
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-NEXTGEN+BOX (2 SEM.)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781119761068
Author: Klein
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 4.6, Problem 4.48P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
Directing effects of the given compound have to be predicted. The given compound is shown as,
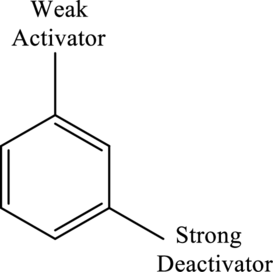
Concept Introduction:
Deactivators are electron withdrawing groups attached to the benzenes that have either positive charge or an atom with high electronegativity. They are meta directors.
- Strong deactivators: They are very strong electron withdrawing groups.
- Moderate deactivators: It contains a pi bond that is attached to a strong electronegative group.
- Weak deactivators: It consists of halogens.
Activators are electron donating groups attached to the benzenes that have either electron density that is able to push into benzene ring or a lone pair of electrons. They are ortho-para directing.
- Strong activators: It contains a lone pair next to the
aromatic ring. - Moderate activators: It has a lone pair next to the aromatic ring that can take part in the resonance outside the ring as well.
- Weak activators: It consists of alkyl groups.
Halogens are deactivators that are ortho-para directing.
Rules to identify the group that dominates the directing effects:
- Ortho-para directors will always dominate meta directors.
- Strong activators will always dominate weak activators.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The aim of the lab is to measure the sodium content from tomato sauce using the Mohr titration method. There are two groups being: Regular Tomato sauce & Salt Reduced tomato sauce
QUESTION: State how you would prepare both Regular & Salt reduced tomato sauce samples for chemical analysis using the Mohr titration method
Using the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS
Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy
AS.
Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option.
reaction
observations
conclusions
A
The reverse of this reaction is always
spontaneous but proceeds faster at
temperatures above -48. °C.
ΔΗ is
(pick one)
✓
AS is
(pick one)
B
This reaction is spontaneous except below
114. °C but proceeds at a slower rate
below 135. °C.
ΔΗ is
(pick one)
AS is
(pick one)
ΔΗ is
C
This reaction is exothermic and proceeds
faster at temperatures above -43. °C.
(pick one)
AS is
(pick one) v
Х
5
?
18
Ar
ion.
A student proposes the following Lewis structure for the perchlorate (CIO) io
:
:0:
: Cl
:
-
-
:
:0:
ك
Assign a formal charge to each atom in the student's Lewis structure.
atom
central O
formal charge
☐
top O
☐
right O
☐
bottom O
☐
Cl
☐
Chapter 4 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-NEXTGEN+BOX (2 SEM.)
Ch. 4.1 - Consider the following reaction, in which an...Ch. 4.1 - Prob. 4.3PCh. 4.1 - Aromatic rings will also undergo iodination when...Ch. 4.2 - In each of the following cases, identify the...Ch. 4.2 - In each of the following cases, identify the...Ch. 4.2 - In each of the following cases, identify the...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.10PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.11PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.12PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.13P
Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.14PCh. 4.3 - Predict the products of the following reaction.Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 4.16PCh. 4.3 - Prob. 4.17PCh. 4.4 - Identify the reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 4.4 - Identify the reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 4.4 - Identify the reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 4.4 - Identify the reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 4.4 - fill in the reagents you would use for the...Ch. 4.4 - fill in the reagents you would use for the...Ch. 4.4 - fill in the reagents you would use for the...Ch. 4.4 - fill in the reagents you would use for the...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 4.27PCh. 4.4 - Prob. 4.28PCh. 4.4 - And now, for a challenging problem, try to draw...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 4.31PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.32PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.33PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.34PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.35PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.36PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.37PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.40PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.41PCh. 4.6 - Predict the products for each of the following...Ch. 4.6 - Predict the products for each of the following...Ch. 4.6 - Predict the products for each of the following...Ch. 4.6 - Predict the products for each of the following...