
Concept explainers
(a)
To find: The find the region where the
(a)
Answer to Problem 57E
The region where the
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given table is shown in Table 1
Table 1
| | | | |
| -2 | 7 | 0.25 | 4.81 |
| -1.75 | 4.19 | 0.5 | -4.25 |
| -1.5 | 1.75 | 0.75 | -3.31 |
| -1.25 | -0.31 | 1 | -2 |
| -1 | -2 | 1.25 | -0.31 |
| -0.75 | -3.31 | -1.5 | 1.75 |
| -0.5 | -4.25 | 1.75 | 4.19 |
| -0.25 | -4.81 | 2 | 7 |
| 0 | -5 |
Calculation:
The graph for the values given in the table is shown in Figure 1
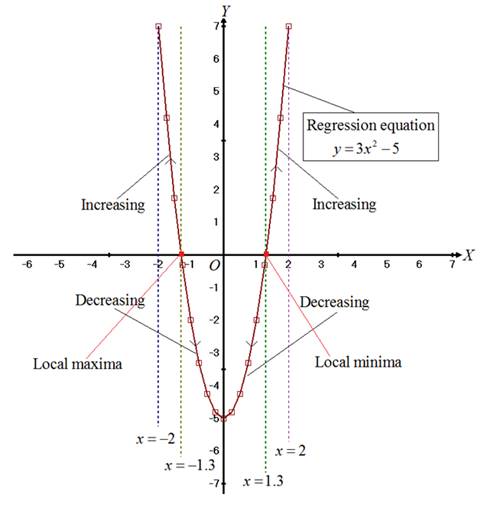
Figure 1
Consider that the
Then, if the function has the maximum value or the local minimum value at the interior point
Consider that
Consider that
Consider that
Consider that for the given table
From this it is clear that the function increases on the interval
Consider that for the given table
From this it is clear that the function decrease on the interval
Thus, the local maxima for the given function is at
(b)
To find: The quadratic regression of the equation for the data in the table and superimpose the graph on the
(b)
Answer to Problem 57E
The required regression equation is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From the table 1 when the values are entered in the calculator the regression equation is obtained as,
(c)
To find: The formula for the
(c)
Answer to Problem 57E
The function is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Consider the regression equation is,
Then,
Then the function is
Chapter 5 Solutions
Calculus: Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Which sign makes the statement true? 9.4 × 102 9.4 × 101arrow_forwardDO these math problems without ai, show the solutions as well. and how you solved it. and could you do it with in the time spandarrow_forwardThe Cartesian coordinates of a point are given. (a) (-8, 8) (i) Find polar coordinates (r, 0) of the point, where r > 0 and 0 ≤ 0 0 and 0 ≤ 0 < 2π. (1, 0) = (r. = ([ (ii) Find polar coordinates (r, 8) of the point, where r < 0 and 0 ≤ 0 < 2π. (5, 6) = =([arrow_forward
- The Cartesian coordinates of a point are given. (a) (4,-4) (i) Find polar coordinates (r, e) of the point, where r > 0 and 0 0 and 0 < 0 < 2π. (r, 6) = X 7 (ii) Find polar coordinates (r, 8) of the point, where r < 0 and 0 0 < 2π. (r, 0) = Xarrow_forwardr>0 (r, 0) = T 0 and one with r 0 2 (c) (9,-17) 3 (r, 8) (r, 8) r> 0 r<0 (r, 0) = (r, 8) = X X X x x Warrow_forward74. Geometry of implicit differentiation Suppose x and y are related 0. Interpret the solution of this equa- by the equation F(x, y) = tion as the set of points (x, y) that lie on the intersection of the F(x, y) with the xy-plane (z = 0). surface Z = a. Make a sketch of a surface and its intersection with the xy-plane. Give a geometric interpretation of the result that dy dx = Fx F χ y b. Explain geometrically what happens at points where F = 0. yarrow_forward
- Example 3.2. Solve the following boundary value problem by ADM (Adomian decomposition) method with the boundary conditions მი მი z- = 2x²+3 дг Əz w(x, 0) = x² - 3x, θω (x, 0) = i(2x+3). ayarrow_forward6. A particle moves according to a law of motion s(t) = t3-12t2 + 36t, where t is measured in seconds and s is in feet. (a) What is the velocity at time t? (b) What is the velocity after 3 s? (c) When is the particle at rest? (d) When is the particle moving in the positive direction? (e) What is the acceleration at time t? (f) What is the acceleration after 3 s?arrow_forwardConstruct a table and find the indicated limit. √√x+2 If h(x) = then find lim h(x). X-8 X-8 Complete the table below. X 7.9 h(x) 7.99 7.999 8.001 8.01 8.1 (Type integers or decimals rounded to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





