
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781118921876
Author: Pritchard, Philip J.; Leylegian, John C.; Bhaskaran, Rajesh
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 80P
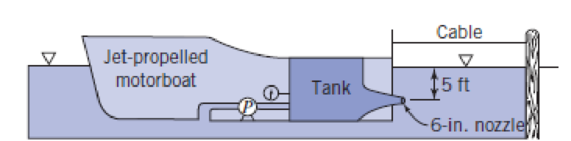
The pump maintains a pressure of 10 psi at the gauge. The velocity leaving the nozzle is 34 ft/s. Calculate the tension force in the cable.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fox And Mcdonald's Introduction To Fluid Mechanics
Ch. 4 - An ice-cube tray containing 250 mL of freshwater...Ch. 4 - A hot air balloon with an initial volume of 2600...Ch. 4 - A fully loaded Boeing 777-200 jet transport...Ch. 4 - On the Milford Trek in New Zealand, there is a...Ch. 4 - A high school experiment consists of a block of...Ch. 4 - For a small particle of styrofoam (density = 19.2...Ch. 4 - Air at 20C and an absolute pressure of 101.3 kpa...Ch. 4 - A block of copper of mass 5 kg is heated to 90C...Ch. 4 - The average rate of heat loss from a person to the...Ch. 4 - The velocity field in the region shown is given by...
Ch. 4 - The area shown shaded is in a flow where the...Ch. 4 - Obtain an expression for the kinetic energy flux,...Ch. 4 - A 0.3 m by 0.5 m rectangular air duct carries a...Ch. 4 - Across a shock wave in a gas flow there is a great...Ch. 4 - Water flows in a pipeline composed of 75-mm and...Ch. 4 - The velocity distribution for laminar flow in a...Ch. 4 - A farmer is spraying a liquid through 10 nozzles,...Ch. 4 - A university laboratory that generates 15 m3/s of...Ch. 4 - Hydrogen is being pumped through a pipe system...Ch. 4 - Calculate the mean velocities for these...Ch. 4 - If the velocity profile in a passage of width 2R...Ch. 4 - Fluid with 1040 kg/m3 density is flowing steadily...Ch. 4 - A rice farmer needs to fill a 150 m 400 m field...Ch. 4 - In your kitchen, the sink is 60 cm by 45.7 cm. by...Ch. 4 - Fluid passes through this set of thin closely...Ch. 4 - A pipeline 0.3 m in diameter divides at a Y into...Ch. 4 - A manifold pipe of 3 in. diameter has four...Ch. 4 - You are trying to pump storm water out of your...Ch. 4 - In the incompressible flow through the device...Ch. 4 - Water enters a wide, flat channel of height 2h...Ch. 4 - Find the average efflux velocity V if the flow...Ch. 4 - Find V for this mushroom cap on a pipeline. P4.32Ch. 4 - Incompressible fluid flows steadily through a...Ch. 4 - A two-dimensional reducing bend has a linear...Ch. 4 - Water enters a two-dimensional, square channel of...Ch. 4 - Viscous liquid from a circular tank. D = 300 mm in...Ch. 4 - A rectangular tank used to supply water for a...Ch. 4 - A cylindrical tank, 0.3 m in diameter, drains...Ch. 4 - Air enters a tank through an area of 0.018 m2 with...Ch. 4 - A cylindrical tank, of diameter D = 50 mm, drains...Ch. 4 - A conical flask contains water to height H = 36.8...Ch. 4 - Water flows steadily past a porous flat plate....Ch. 4 - A tank of fixed volume contains brine with initial...Ch. 4 - A conical funnel of half-angle = 30 drains...Ch. 4 - Evaluate the net rate of flux of momentum out...Ch. 4 - Water flows steadily through a pipe of length L...Ch. 4 - Evaluate the net momentum flux through the bend of...Ch. 4 - Evaluate the net momentum flux through the channel...Ch. 4 - A conical enlargement in a vertical pipeline is 5...Ch. 4 - A 100-mm nozzle is bolted (with 6 bolts) to the...Ch. 4 - The projectile partially fills the end of the 0.3...Ch. 4 - Considering that in the fully developed region of...Ch. 4 - A jet of water issuing from a stationary nozzle at...Ch. 4 - A circular cylinder inserted across a stream of...Ch. 4 - A 6-in.-diameter horizontal pipeline bends through...Ch. 4 - The axes of the pipes are in a vertical plane. The...Ch. 4 - Water flows through a tee in a horizontal pipe...Ch. 4 - In a laboratory experiment, the water flow rate is...Ch. 4 - A gate is 1 m wide and 1.2 m tall and hinged at...Ch. 4 - Water flows steadily through a fire hose and...Ch. 4 - Two types of gasoline are blended by passing them...Ch. 4 - A circular cylinder inserted across a stream of...Ch. 4 - The pressure difference results from head loss...Ch. 4 - Obtain expressions for the rate of change in mass...Ch. 4 - Water is flowing steadily through the 180 elbow...Ch. 4 - Water flows steadily through the nozzle shown,...Ch. 4 - The pump, suction pipe, discharge pipe, and nozzle...Ch. 4 - The passage is 1.2 m wide normal to the paper....Ch. 4 - If the two-dimensional flow rate through this...Ch. 4 - Assume the bend of Problem 4.35 is a segment of a...Ch. 4 - A flat plate orifice of 50 mm diameter is located...Ch. 4 - At rated thrust, a liquid-fueled rocket motor...Ch. 4 - Flow from the end of a two-dimensional open...Ch. 4 - Calculate the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 4 - This water jet of 50 mm diameter moving at 30 m/s...Ch. 4 - If the splitter is removed from the plate of...Ch. 4 - Consider flow through the sudden expansion shown....Ch. 4 - A conical spray head is shown. The fluid is water...Ch. 4 - A curved nozzle assembly that discharges to the...Ch. 4 - The pump maintains a pressure of 10 psi at the...Ch. 4 - A motorboat moves up a river at a speed of 9 m/s...Ch. 4 - A 30 reducing elbow is shown. The fluid is water....Ch. 4 - A monotube boiler consists of a 6 m length of...Ch. 4 - Water is discharged at a flow rate of 0.3m3/s from...Ch. 4 - A nozzle for a spray system is designed to produce...Ch. 4 - The horizontal velocity in the wake behind an...Ch. 4 - An incompressible fluid flows steadily in the...Ch. 4 - Consider the incompressible flow of fluid in a...Ch. 4 - Air at standard conditions flows along a flat...Ch. 4 - Gases leaving the propulsion nozzle of a rocket...Ch. 4 - Two large tanks containing water have small...Ch. 4 - Students are playing around with a water hose....Ch. 4 - A 2-kg disk is constrained horizontally but is...Ch. 4 - A stream of water from a 50-mm-diameter nozzle...Ch. 4 - A plane nozzle discharges vertically 1200 L/s per...Ch. 4 - In ancient Egypt, circular vessels filled with...Ch. 4 - Incompressible fluid of negligible viscosity is...Ch. 4 - The narrow gap between two closely spaced circular...Ch. 4 - Design a clepsydra (Egyptian water clock), which...Ch. 4 - Water from a stationary nozzle impinges on a...Ch. 4 - A freshwater jet boat takes in water through side...Ch. 4 - The Canadair CL-215T amphibious aircraft is...Ch. 4 - Water, in a 100-mm-diameter jet with speed of 30...Ch. 4 - Consider a series of turning vanes struck by a...Ch. 4 - A steady jet of water is used to propel a small...Ch. 4 - The cart of Problem 4.105 is accelerated by a jet...Ch. 4 - A vane/slider assembly moves under the influence...Ch. 4 - A cart is propelled by a liquid jet issuing...Ch. 4 - For the vane/slider problem of Problem 4.107, find...Ch. 4 - If the cart of Problem 4.105 is released at t = 0,...Ch. 4 - The wheeled cart shown rolls with negligible...Ch. 4 - A rocket sled is to be slowed from an initial...Ch. 4 - Starting from rest, the cart shown is propelled by...Ch. 4 - Solve Problem 4.107 if the vane and slider ride on...Ch. 4 - For the vane/slider problem of Problem 4.114, plot...Ch. 4 - A rectangular block of mass M, with vertical...Ch. 4 - A vertical jet of water impinges on a horizontal...Ch. 4 - A rocket sled traveling on a horizontal track is...Ch. 4 - A rocket sled accelerates from rest on a level...Ch. 4 - A rocket sled with initial mass of 900 kg is to be...Ch. 4 - A rocket sled with initial mass of 3 metric tons,...Ch. 4 - A home-made solid propellant rocket has an initial...Ch. 4 - Neglecting air resistance, what speed would a...Ch. 4 - The moving tank shown is to be slowed by lowering...Ch. 4 - The 90 reducing elbow of Example 4.6 discharges to...Ch. 4 - Crude oil (SG = 0:95) from a tanker dock flows...Ch. 4 - The simplified lawn sprinkler shown rotates in the...Ch. 4 - Calculate the torque about the pipes centerline in...Ch. 4 - A fire truck is equipped with a 66 ft long...Ch. 4 - Calculate the torque exerted on the flange joint...Ch. 4 - Consider the sprinkler of Problem 4.130 again....Ch. 4 - A small lawn sprinkler is shown. The sprinkler...Ch. 4 - When a garden hose is used to fill a bucket, water...Ch. 4 - A pipe branches symmetrically into two legs of...Ch. 4 - Compressed air is stored in a pressure bottle with...Ch. 4 - A turbine is supplied with 0.6 m3/s of water from...Ch. 4 - Air is drawn from the atmosphere into a...Ch. 4 - At high speeds the compressor and turbine of the...Ch. 4 - Transverse thrusters are used to make large ships...Ch. 4 - All major harbors are equipped with fire boats for...Ch. 4 - A pump draws water from a reservoir through a...Ch. 4 - Liquid flowing at high speed in a wide, horizontal...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A statement in one function can access a local variable in another function.
