
Concept explainers
What is each compound’s systematic name?
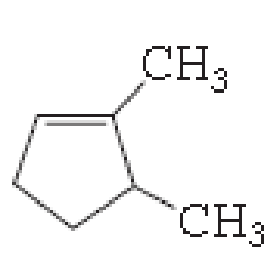
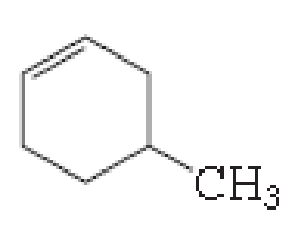
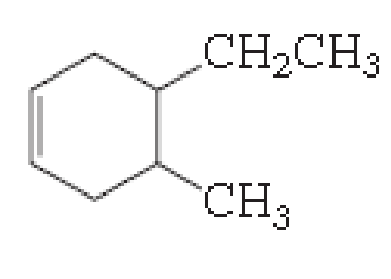
(a)
Interpretation:
The systematic name should be given for the compound.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry).IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. To add suffix to name a compound, the suffix “-ane” in the parent alkane is replaced by the respective suffix, which corresponds to the functional group present in the given compound. For carboxylic acid, suffix “-oic” will be added, for alcohol, suffix “-ol” will be added and so on
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Alkenes:
Alkenes are a class of hydrocarbons. The carbon-carbon double bond is called as alkenes and it is also called as olefins.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
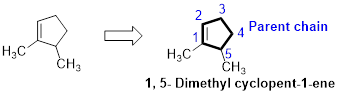
The number of carbon in parent chain is five, hence it is called as pentane, it is in cycle form therefore cyclopentane. The functional group of the given molecule is alkene therefore the suffix “-ane” is replaced with “-ene” indicating the presence of double bond. In the given structure the first and fifth carbon is bonded with methyl group, double bond in first carbon. Therefore the name of the compound is 1, 5- Dimethyl cyclopent-1-ene.
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name should be given for the compound.
Concept introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry).IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. To add suffix to name a compound, the suffix “-ane” in the parent alkane is replaced by the respective suffix, which corresponds to the functional group present in the given compound. For carboxylic acid, suffix “-oic” will be added, for alcohol, suffix “-ol” will be added and so on
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Alkenes:
Alkenes are a class of hydrocarbons. The carbon-carbon double bond is called as alkenes and it is also called as olefins.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
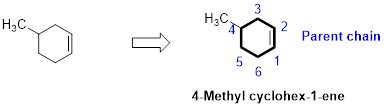
The number of carbon in parent chain is six, hence it is called as hexane, it is in cycle form therefore cyclohexane. The functional group of the given molecule is alkene therefore the suffix “-ane” is replaced with “-ene” indicating the presence of double bond. In the given structure the fourth carbon is bonded with methyl group, double bond in first carbon. Therefore the name of the compound is 4-Methyl cyclohex-1-ene.
(c)
Interpretation:
The systematic name should be given for the compound.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry).IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc. To add suffix to name a compound, the suffix “-ane” in the parent alkane is replaced by the respective suffix, which corresponds to the functional group present in the given compound. For carboxylic acid, suffix “-oic” will be added, for alcohol, suffix “-ol” will be added and so on
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Alkenes:
Alkenes are a class of hydrocarbons. The carbon-carbon double bond is called as alkenes and it is also called as olefins.
Explanation of Solution
The name of the compound is given below,
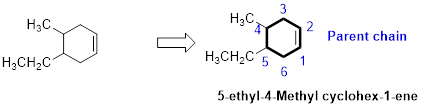
The number of carbon in parent chain is six, hence it is called as hexane, it is in cycle form therefore cyclohexane. The functional group of the given molecule is alkene therefore the suffix “-ane” is replaced with “-ene” indicating the presence of double bond. In the given structure the fourth carbon is bonded with methyl group, fifth carbon is bonded with ethyl group, double bond in first carbon. Therefore the name of the compound is 5-ethyl-4-Methyl cyclohex-1-ene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- Draw a structural formula for the major product of the acid-base reaction shown. H 0 N + HCI (1 mole) CH3 N' (1 mole) CH3 You do not have to consider stereochemistry. ● • Do not include counter-ions, e.g., Na+, I, in your answer. . In those cases in which there are two reactants, draw only the product from 989 CH3 344 ? [Farrow_forwardQuestion 15 What is the major neutral organic product for the following sequence? 1. POCI₂ pyridine ? 2. OsO4 OH 3. NaHSO Major Organic Product ✓ OH OH 'OH OH 'OH 'CIarrow_forwardURGENT! PLEASE HELP!arrow_forward
- Could you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but (color-coded) and step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you! I want to see what they are doingarrow_forwardCan you please help mne with this problem. Im a visual person, so can you redraw it, potentislly color code and then as well explain it. I know im given CO2 use that to explain to me, as well as maybe give me a second example just to clarify even more with drawings (visuals) and explanations.arrow_forward
