
The multitransistor circuit in Figure 5.61 is to be redesigned. The bias voltages are to be ±3.3 V and the nominal transistor current gains are
The design parameters of the bias stable circuit.
Answer to Problem D5.91DP
The value of the resistance required to design the circuit are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given circuit is shown in Figure 1.
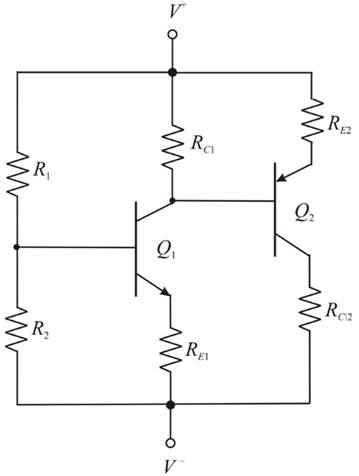
Figure 1
Calculation:
Mark the current and other parameters than redraw the circuit.
The required diagrams is shown in Figure 2
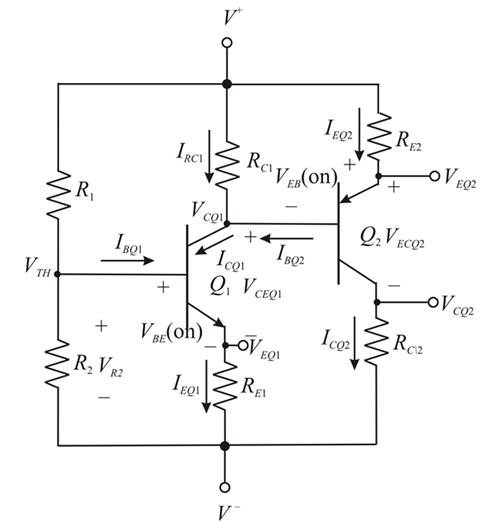
Figure 2
The value of the base current of the first transistor is calculated as,
Substitute
The value of the base current of the second transistor is calculated as,
Substitute
Apply KCL to the above circuit.
The expression for the current
Substitute
From KCL the expression for the emitter current of the second transistor is given by,
The expression to determine the voltage
The expression to determine the value of the resistance
The expression to determine the value of the collector voltage is
The expression to determine the value of the resistance
Substitute
By KCL in Figure 2 the expression for the current
Substitute
The expression to determine the value of the emitter voltage
The expression to determine the value of the resistance
Substitute
The expression for the Thevenin voltage is evaluated as,
The Thevenin equivalent base circuit is shown in Figure 3.
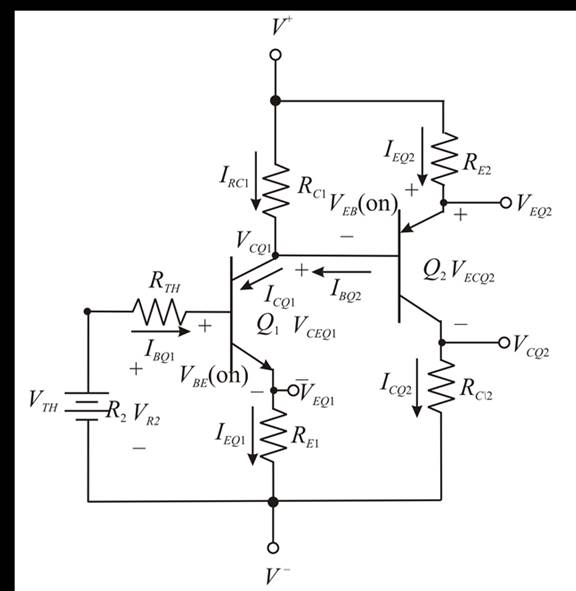
Figure 3
Apply KVL to the above circuit.
For bias stable voltage the value of the Thevenin equivalent resistance is given by,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The expression to determine the value of the Thevenin equivalent resistance is given by,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of the resistance required to design the circuit are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
- 7. Complete the following problems for the circuit below. (a) When VDD = 120V, What is the voltage drop V1 across the 7Ω resistor? (b) If the voltage source VDD is set to obtain I1 = 2A, find the value of VDD. (c) If I1 = 100A, What is the value of I2arrow_forwarda) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 =x12x2 + 9u1 dt dx2 =x1+x3+3u2 dt dx3 = 4x1 +5x2 - 12x3 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forwardCircuit Logic. Match each statement to the proper circuit. All circuits have been drawn with a light (L) to represent the load, whether it is a motor, bell, light, or any other load. In addition, each switch is illustrated as a pushbutton whether it is a maintained switch, momentary contact switch, pushbutton, switch-on target, or any other type of switch.arrow_forward
- a) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 = 4x1 = x2 dt dx2 =-3x12x2 +U1 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forwardmatch each statement to the proper circuit. All circuits have been drawn with a light (L) to represent the load, whether it is a motor, bell, light or any other load. In addition, each switch is illustrated as a push button whether it is maintained switch, momentary contact switch, pushbutton, switch-on target, or any other type of switch.arrow_forwarda) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 =-7x1 + x2 + 5u1 dt dx2 =-11x1+x3 + 2u1 dt dx3 = -8x16u1 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forward
- Question 2 (20 points) a) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 dt =x1- 2x2 dx2 = 3x1 - 4x2 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forwardStuck on the question. Please do not use AI, it will get the answer wrong.arrow_forwardConsider a particle confined in an infinite potential well as shown below and its wave function Solve the following problems. is derived as √(x) = A sin (TA), and energy E= H U 0 U=0 a x πλη 2ma² €30 (iii) Calculate the value of A. [Hint: The probability of finding the particle in 0arrow_forwardQ2: Using D flip-flops, design a synchronous counter. The counter counts in the sequence 1,3,5,7, 1,7,5,3,1,3,5,7,.... when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter count 0.arrow_forward8.19 In the circuit shown in Fig. P8.19, u(t) = 40cos(105t) V,R1 = 100 W, R2 = 500 W, C = 0.1 μF, and L = 0.5 mH.Determine the complex power for each passive element, and verifythat conservation of energy is satisfied.arrow_forwardIn the circuit shown, let R₁=7, R₂=12, R3=24, R4-2, V₁ =26, V2=104, and V3-78, to calculate the power delivered (or absorbed) by the circuit inside the box, as follows: {NOTE: On Multiple Choice Questions, like this problem, you have only one attempt } 1. The current I is equal to (choose the closed values in amperes) O 1.156 -1.156 -1.209 -4.622 1.209 0 (A) 4.622 2. The power delivered (or absorbed) (choose the closest value in watts) (W) -873.292 152.225 O 873.292 -122.181 -58.086 0 O 122.181 R₁ ww V₂ R₂ R3 V1 ww R4 √3arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





