
ENGINEERING CIRCUIT...(LL)>CUSTOM PKG.<
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781260540666
Author: Hayt
Publisher: MCG CUSTOM
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 42E
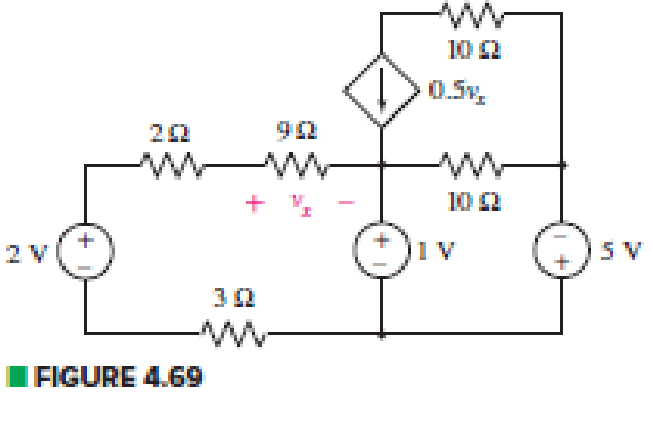
Define three clockwise mesh currents for the circuit of Fig. 4.69, and employ mesh analysis to obtain a value for each.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve it in a different way than the previous solution that I searched for
A lossless uncharged transmission line of length L = 0.45 cm has a characteristic impedance of 60 ohms. It is driven by an ideal voltage generator producing a pulse of amplitude 10V and width 2 nS. If the transmission line is connected to a load of 200 ohms, sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for the interval 0 < t < 20 nS. You may assume that the propagation velocity of the transmission is c/2. Answered now answer number 2.
Repeat Q.1 but now assume the width of the pulse produced by the generator is 4 nS. Sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for 0 < t < 20 nS.
Solve this experiment with an accurate solution, please. Thank you.
Chapter 4 Solutions
ENGINEERING CIRCUIT...(LL)>CUSTOM PKG.<
Ch. 4.1 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.3, determine the nodal...Ch. 4.1 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.5, compute the voltage...Ch. 4.1 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.8, determine the nodal...Ch. 4.2 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.11, compute the voltage...Ch. 4.3 - Determine i1 and i2 in the circuit in Fig. 4.19....Ch. 4.3 - Determine i1 and i2 in the circuit of Fig 4.21....Ch. 4.3 - Determine i1 in the circuit of Fig. 4.24 if the...Ch. 4.4 - Determine the current i1 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 4.4 - Determine v3 in the circuit of Fig. 4.28. FIGURE...Ch. 4 - Solve the following systems of equations: (a) 2v2 ...
Ch. 4 - (a) Solve the following system of equations:...Ch. 4 - (a) Solve the following system of equations:...Ch. 4 - Correct (and verify by running) the following...Ch. 4 - In the circuit of Fig. 4.35, determine the current...Ch. 4 - Calculate the power dissipated in the 1 resistor...Ch. 4 - For the circuit in Fig. 4.37, determine the value...Ch. 4 - With the assistance of nodal analysis, determine...Ch. 4 - Prob. 9ECh. 4 - For the circuit of Fig. 4.40, determine the value...Ch. 4 - Use nodal analysis to find vP in the circuit shown...Ch. 4 - Prob. 12ECh. 4 - Prob. 13ECh. 4 - Determine a numerical value for each nodal voltage...Ch. 4 - Prob. 15ECh. 4 - Using nodal analysis as appropriate, determine the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 17ECh. 4 - Determine the nodal voltages as labeled in Fig....Ch. 4 - Prob. 19ECh. 4 - Prob. 20ECh. 4 - Employing supernode/nodal analysis techniques as...Ch. 4 - Prob. 22ECh. 4 - Prob. 23ECh. 4 - Prob. 24ECh. 4 - Repeat Exercise 23 for the case where the 12 V...Ch. 4 - Prob. 26ECh. 4 - Prob. 27ECh. 4 - Determine the value of k that will result in vx...Ch. 4 - Prob. 29ECh. 4 - Prob. 30ECh. 4 - Prob. 31ECh. 4 - Determine the currents flowing out of the positive...Ch. 4 - Obtain numerical values for the two mesh currents...Ch. 4 - Use mesh analysis as appropriate to determine the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 35ECh. 4 - Prob. 36ECh. 4 - Find the unknown voltage vx in the circuit in Fig....Ch. 4 - Prob. 38ECh. 4 - Prob. 39ECh. 4 - Determine the power dissipated in the 4 resistor...Ch. 4 - (a) Employ mesh analysis to determine the power...Ch. 4 - Define three clockwise mesh currents for the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 43ECh. 4 - Prob. 44ECh. 4 - Prob. 45ECh. 4 - Prob. 46ECh. 4 - Prob. 47ECh. 4 - Prob. 48ECh. 4 - Prob. 49ECh. 4 - Prob. 50ECh. 4 - Prob. 51ECh. 4 - Prob. 52ECh. 4 - For the circuit represented schematically in Fig....Ch. 4 - The circuit of Fig. 4.80 is modified such that the...Ch. 4 - The circuit of Fig. 4.81 contains three sources....Ch. 4 - Solve for the voltage vx as labeled in the circuit...Ch. 4 - Consider the five-source circuit of Fig. 4.83....Ch. 4 - Replace the dependent voltage source in the...Ch. 4 - After studying the circuit of Fig. 4.84, determine...Ch. 4 - Prob. 60ECh. 4 - Employ LTspice (or similar CAD tool) to verify the...Ch. 4 - Employ LTspice (or similar CAD tool) to verify the...Ch. 4 - Employ LTspice (or similar CAD tool) to verify the...Ch. 4 - Verify numerical values for each nodal voltage in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 65ECh. 4 - Prob. 66ECh. 4 - Prob. 67ECh. 4 - Prob. 68ECh. 4 - Prob. 69ECh. 4 - (a) Under what circumstances does the presence of...Ch. 4 - Referring to Fig. 4.88, (a) determine whether...Ch. 4 - Consider the LED circuit containing a red, green,...Ch. 4 - The LED circuit in Fig. 4.89 is used to mix colors...Ch. 4 - A light-sensing circuit is in Fig. 4.90, including...Ch. 4 - Use SPICE to analyze the circuit in Exercise 74 by...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A lossless uncharged transmission line of characteristic impedance Zo = 600 and length T = 1us is connected to a 180 load. If this transmission line is connected at t = 0 to a 90 V dc source with an internal resistance of 900, from a bounce diagram of this system sketch (a) the voltage at z=0, z=L, and z = L/2 for up to 7.25μs and (b) calculate the load voltage after an infinite amount of time.arrow_forwardA lossless uncharged transmission line of length L = 0.45 cm has a characteristic impedance of 60 ohms. It is driven by an ideal voltage generator producing a pulse of amplitude 10V and width 2 nS. If the transmission line is connected to a load of 200 ohms, sketch the voltage at the load as a function of time for the interval 0 < t < 20 nS. You may assume that the propagation velocity of the transmission is c/2.arrow_forwardThe VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio) is measured to be 2 on a transmission line. Find two values of the reflection coefficient with one corresponding to Z > Zo and the other to Zarrow_forwardA dc voltage of unknown value Vand internal resistance Reis connected through a switch to a lossless transmission line of Zo = 1000. If the first 5 μS of the voltages at z = 0 and z = L are observed to be as shown below, calculate Vo, RG, the load resistanceR,, and the transit time T. 100 + [V]:-0. V 90 [V]:-V 100 75 I, Տ 1,μs 2 4 6 0 2 4 6arrow_forwardA lossless open circuited transmission line behaves as an equivalent capacitance of Ceq = Tan (BL) Show for BL << 1 that Ceq = C'L where L is the length of the transmission line and wZo C' is the lumped parameter capacitance per unit length of the transmission line. Hint: For x small, Tan(x) = x.arrow_forward= A generator with VG 300V and R = 50 is connected to a load R = 750 through a 50 lossless transmission line of length L = 0.15 m. (a) Compute Zin, the input impedance of the line at the generator end. (b) Compute and V. (c) Compute the time-average power Pin delivered to the line. (d) Compute VL, IL, and the time-average power delivered to the load, PL (e) How does Pin compare to PL? Explain.arrow_forwardFor the regulated power supply circuit, assume regular diodes with 0.7V forward drop. Use a 15V (peak), 60Hz sine wave at the transformer secondary and assume a maximum ripple level of 1V. (a) Compute the unknown components needed to design 10V DC supply.Hint: find R first, and then C. What is the ripple level for C=22µF?Sketch the rectified, filtered, and regulated outputsarrow_forwardA) Find the solution of B) Find the convolution of Sewt (t-π)dt 8 e-atu(t)e-blu(t)arrow_forwardConsider the signal: f(t)= 0, ㅠ 1 Use the Fourier transform formula to find F(w). otherwisearrow_forwardA half-wave controlled rectifier is supplied by a 230 Vrms voltage source and has load resistance of 2502. Calculate the delay angle a that produces a load-absorbed power of 200W.arrow_forwardQ6 The FET shown in Fig. 1.43 has gm = 3.4 mS and rd =100 K. Find the approximate lower cutoff frequency. Ans: 735.1 Hz. 25V 1.5ΜΩ 20 ΚΩ 0.02µF HH 2ΚΩ 0.02µF HH 330kQ 820 ΩΣ 1.0µF www 40ΚΩarrow_forwardThe solution is with a pen and paper, without artificial intelligence.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Nodal Analysis for Circuits Explained; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f-sbANgw4fo;License: Standard Youtube License