
Concept explainers
Find the value of
Answer to Problem 43E
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The circuit diagram is redrawn as shown in Figure 1,
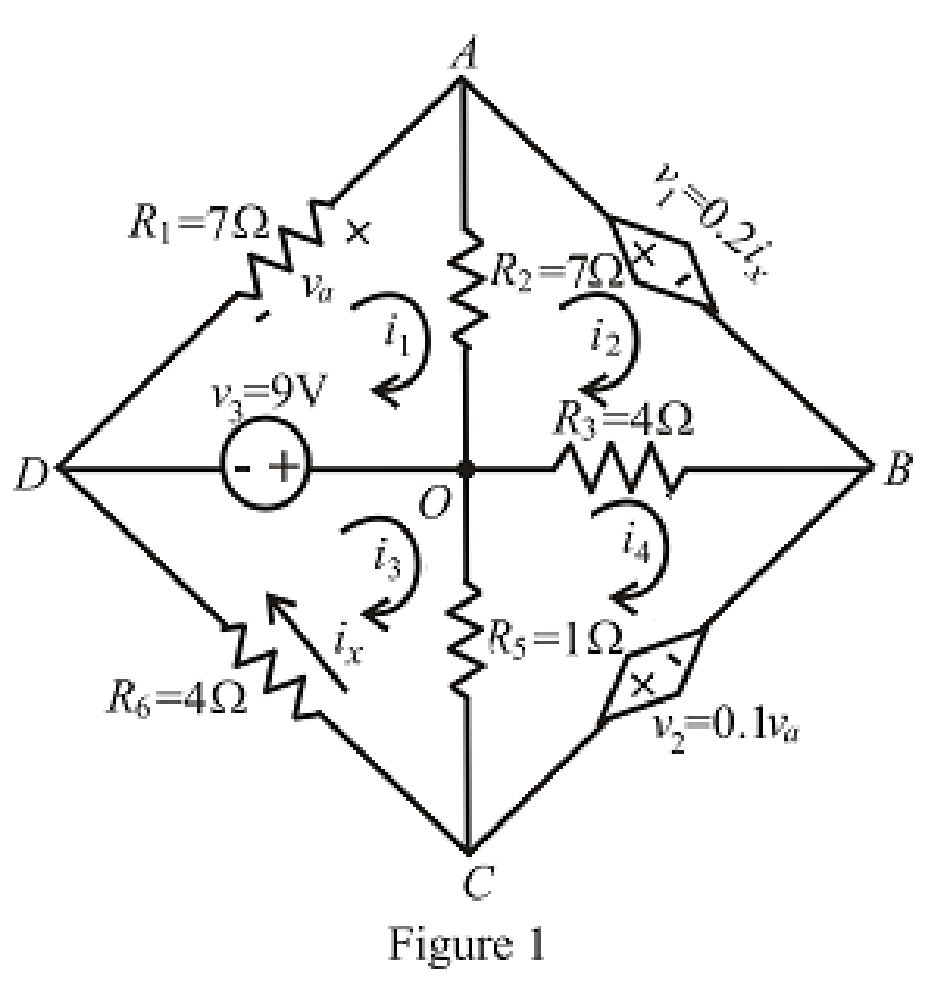
Refer to the redrawn Figure 1,
Apply KVL in the mesh
Here,
Apply KVL in the mesh
Here,
Apply KVL in the mesh
Here,
Apply KVL in the mesh
Here,
The expression for the voltage across
Here,
Refer to the redrawn Figure 1,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange the above equation for
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange the equation (6), (10) and (11),
The equations so formed can be written in matrix form as,
Therefore, by Cramer’s rule,
The determinant of the coefficient matrix is as follows,
The 1st determinant is as follows,
The 2nd determinant is as follows,
The 3rd determinant is as follows,
Simplify for
Simplify for
Simplify for
The value of
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
ENGINEERING CIRCUIT...(LL)>CUSTOM PKG.<
- 1. Consider the following LTI system. d²y dy du +7 +6y= -- +2u, t≥0 dt² dt dt a) What is the impulse response of the system? Recall, h(t) = L-¹(H(s)). b) What are poles and zeros of the system? c) Suppose the initial condition of the system is y(0) = 1 and y'(0) = 4. What is the zero-input response of the system? d) Consider an input u(t) = (1 + et) 1(t) to the system. What is the zero-state response of the system for this input? e) Suppose, the initial condition was y(0) = -2 and y'(0) = -8 and the input is u(t)=(1+e) 1(t). What will be the total response of the system? You should be able to answer this using the linearity property of the system and your answers in part b and part c without taking any inverse Laplace transform.arrow_forwardGiven a normally distributed variable X with mean 4 and standard deviation 2, fi (a) P(X5). (d) P(1.8arrow_forwardTask 2 (2 credits) Consider the circuit in the figure below. The Zener diode has a Zener voltage of 15 V. What is the voltage Vout? 22 V 4.0 ΚΩ Vout 3.0 ΚΩarrow_forwardGiven a normally distributed variable X with mean 4 and standard deviation 2, fi (a) P(X5). (d) P(1.8arrow_forwardGiven a normally distributed variable X with mean 4 and standard deviation 2, fi (a) P(X5). (d) P(1.8arrow_forwardQ1. The three-phase full-wave converter in Figure shown is operated from a three phase Y-connected supply. Sketch the output