
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The condensed structural formula and systematic name should be given for the molecular formula of
Concept introduction:
A condensed structural formula is a system of writing organic structures in a line of text.
Isomer: A molecule having the same molecular formula but with different chemical structure is called isomer.
Constitutional Isomers: A molecule having same molecular formula with different structural formulas (Difference in the connectivity of the molecule is called constitutional isomer).
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry).IUPAC name consists of three parts, namely Prefix, suffix and root word.
Prefix- Represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix- Denotes the presence of
Root word - Represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
Alkenes are a class of hydrocarbons. The carbon-carbon double bond is called as alkenes and it is also called as olefins.
(b)
Interpretation:
The E and Z isomer of the alkene has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
E and Z isomerism:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
Example:
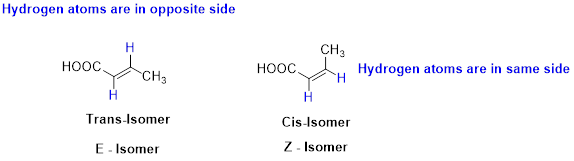
(c)
Interpretation:
The most stable alkene has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Stability of alkene:
Stability of alkene depends on the following factors,
The smallest heat hydrogenation of alkene is more stable. The number of hydrogens bonded to its
Stability of Cis–trans alkene:
The two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are in same side in double bond of alkenes is called as cis isomer (or Z-isomer). Two similar groups (or higher priority groups) are opposite side in double bond of alkenes is called as trans isomer (or E-isomer).
In cis alkene, molecule are close to each other, hence electron clouds interfere each other therefore strain in the molecule so cis alkene is less stable. Whereas molecule is away from each other, hence electron clouds are will not interfere each other therefore less strain in the molecule, so trans alkene is stable.
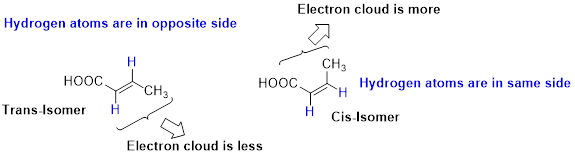
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry, Global Edition
- 7. The three sets of replicate results below were accumulated for the analysis of the same sample. Pool these data to obtain the most efficient estimate of the mean analyte content and the standard deviation. Lead content/ppm: Set 1 Set 2 Set 3 1. 9.76 9.87 9.85 2. 9.42 9.64 9.91 3. 9.53 9.71 9.42 9.81 9.49arrow_forwardDraw the Zaitsev product famed when 2,3-dimethylpentan-3-of undergoes an El dehydration. CH₂ E1 OH H₁PO₁ Select Draw Templates More QQQ +H₂Oarrow_forwardComplete the clean-pushing mechanism for the given ether synthesia from propanol in concentrated sulfurica140°C by adding any mining aloms, bands, charges, nonbonding electron pairs, and curved arrows. Draw hydrogen bonded to cayan, when applicable. ore 11,0 HPC Step 1: Draw curved arrows Step 2: Complete the intend carved Q2Q 56 QQQ Step 3: Complete the intermediate and add curved Step 4: Modify the structures to draw the QQQ QQQarrow_forward
- 6. In an experiment the following replicate set of volume measurements (cm3) was recorded: (25.35, 25.80, 25.28, 25.50, 25.45, 25.43) A. Calculate the mean of the raw data. B. Using the rejection quotient (Q-test) reject any questionable results. C. Recalculate the mean and compare it with the value obtained in 2(a).arrow_forwardA student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more reactants missing from the left-hand side, but there are no products missing from the right-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. • If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing reactants to the left-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + T G OH де OH This transformation can't be done in one step.arrow_forwardMacmillan Leaming Draw the major organic product of the reaction. 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H+ - G Select Draw Templates More H о QQarrow_forward
- Draw the condensed structure of 3-hydroxy-2-butanone. Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardGive the expected major product of reaction of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane with each of the following reagents. 2. Reaction with dilute H₂SO, in methanol. Select Draw Templates More CHC Erase QQQ c. Reaction with dilute aqueous HBr. Select Drew Templates More Era c QQQ b. Reaction with NaOCH, in methanol. Select Draw Templates More d. Reaction with concentrated HBr. Select Draw Templates More En a QQQ e. Reaction with CH, Mg1, then H*, H₂O 1. Reaction with CH,Li, then H', H₂Oarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure O OH OH name X ☐arrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning One of the molecules shown can be made using the Williamson ether synthesis. Identify the ether and draw the starting materials. А со C Strategy: Review the reagents, mechanism and steps of the Williamson ether synthesis. Determine which of the molecules can be made using the steps. Then analyze the two possible disconnection strategies and deduce the starting materials. Identify the superior route. Step 6: Put it all together. Complete the two-step synthesis by selecting the reagents and starting materials. C 1. 2. Answer Bank NaH NaOH NaOCH, снен, сен, он Сиси, Сне (СН), СОН (Сн, Свarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure CH3 O CH3-CH-CH-C-CH3 OH HV. CH3-C-CH-CH2-CH3 OH CH3 O HO—CH, CH–CH—C CH3 OH 오-오 name X G ☐arrow_forwardHI Organic Functional Groups Predicting the reactants or products of esterification What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? HO OH H +回 + H₂O 60013 Naomi V Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check 1 2 #3 $ 4 2025 % ala5 'a :☐ G & 67 8 Ar K enter Accessible 9 Q W E R TY U 1 tab , S H J Karrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning


