
Concept explainers
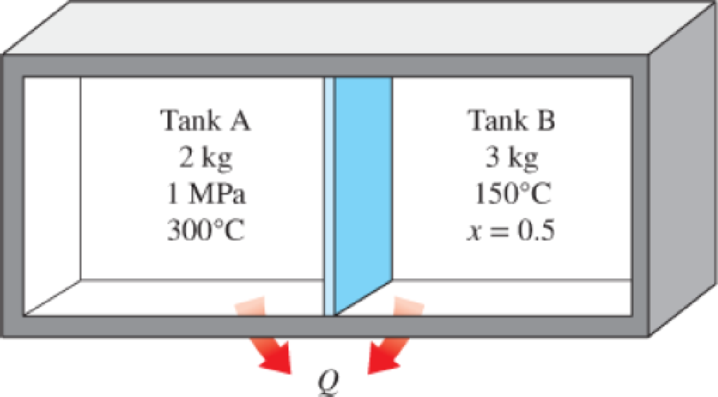
Two tanks (Tank A and Tank B) are separated by a partition. Initially Tank A contains 2 kg of steam at 1 MPa and 300°C while Tank B contains 3 kg of saturated liquid–vapor mixture at 150°C with a vapor mass fraction of 50 percent. The partition is now removed and the two sides are allowed to mix until
FIGURE P4–44
(a)
The final temperature of the steam for a tank.
The quality of the steam at the final state for a tank.
Answer to Problem 44P
The final temperature of the steam is
The quality of the steam at the final state is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the energy balance equation.
Here, the total energy entering the system is
Simplify Equation (I) and write energy balance relation of two tanks.
Here, the boundary work to be done into the system is
Substitute 0 for
Here, the initial mass of tank A is
Write the expression for volume of tank A.
Here, the volume of the tank A is
Write the expression for volume of tank B.
Here, the volume of the tank B is
Write the expression for total mass of tank.
Write the expression for total volume contained in both tanks.
Write the expression for final specific volume of tank.
Conclusion:
Convert the unit of pressure from kPa to MPa.
From the Table A-6, “Superheated water”, obtain the value of initial specific volume
From the Table A-4, “Superheated water”, obtain the value of initial specific volume and specific internal energy for tank B.
At the initial temperature and quality of the steam at the final state of tank B as 150 C and 0.50.
Determine the specific volume of a two-phase system for tank B.
Here, the specific volume of saturated liquid for tank B is
Here, the specific internal energy of saturated liquid for tank B is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-pressure”, obtain the final temperature of the steam.
At final pressure of the steam is
Thus, the final temperature of the steam is
From the Table A-5, “Saturated water-pressure”, obtain the value of quality of the steam at the final state and final specific internal energy for tank B.
At the final pressure and specific volume at the final state as 300 kPa and
Determine the specific volume of a two-phase system for steam.
Here, the specific volume of saturated liquid for steam is
Here, the specific internal energy of saturated liquid for steam is
Substitute
Thus, the quality of the steam at the final state is
Substitute
(b)
The amount of heat lost from the tanks.
Answer to Problem 44P
The amount of heat lost from the tanks is
Explanation of Solution
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the amount of heat lost from the tanks is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- A vertical force of F = 3.4 kN is applied to the hook at A as shown in. Set d = 1 m. Part A 3 m 3m 0.75 m 1.5 m. Determine the tension in cable AB for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAB= Value Submit Request Answer Part B Units ? Determine the tension in cable AC for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAC = Value Submit Request Answer Part C ? Units Determine the tension in cable AD for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardConsider the heat engine operating at steady state between the two thermal reservoirs shown at the right while producing a net power output of 700 kW. If 1000 kW of heat (Q̇H) is transferred to the heat engine from a thermal reservoir at a temperature of TH = 900 K, and heat is rejected to a thermal reservoir at a temperature of TL = 300 K, is this heat engine possible? Can you answer this question for me and show all of the workarrow_forward1.12 A disk of constant radius r is attached to a telescoping rod that is extending at a constant rate as shown in Fig. P1.12. Both the disk and the rod are rotating at a constant rate. Find the inertial velocity and acceleration of point P at the rim of the disk. ท2 L 0 SS P α e 0 O' êL Fig. P1.12 Rotating disk attached to telescoping rod. 60 LLarrow_forward
- Two different options A and B with brake pads for disc brakes are connected to the rope drum. The diameter of the rope drum is 150 mm. What distance must the pads B be at from the center of rotation to cover the same distance as A?A B- Width 50 mm - Width 60 mm- Evidence center 120mm - Construction power 900 N from rotation center.- Maintains a weight of 200 kgwhen the installation force is 1.4kN (μ is missing from the data)M=μF(Ry-Ri)Right answer R=187 mmarrow_forwardAssume the xy plane is level ground, and that the vertical pole shown in the diagram lies along the z-axis with its base at the origin. If the pole is 5 m tall, and a rope is used to pull on the top of the pole with a force of 400 N as shown, determine the magnitudes of the parallel and perpendicular components of the force vector with respect to the axis of the post i.e. with respect to the z-axis.arrow_forward4-1 Q4: Q5: (20 Marks) Find √48 using False Position Method with three iterations. Hint: the root lies between 3 and 4. (20 Marks)arrow_forward
- Determine the angle between vectors FA and FB that is less than 180 degrees. FA is the vector drawn from the origin to point A (-4, 4, 2) while FB is the vector drawn from the origin to point B (3, 1, -3).arrow_forwardFind the resultant force vector from adding F1, F2 and F3, where … F1 = {-8i+10j-32k} N F2 is 40 N in magnitude with coordinate direction angles α, β, and γ, of 45, 120 and 60 degrees, respectively and F3 is 22 N in magnitude with transverse and azimuth angles of 65 and 40 degrees, respectively Express your final answer as a Cartesian vector as well as a magnitude with angles.arrow_forwardA 2-kW resistance heater wire with thermal conductivity of k=20 W/mK, a diameter of D=4mm, and a length of L=0.9m is used to boil water. If the outer surface temp of the resistance wire is Ts=110 degrees C, determine the temp at the center of the wire.arrow_forward
- A flat-plate solar collector is used to heat water by having water flow through tubes attached at the back of the thin solar absorber plate. The absorber plate has emmisssivity and an absorptivity of 0.9. The top surface where x=0 temp of the absorber is T0=35 degrees C, and solar radiation is incident on the basorber at 500 W/m^2 with a surrounding temp of 0 degrees C. The convection heat transfer coefficient at the absorber surface is 5 W/m^2 K, while the ambient temp is 25 degrees C. Show that the variation of the temp in the basorber plate can be expressed as T(x)=-(q0/k)x+T0, and determine net heat flux, q, absorbed by solar collector.arrow_forwardUsing properties of a saturated water, explain how you would determine the mole fraction of water vapor at the surface of a lake when the temp of the lake surface and the atmospheric pressure are specified.arrow_forwardConsider a glass of water in a room at 15 degrees C and 97 kPa. If the relative humidity in the room is 100 percent and the water and the air are in thermal and phase equilibrium, determine the mole fraction of the water vapor in the air and the mole fraction of air in the water.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