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Write an SQL statement to display the breed, type, and DOB for all pets having the type Dog and the breed Std. ...
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Write an evaluation of some programming language you know, using the criteria described in this chapter.
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Describe the primary differences between the conceptual and logical data models.
Modern Database Management
ICA 8-38
An ideal gas is kept in a 10-liter [L] container at a pressure of 1.5 atmospheres [atm] and a temperat...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forward= The frame shown is fitted with three 50 cm diameter frictionless pulleys. A force of F = 630 N is applied to the rope at an angle ◊ 43°. Member ABCD is attached to the wall by a fixed support at A. Find the forces indicated below. Note: The rope is tangent to the pully (D) and not secured at the 3 o'clock position. a b •C *су G E e d BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 81 cm b 50 cm с 59 cm d 155 cm For all answers, take x as positive to the right and positive upward. At point A, the fixed support exerts a force of: A = + ĴN and a reaction couple of: →> ΜΑ Member CG is in Select an answer magnitude У as k N-m. and carries a force of N.arrow_forwardThe lower jaw AB [Purple 1] and the upper jaw-handle AD [Yellow 2] exert vertical clamping forces on the object at R. The hand squeezes the upper jaw-handle AD [2] and the lower handle BC [Orane 4] with forces F. (Member CD [Red 3] acts as if it is pinned at D, but, in a real vise-grips, its position is actually adjustable.) The clamping force, R, depends on the geometry and on the squeezing force F applied to the handles. Determine the proportionality between the clamping force, R, and the squeezing force F for the dimensions given. d3 d4 R 1 B d1 2 d2 D... d5 F 4 F Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value d1 65 mm d2 156 mm d3 50 mm 45 d4 d5 113 mm 30 mm R = Farrow_forward
- A triangular distributed load of max intensity w =460 N/m acts on beam AB. The beam is supported by a pin at A and member CD, which is connected by pins at C and D respectively. Determine the reaction forces at A and C. Enter your answers in Cartesian components. Assume the masses of both beam AB and member CD are negligible. cc 040 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl W A C D -a- B Ул -b- x Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value α 5.4 m b 8.64 m C 3.24 m The reaction at A is A = i+ ĴN. λ = i+ Ĵ N. The reaction at C is C =arrow_forward56 Clamps like the one shown are commonly used in woodworking applications. This clamp has the dimensions given in the table below the figure, and its jaws are mm thick (in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the picture). a.) The screws of the clamp are adjusted so that there is a uniform pressure of P = 150 kPa being applied to the workpieces by the jaws. Determine the force carried in each screw. Hint: the uniform pressure can be modeled in 2-D as a uniform distributed load with intensity w = Pt (units of N/m) acting over the length of contact between the jaw and the workpiece. b.) Determine the minimum vertical force (parallel to the jaws) required to pull either one of the workpieces out of the clamp jaws. Use a coefficient of static friction between all contacting surfaces of μs = 0.56 and the same clamping pressure given for part (a). 2013 Michael Swanbom A B C a Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale.…arrow_forwardDetermine the force in each member of the space truss given F=5 kN. Use positive to indicate tension and negative to indicate compression. F E Z -2 m. B 3 m C 5 m 3 m A -4 m. AB = KN FAC = FAD = KN KN KN FBC = KN FBD FBE = = KN Farrow_forward
- A short brass cyclinder (denisty=8530 kg/m^3, cp=0.389 kJ/kgK, k=110 W/mK, and alpha=3.39*10^-5 m^2/s) of diameter 4 cm and height 20 cm is initially at uniform temperature of 150 degrees C. The cylinder is now placed in atmospheric air at 20 degrees C, where heat transfer takes place by convection with a heat transfer coefficent of 40 W/m^2K. Calculate (a) the center temp of the cylinder, (b) the center temp of the top surface of the cylinder, and (c) the total heat transfer from the cylinder 15 min after the start of the cooling. Solve this problem using the analytical one term approximation method. (Answer: (a) 45.7C, (b)45.3C, (c)87.2 kJ)arrow_forwardA short brass cyclinder (denisty=8530 kg/m^3, cp=0.389 kJ/kgK, k=110 W/mK, and alpha=3.39*10^-5 m^2/s) of diameter 4 cm and height 20 cm is initially at uniform temperature of 150 degrees C. The cylinder is now placed in atmospheric air at 20 degrees C, where heat transfer takes place by convection with a heat transfer coefficent of 40 W/m^2K. Calculate (a) the center temp of the cylinder, (b) the center temp of the top surface of the cylinder, and (c) the total heat transfer from the cylinder 15 min after the start of the cooling. Solve this problem using the analytical one term approximation method.arrow_forwardA 6 cm high rectangular ice block (k=2.22 W/mK, and alpha=0.124*10^-7 m^2/s) initially at -18 degrees C is placed on a table on its square base 4 cm by 4cm in size in a room at 18 degrees C. The heat transfer coefficent on the exposed surfaces of the ice block is 12 W/m^2K. Disregarding any heat transfer from the base to the table, determine how long it will be before the ice block starts melting. Where on the ice block will the first liquid droplets appear? Solve this problem using the analytical one-term approximation method.arrow_forward
- Consider a piece of steel undergoing a decarburization process at 925 degrees C. the mass diffusivity of carbon in steel at 925 degrees C is 1*10^-7 cm^2/s. Determine the depth below the surface of the steel at which the concentration of carbon is reduced to 40 percent from its initial value as a result of the decarburization process for (a) an hour and (b) 10 hours. Assume the concnetration of carbon at the surface is zero throughout the decarburization process.arrow_forwardPlease do not rely too much on chatgpt, because its answer may be wrong. Please consider it carefully and give your own answer. You can borrow ideas from gpt, but please do not believe its answer.Very very grateful! Please do not copy other's work,i will be very very grateful!!arrow_forwardMultiple Choice Circle the best answer to each statement. 1. Which geometry attribute deviation(s) can be limited with a profile of a surface tolerance? A. Location B. Orientation C. Form D. All of the above 2. A true profile may be defined with: A. Basic radii B. Basic angles C. Formulas D. All of the above 3. Which modifier may be applied to the profile tolerance value? A B C. D. All of the above 4. The default tolerance zone for a profile tolerance is: A. Non-uniform B. Unilateral C. Bilateral equal distribution D. Bilateral-unequal distribution 5. An advantage of using a profile tolerance in place of a coordinate tolerance is: A. A bonus tolerance is permitted. B. A datum feature sequence may be specified C. A profile tolerance always controls size D. All of the above 6. The shape of the tolerance zone for a profile tolerance is: A. Two parallel planes B. The same as the true profile of the toleranced surface C. Equal bilateral D. Cylindrical when the diameter symbol is speci- fied…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
The Most Common Metal Machining Processes (Metal Machining Video 1); Author: Sofeast Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uxVJ3qtezGw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Machining process and Machine Tools; Author: Amar Gandhi;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X2mUJ8baaE0;License: Standard Youtube License