voltages appeared at the load for firing angle 15°. I need Sketch an Ven จ T1 Q Yi₁ = I₂ a ia = is T₁ T3 T₂ Vbn b ib Load Highly inductive load ▲ T6 T₂ iT4 On T5, T6 T6, T₁ T2, T3 T3, T4 T4, T5 T5, T6 ཅ 0 T₁ الاسم T₁ Is wtarrow_forwardQ4. For the control system is shown in Figure 2, by using second method of Ziegler- Nichols, calculate the PID, PI-D and I-PD parameters and make tuning for this parameters to get accepting response for the هندسة الكم following system, then compare your results for all types controllers? R(S) K C(s) S3+4S² +11S Figure (2)arrow_forwardQ1. Consider the unity feedback control system whose open-loop transfer function is: G(s): = 40(S+2) s(s+3)(s+1)(s + 10) ELECTRIC Ziegler-Nichols, By using second method of Ziegler- Nichols, calculate the PID, PI-D and I-PD parameters and make tuning for this parameters to get accepting response for the following system, then comp controllers? PARTME then compare your results for all types GINEARIarrow_forwardQ2. Consider the control system whose open-loop transfer function is: G(s) = K قسم s (s2 +4.8s + 12.6) By using second method of Ziegler- Nichols, calculate the PID, PI-D and I-PD parameters and make tuning for this parameters to get accepting response for the following system, then compare your results for all types controllers?arrow_forwardQ3. For the control system is shown in Figure 1, by using second method of Ziegler- Nichols, calculate the PID, PI-D and I-PD parameters and make tuning for this parameters to get accepting response for the following system, then compare your results for all types controllers? R(s) + C(s) 1 GES s(s+3)(s+6) PID controller Figure (1) INarrow_forwardUse Newton-Raphson method to solve the system x³+y-1=0 4 y³-x+1=0 with the starting value (xo,yo) = (1,0). Take n=4.arrow_forwardUse Newton-Raphson method to solve the system 3x²y - 10x+7=0 y²-5y+4=0 With the starting value (xo, yo) = (0.5, 0.5). Take n = 1arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,Norton's Theorem and Thevenin's Theorem - Electrical Circuit Analysis; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-kkvqr1wSwA;License: Standard Youtube License
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,Norton's Theorem and Thevenin's Theorem - Electrical Circuit Analysis; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-kkvqr1wSwA;License: Standard Youtube License