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 4.47PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.48PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.49PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.50PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.51PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.52PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.53PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.54PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.55PCh. 4.6 - Prob. 4.56PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.58PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.59PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.60PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.61PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.62PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.63PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.64PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.65PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.66PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.67PCh. 4.7 - Can you explain why the following group is a...Ch. 4.7 - Prob. 4.70PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.71PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.72PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.73PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.74PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.76PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.77PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.78PCh. 4.7 - Prob. 4.79PCh. 4.8 - Propose an efficient synthesis for each of the...Ch. 4.8 - Propose an efficient synthesis for each of the...Ch. 4.8 - Propose an efficient synthesis for each of the...Ch. 4.8 - Propose an efficient synthesis for each of the...Ch. 4.8 - Propose an efficient synthesis for each of the...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 4.87PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 4.88PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 4.89PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 4.90PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 4.91PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 4.92PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.94PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.95PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.96PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.97PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.98PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.99PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.100PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.101PCh. 4.9 - Prob. 4.102P
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Decide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Yes. Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Cl- : 2: :Z: :Z: N—N : 0: C C1: O CO No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0". ☑arrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions ΔΗ is (pick one) A This reaction is faster above 103. °C than below. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous only above -9. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) C The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous. AS is (pick one) 18 Ararrow_forwardUse the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds slower at temperatures below 41. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 94. °C. AS is (pick one) This reaction is always spontaneous, but ΔΗ is (pick one) C proceeds slower at temperatures below −14. °C. AS is (pick one) Х 00. 18 Ar 무ㅎ B 1 1arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. + H CH3CH2OH HCI Drawingarrow_forwardplease explain this in simple termsarrow_forwardK Most Reactive Na (3 pts) Can the metal activity series (shown on the right) or a standard reduction potential table explain why potassium metal can be prepared from the reaction of molten KCI and Na metal but sodium metal is not prepared from the reaction of molten NaCl and K metal? Show how (not). Ca Mg Al с Zn Fe Sn Pb H Cu Ag Au Least Reactivearrow_forward
- (2 pts) Why is O2 more stable as a diatomic molecule than S2?arrow_forwardDraw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic phosphite (PO¾³¯) a anion. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. C I A [ ]¯arrow_forwardDecide whether these proposed Lewis structures are reasonable. proposed Lewis structure Is the proposed Lewis structure reasonable? Yes. :0: Cl C C1: 0=0: : 0 : : 0 : H C N No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* ☐ Yes. No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* Yes. ☐ No, it has the wrong number of valence electrons. The correct number is: ☐ No, it has the right number of valence electrons but doesn't satisfy the octet rule. The symbols of the problem atoms are:* | * If two or more atoms of the same element don't satisfy the octet rule, just enter the chemical symbol as many times as necessary. For example, if two oxygen atoms don't satisfy the octet rule, enter "0,0".arrow_forward
- Draw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic trisulfide anion. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule. с [ ] - Garrow_forward1. Calculate the accurate monoisotopic mass (using all 1H, 12C, 14N, 160 and 35CI) for your product using the table in your lab manual. Don't include the Cl, since you should only have [M+H]*. Compare this to the value you see on the LC-MS printout. How much different are they? 2. There are four isotopic peaks for the [M+H]* ion at m/z 240, 241, 242 and 243. For one point of extra credit, explain what each of these is and why they are present. 3. There is a fragment ion at m/z 184. For one point of extra credit, identify this fragment and confirm by calculating the accurate monoisotopic mass. 4. The UV spectrum is also at the bottom of your printout. For one point of extra credit, look up the UV spectrum of bupropion on Google Images and compare to your spectrum. Do they match? Cite your source. 5. For most of you, there will be a second chromatographic peak whose m/z is 74 (to a round number). For one point of extra credit, see if you can identify this molecule as well and confirm by…arrow_forwardPlease draw, not just describe!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning