
College Physics
OER 2016 Edition
ISBN: 9781947172173
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 11PE
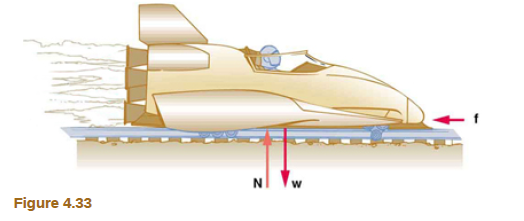
The rocket sled shown in Figure 4.33 accelerates at a rate of 49.0 m/s2. Its passenger has a mass of 75.0 kg. (a) Calculate the horizontal component of the force the seat exerts against his body. Compare this with his weight by using a ratio. (b) Calculate the direction and magnitude of the total force the seat exerts against his body.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Three slits, each separated from its neighbor by d = 0.06 mm, are illuminated by a coherent light source of
wavelength 550 nm. The slits are extremely narrow. A screen is located L = 2.5 m from the slits. The
intensity on the centerline is 0.05 W. Consider a location on the screen x = 1.72 cm from the centerline.
a) Draw the phasors, according to the phasor model for the addition of harmonic waves, appropriate for this
location.
b) From the phasor diagram, calculate the intensity of light at this location.
A Jamin interferometer is a device for measuring or for comparing the indices of refraction of gases. A beam
of monochromatic light is split into two parts, each of which is directed along the axis of a separate cylindrical
tube before being recombined into a single beam that is viewed through a telescope. Suppose we are given the
following,
•
Length of each tube is L = 0.4 m.
• λ= 598 nm.
Both tubes are initially evacuated, and constructive interference is observed in the center of the field of view. As
air is slowly let into one of the tubes, the central field of view changes dark and back to bright a total of 198
times.
(a) What is the index of refraction for air?
(b) If the fringes can be counted to ±0.25 fringe, where one fringe is equivalent to one complete cycle of
intensity variation at the center of the field of view, to what accuracy can the index of refraction of air be
determined by this experiment?
1. An arrangement of three charges is shown below where q₁ = 1.6 × 10-19 C, q2 = -1.6×10-19 C,
and q3 3.2 x 10-19 C.
2 cm
Y
93
92
91
X
3 cm
(a) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the net force on q₁.
(b) Sketch the direction of the forces on qi
Chapter 4 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 4 - Propose a force standard different from the...Ch. 4 - What properties do forces have that allow us to...Ch. 4 - How are inertia and mass related?Ch. 4 - What is the relationship between weight and mass?...Ch. 4 - Which statement is correct? (a) Net force causes...Ch. 4 - Why can we neglect forces such as those holding a...Ch. 4 - Explain how the choice of the “Stem of interest”...Ch. 4 - Describe a situation in which the net external...Ch. 4 - A system can have a nonzero velocity while the net...Ch. 4 - A rock is thrown straight up. What is the net...
Ch. 4 - (a) Give an example of different net external...Ch. 4 - If the acceleration of a system is zero, are no...Ch. 4 - If a constant, nonzero force is applied to an...Ch. 4 - The gravitational force on the basketball in...Ch. 4 - When you take off in a jet aircraft, there is a...Ch. 4 - A device used since the 1940s to measure the kick...Ch. 4 - Describe a Situation in which one a force on and,...Ch. 4 - Why does an ordinary rifle recoil (kick backward)...Ch. 4 - An American football lineman reasons that it is...Ch. 4 - Newton's third law of motion tells us that forces...Ch. 4 - If a leg is suspended by a traction setup as shown...Ch. 4 - Ina traction setup a broken bone, with pulleys and...Ch. 4 - To simulate the apparent weightlessness of space...Ch. 4 - A cartoon shows the toupee coming off the head of...Ch. 4 - Explain, in terms of the properties of the four...Ch. 4 - What is the dominant force between astronomical...Ch. 4 - Give a detailed example of the exchange of a...Ch. 4 - A 63.0-kg sprinter starts a race with an...Ch. 4 - If the sprinter from the previous problem...Ch. 4 - A cleaner pushes a 4.50-kg laundry cart in such a...Ch. 4 - Since astronauts in orbit are apparently...Ch. 4 - In Figure 4.7, the net external force on the 24-kg...Ch. 4 - The same rocket sled drawn in Figure 4.31 is...Ch. 4 - (a) If the rocket sled shown in Figure 4.32 starts...Ch. 4 - What is the deceleration of the rocket sled if it...Ch. 4 - Suppose two children push horizontally, but in...Ch. 4 - A powerful motorcycle can produce an acceleration...Ch. 4 - The rocket sled shown in Figure 4.33 accelerates...Ch. 4 - Repeat the previous problem for the situation in...Ch. 4 - The weight of an astronaut plus his space suit on...Ch. 4 - Suppose the mass of a fully loaded module in which...Ch. 4 - What net external force is exerted on a 1100-kg...Ch. 4 - A brave but inadequate rugby player is being...Ch. 4 - Two teams of nine members each engage in a tug of...Ch. 4 - What force does a trampoline have to apply to a...Ch. 4 - (a) Calculate the tension in a vertical strand of...Ch. 4 - Suppose a 60.0-kg gymnast climbs a rope. (a) What...Ch. 4 - Show that, as stated in the text, a force F...Ch. 4 - Consider the baby being weighed in Figure 4.34....Ch. 4 - A 5.00105 -kg rocket is accelerating straight up....Ch. 4 - The wheels of a midsize car exert a force of 2100...Ch. 4 - Calculate the force a 70.0-kg high jumper must...Ch. 4 - When landing after a spectacular somersault, a...Ch. 4 - A freight train consists of two 8.00104 -kg...Ch. 4 - Commercial airplanes are sometimes pushed out of...Ch. 4 - A 1100-kg car pulls a boat on a trailer. (a) What...Ch. 4 - (a) Find the magnitudes of the forces F1 and F2...Ch. 4 - Two children pull a third child on a snow saucer...Ch. 4 - Suppose your car was mired deeply in the mud and...Ch. 4 - What force is exerted on the tooth in Figure 4.38...Ch. 4 - Figure 4.39 shows Superhero and Trusty Sidekick...Ch. 4 - A nurse pushes a cart by exerting a force on the...Ch. 4 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider the tension in...Ch. 4 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider people pushing...Ch. 4 - Unreasonable Results (a) Repeat Exercise 4.29, but...Ch. 4 -
