
Concept explainers
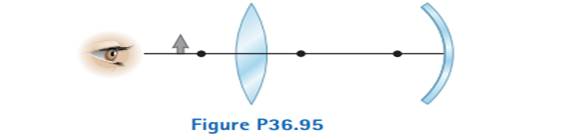
Figure P36.95 shows a thin converging lens for which the radii of curvature of its surfaces have magnitudes of 9.00 cm and 11.0 cm. The lens is in front of a concave spherical mirror with the radius of curvature R = 8.00 cm. Assume the focal points F1 and F2 of the lens are 5.00 cm from the center of the lens, (a) Determine the index of refraction of the lens material. The lens and mirror are 20.0 cm apart, and an object is placed 8.00 cm to the left of the lens. Determine (b) the position of the filial image and (c) its magnification as seen by the eye in the figure. (d) Is the final image inverted or upright? Explain.
(a)
The index of refraction of the lens material.
Answer to Problem 36.95CP
The index of refraction of the lens material is
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The radii of curvature for the converging Len’s surfaces are
Write the expression for the focal length of the lens,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore the index of refraction of the lens material is
(b)
The position of the final image.
Answer to Problem 36.95CP
The position of the final image is
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The radii of curvature for the converging Len’s surfaces are
The expression for the focal length is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus the focal length is
The expression for the lens equation is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus the image distance from the lens is
The expression for the object distance for mirror is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus the object distance for mirror is
The expression for the mirror equation is,
Here,
Substitute
Thus the image distance from the mirror is
The expression for the object distance for lens is,
Substitute
Thus the object distance for lens is
The expression for the lens equation is,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore the position of the final image is
(c)
The magnification as seen by the eye in the figure.
Answer to Problem 36.95CP
The magnification as seen by the eye in the figure is
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The radii of curvature for the converging Len’s surfaces are
The overall magnification factor is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore the magnification as seen by the eye in the figure is
(d)
Whether the final image is inverted or upright.
Answer to Problem 36.95CP
The final image is inverted.
Explanation of Solution
Given data: The radii of curvature for the converging Len’s surfaces are
From part (c) of the question the value of the magnification factor is,
It is known that the image will be upright when the magnification factor is positive and the image will be inverted when the magnification factor is negative.
Since the magnification factor is negative so the image will be upright.
Conclusion:
Therefore the final image is inverted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 36 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
- 2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal. V A 50.00 (a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell. The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor. V A 50.00 R (b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m², resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation R = KL where k is a constant. (b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2] (b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2] (c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3] [2]arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- A rod 12.0 cm long is uniformly charged and has a total charge of -20.0 μc. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field along the axis of the rod at a point 32.0 cm from its center. 361000 ☑ magnitude What is the general expression for the electric field along the axis of a uniform rod? N/C direction toward the rodarrow_forwardA certain brand of freezer is advertised to use 730 kW h of energy per year. Part A Assuming the freezer operates for 5 hours each day, how much power does it require while operating? Express your answer in watts. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? P Submit Request Answer Part B W If the freezer keeps its interior at a temperature of -6.0° C in a 20.0° C room, what is its theoretical maximum performance coefficient? Enter your answer numerically. K = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Part C What is the theoretical maximum amount of ice this freezer could make in an hour, starting with water at 20.0°C? Express your answer in kilograms. m = Ο ΑΣΦ kgarrow_forwardDescribe the development of rational choice theory in sociology. Please includearrow_forward
- A-E pleasearrow_forwardA 11.8 L gas tank containing 3.90 moles of ideal He gas at 26.0°C is placed inside a completely evacuated insulated bell jar of volume 39.0 L .A small hole in the tank allows the He to leak out into the jar until the gas reaches a final equilibrium state with no more leakage. Part A What is the change in entropy of this system due to the leaking of the gas? ■ ΜΕ ΑΣΦ AS = ? J/K Submit Request Answer Part B Is the process reversible or irreversible?arrow_forwardA-E pleasearrow_forward
- Three moles of an ideal gas undergo a reversible isothermal compression at 20.0° C. During this compression, 1900 J of work is done on the gas. For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Entropy change in a free expansion. Part A What is the change of entropy of the gas? ΤΕ ΑΣΦ AS = Submit Request Answer J/Karrow_forward5.97 Block A, with weight 3w, slides down an inclined plane S of slope angle 36.9° at a constant speed while plank B, with weight w, rests on top of A. The plank is attached by a cord to the wall (Fig. P5.97). (a) Draw a diagram of all the forces acting on block A. (b) If the coefficient of kinetic friction is the same between A and B and between S and A, determine its value. Figure P5.97 B A S 36.9°arrow_forwardPlease take your time and solve each part correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





