardChoose the option that is decreasing from biggest to smallest. Group of answer choices: 100 m, 10000 mm, 100 cm, 100000 um, 10000000 nm 10000000 nm, 100000 um, 100 cm, 10000 mm, 100 m 10000000 nm, 100000 um, 10000 mm, 100 cm, 100 m 100 m, 100 cm, 10000 mm, 100000 um, 10000000 nmarrow_forward
- Q1. (a) Draw equations for homolytic and heterolytic cleavages of the N-H bond in NH3. Use curved arrows to show the electron movement. (b) Draw equations for homolytic and heterolytic cleavages of the N-H bond in NH4*. Use curved arrows to show the electron movement.arrow_forwardWhich is NOT the typical size of a bacteria? 1000 nm 0.001 mm 0.01 mm 1 umarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License