Ch. 4 - A flea jumps by exerting a force of 1.20105 N...Ch. 4 - Two muscles in the back of the leg pull upward on...Ch. 4 - A 76.0-kg person is being pulled away from a...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts A 35.0-kg dolphin decelerates...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts When starting a foot race, a...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts A large rocket has a mass of...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts A basketball player jumps...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts A 2.50-kg fireworks shell is...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts Repeat Exercise 4.47 for a...Ch. 4 - Integrated Concepts An elevator filled with...Ch. 4 - Unreasonable Results (a) What is the final...Ch. 4 - Unreasonable Results A 75.0-kg man stands on a...Ch. 4 - (a) What is the strength of the weak nuclear force...Ch. 4 - (a) What is the ratio of the strength of the...Ch. 4 - What is the ratio of the strength of the strong...Ch. 4 - Prob. 1TPCh. 4 - Prob. 2TPCh. 4 - Prob. 3TPCh. 4 - Prob. 4TPCh. 4 - Prob. 5TPCh. 4 - Prob. 6TPCh. 4 - Prob. 7TPCh. 4 - Prob. 8TPCh. 4 - Prob. 9TPCh. 4 - Prob. 10TPCh. 4 - Prob. 11TPCh. 4 - Prob. 12TPCh. 4 - Prob. 13TPCh. 4 - Prob. 14TPCh. 4 - Prob. 15TPCh. 4 - Prob. 16TPCh. 4 - Prob. 17TPCh. 4 - Prob. 18TPCh. 4 - Prob. 19TPCh. 4 - Prob. 20TPCh. 4 - Prob. 21TPCh. 4 - Prob. 22TPCh. 4 - Prob. 23TPCh. 4 - Prob. 24TPCh. 4 - Prob. 25TPCh. 4 - Prob. 26TPCh. 4 - Prob. 27TPCh. 4 - Prob. 28TPCh. 4 - Prob. 29TPCh. 4 - Prob. 30TPCh. 4 - Prob. 31TPCh. 4 - Prob. 32TPCh. 4 - Prob. 33TPCh. 4 - Prob. 34TP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
8. A 1000 kg car pushes a 2000 kg truck that has a dead battery. When the driver steps on the accelerator, the ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
1. A cyclist goes around a level, circular track at constant speed. Do you agree or disagree with the following...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
If someone at the other end of a room smokes a cigarette, you may breathe in some smoke. The movement of smoke ...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Why is living epithelial tissue limited to a certain thickness?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Match each of the following items with all the terms it applies to:
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
a. How can aspirin be synthesized from benzene? b. Ibuprofen is the active ingredient in pain relievers such as...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Figure 1)In each case let w be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (a). Express your answer in degrees. Find the tension Tb in the cable in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in terms of w. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in terms of w.arrow_forward(Figure 1)In each case let ww be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w. Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in degrees.arrow_forwardA 70.0 cm, uniform, 40.0 N shelf is supported horizontally by two vertical wires attached to the sloping ceiling (Figure 1). A very small 20.0 N tool is placed on the shelf midway between the points where the wires are attached to it. Find the tension in the left-hand wire. Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forward
- Find the total bind Mev. binding energy for 13 Carbon, 6C (atomic mass = 13.0033554)arrow_forwardWhat is the 27 energy absorbed in this endothermic Auclear reaction 2] Al + 'n → 27 Mg + ! H? (The atom mass of "Al is 26.981539u. and that of 11 Mg is 26.984341u) MeVarrow_forwardWhat is the energy released in this nuclear reaction 1 F + "', H-1 O+ He? 19 19 16 (The atomic mass of 1F is 18.998403 u, and that of 20 is 15.9949154) MeV.arrow_forward
- What is the energy released in this B+ nuclear reaction خالد 2½ Al w/ Mg + ie? (The atomic mass of 11 Al is 23.9999394 and that > of 12 Mg is 23.985041 u) MeV.arrow_forwardWhat is the energy released / absorbed in this nuclear reaction 14 N+ & He → » O + ! N? (The atomic mass of 14 N is 14.003074u. 17N+ and that of 10 is 16.9991324). MeVarrow_forwardCan someone help me answer this question thanks.arrow_forward
- Can someone help me with this question thanks.arrow_forward4B. Four electrons are located on the corners of a square, one on each corner, with the sides of the square being 25 cm long. a) Draw a sketch of the scenario and use your sketch to b) Determine the total force (magnitude and direction) on one of the electrons from the other three?arrow_forwardPortfolio Problem 3. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed vo from the floor of a room of height h. It hits the ceiling and then returns to the floor, from which it rebounds, managing just to hit the ceiling a second time. Assume that the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the floor, e, is equal to that between the ball and the ceiling. Compute e.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY