
Concept explainers
a.
To show that
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
According to mean value theorem
Below is the graph of
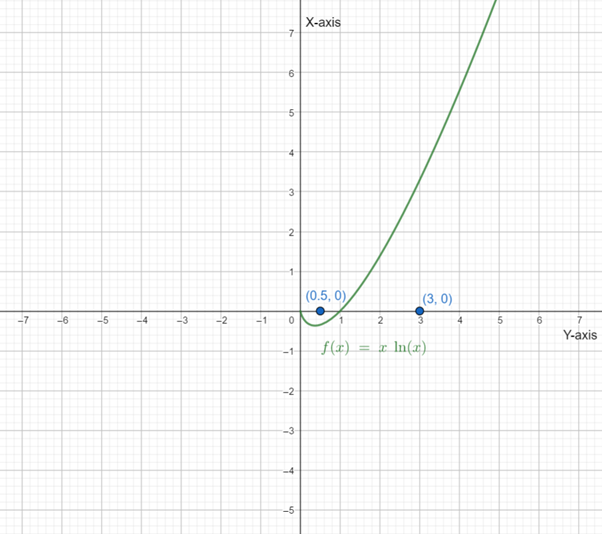
From graph of
Therefore,
b.
To find the values of
b.
Answer to Problem 37RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
According to mean value theorem
Since, from part (a) it is proved that
Here
So ,
Since,
Therefore, the value of
c.
To write an equation for the secant line
c.
Answer to Problem 37RE
The equation of secant is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
,
Therefore,
Equation of secant given two points
Therefore, the equation of secant is
d.
To write an equation for the tangent line that is parallel to the secant line
d.
Answer to Problem 37RE
The equation of tangent is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
Since, it is given that tangent line is parallel to the secant line
General equation of line with slope
Equation of secant line is
On comparing equation of secant line with general equation of line
Slope
Equation of tangent is
Therefore, the equation of tangent is
Chapter 5 Solutions
Calculus: Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
- The spread of an infectious disease is often modeled using the following autonomous differential equation: dI - - BI(N − I) − MI, dt where I is the number of infected people, N is the total size of the population being modeled, ẞ is a constant determining the rate of transmission, and μ is the rate at which people recover from infection. Close a) (5 points) Suppose ẞ = 0.01, N = 1000, and µ = 2. Find all equilibria. b) (5 points) For the equilbria in part a), determine whether each is stable or unstable. c) (3 points) Suppose ƒ(I) = d. Draw a phase plot of f against I. (You can use Wolfram Alpha or Desmos to plot the function, or draw the dt function by hand.) Identify the equilibria as stable or unstable in the graph. d) (2 points) Explain the biological meaning of these equilibria being stable or unstable.arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. Check Answer: 7x 4 + 1x dxarrow_forwardshow sketcharrow_forward
- Find the indefinite integral. Check Answer: 7x 4 + 1x dxarrow_forwardQuestion 1: Evaluate the following indefinite integrals. a) (5 points) sin(2x) 1 + cos² (x) dx b) (5 points) t(2t+5)³ dt c) (5 points) √ (In(v²)+1) 4 -dv ขarrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. Check Answer: In(5x) dx xarrow_forward
- Find the indefinite integral. Check Answer: 7x 4 + 1x dxarrow_forwardHere is a region R in Quadrant I. y 2.0 T 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 + 55 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 X It is bounded by y = x¹/3, y = 1, and x = 0. We want to evaluate this double integral. ONLY ONE order of integration will work. Good luck! The dA =???arrow_forward43–46. Directions of change Consider the following functions f and points P. Sketch the xy-plane showing P and the level curve through P. Indicate (as in Figure 15.52) the directions of maximum increase, maximum decrease, and no change for f. ■ 45. f(x, y) = x² + xy + y² + 7; P(−3, 3)arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





