
Fuel oils contain primarily organic compounds and sulfur. The molar composition of the organic fraction of a fuel oil may be represented by the formula
the mass fraction of sulfur in the fuel is
As (kg S/kg fuel); and the percentage excess air, Pn, is defined in terms of the theoretical air required to burn only the carbon and hydrogen in the fuel.
- For a certain high-sulfur No. 6 fuel oil, p = 0.71, 2, SO2, and H2O and expressing the SO2 fraction as ppm (mol SO2/I()6mol dry gas).
- Create a spreadsheet to calculate the mole fractions of the stack gas components on a dry basis for specified values of p, q, r, as, and PXi. The output should appear as follows:
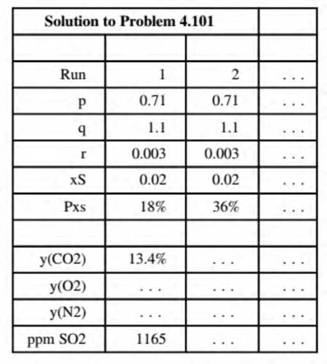
(Rows below the last one shown can be used to calculate intermediate quantities.) Execute enough runs (including the two show n above) to determine the effect on the stack gas composition of each of the five input parameters. Then for the values of p, q, r. and As given in Part (a), find the minimum percentage excess air needed to keep the dry-basis SO2 composition below 700 ppm. (Make this the last run in the output table.)
You should find that for a given fuel oil composition, increasing the percentage excess air decreases the SO2 concentration in the stack gas. Explain w hy this should be the case.
- Someone has proposed using the relationship betw een PX5 and ppm SO2 as the basis of a pollution control strategy. The idea is to determine the minimum acceptable concentration of SO2 in the stack gas, then run with the percentage excess air high enough to achieve this value. Give several reasons w hy this is a poor idea.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
ELEM.PRIN.OF CHEMICAL PROC.-W/ACCESS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
- Problem 54, could you please explain it in detail? Thank you! Step by step, I'm really confused, so please don't make it overly complex. My question is to visually draw it out and demonstrate it to me; I'm confused about that problem, please (not just in words) but demonstrate it to me in all due essence (visually) with descriptions.arrow_forwardExplain the types of electromeric effects +E and -E.arrow_forwardBriefly describe the electromeric effect (Organic Chemistry)arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. (CH3)2NH, TSOH Drawingarrow_forwardSo, the first image is what I'm trying to understand regarding my approach. The second image illustrates my teacher's method, and the third image includes my notes on the concepts behind these types of problems.arrow_forwardHAND DRAWarrow_forward
- Draw a mental model for calcium chloride mixed with sodium phosphatearrow_forwardhere is my question (problem number 20) please explain to me thanks!arrow_forwardThe bromination of anisole is an extremely fast reaction. Complete the resonance structures of the intermediate arenium cation for the reaction (Part 1), and then answer the question that follows (Part 2).arrow_forward
 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
