
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The fraction of the receptor bonded with the hormone needs to be calculated.
Concept Introduction :
While considering the simple equilibrium binding of receptor to hormone the below equilibrium could be used:
Within this equilibrium, [HR] is representative of the hormone’s concentration receptor complex. [H] signifies the free hormone’s concentration while [R] signifies the noncomplexed receptor’s concentration. The equilibrium dissociation constant for this specific reaction could be found to be as:
Answer to Problem 9P
Explanation of Solution
The equilibrium equation can also be written as follows:
After substituting,
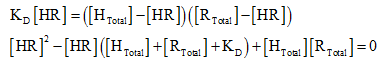
The quadratic equation to solve for the variables:
Substituting in the initial hormone and receptor concentration gives:
Since [HR] must be 0 when
To determine the fraction receptor bound divide [HR] by
These calculations can be repeated for when the concentration of receptor is decreased to 0.33 nM.
Taking the negative root again:
Finding the fraction receptor bound gives:
The fraction of the receptor bonded with the hormone is 0.496.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Sodium fluoroacetate (FCH 2CO2Na) is a very toxic molecule that is used as rodentpoison. It is converted enzymatically to fluoroacetyl-CoA and is utilized by citratesynthase to generate (2R,3S)-fluorocitrate. The release of this product is a potentinhibitor of the next enzyme in the TCA cycle. Show the mechanism for theproduction of fluorocitrate and explain how this molecule acts as a competitiveinhibitor. Predict the effect on the concentrations of TCA intermediates.arrow_forwardIndicate for the reactions below which type of enzyme and cofactor(s) (if any) wouldbe required to catalyze each reaction shown. 1) Fru-6-P + Ery-4-P <--> GAP + Sed-7-P2) Fru-6-P + Pi <--> Fru-1,6-BP + H2O3) GTP + ADP <--> GDP + ATP4) Sed-7-P + GAP <--> Rib-5-P + Xyl-5-P5) Oxaloacetate + GTP ---> PEP + GDP + CO 26) DHAP + Ery-4-P <--> Sed-1,7-BP + H 2O7) Pyruvate + ATP + HCO3- ---> Oxaloacetate + ADP + Piarrow_forwardTPP is also utilized in transketolase reactions in the PPP. Give a mechanism for theTPP-dependent reaction between Xylulose-5-phosphate and Ribose-5-Phosphate toyield Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and Sedoheptulose-7-Phosphate.arrow_forward
- What is the difference between a ‘synthetase’ and a ‘synthase’?arrow_forwardIn three separate experiments, pyruvate labeled with 13C at C-1, C-2, or C-3 is introduced to cells undergoing active metabolism. Trace the fate of each carbon through the TCA cycle and show when each of these carbons produces 13CO2.a. Glucose is similarly labeled at C-2 with 13C. During which reaction will this labeled carbon be released as 13CO2?arrow_forwardDraw the Krebs Cycle and show the entry points for the amino acids Alanine,Glutamic Acid, Asparagine, and Valine into the Krebs Cycle. How many rounds of Krebs will be required to waste all Carbons of Glutamic Acidas CO2?arrow_forward
- Suppose the data below are obtained for an enzyme catalyzed reaction with and without the inhibitor I. (s)( mM) 0.2 0.4 0.8 1.0 2.0 4.0 V without i (mM/min) 5.0 7.5 10.0 10.7 12.5 13.6 V with I (mM/min) 3.0 5.0 7.5 8.3 10.7 12.5 Make a Lineweaver Burke plot for this data using graph paper or a spreadsheet Calculate KM and Vmax without inhibitor. What type of inhibition is observed? show graph and work 2. Give the Lineweaver Burk equation and define all the parameters. 3. When substrate concentration is much greater than Km, the rate of catalysis is almost equal to a. kcat b. none of these c. all of these d. Kd e. Vmaxarrow_forwardPlease explain the process of how an axon degenerates in the central nervous system following injury and how it affects the neuron/cell body, as well as presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons. Explain processes such as chromatolysis and how neurotrophin signaling works.arrow_forwardPlease help determine the Relative Response Ratio of my GC-MS laboratory: Laboratory: Alcohol Content in Hand Sanditizers Internal Standard: Butanol Standards of Alcohols: Methanol, Ethanol, Isopropyl, n-Propanol, Butanol Recorded Retention Times: 0.645, 0.692, 0.737, 0.853, 0.977 Formula: [ (Aanalyte / Canalyte) / (AIS / CIS) ]arrow_forward
- Please help determine the Relative Response Ratio of my GC-MS laboratory: Laboratory: Alcohol Content in Hand Sanditizers Internal Standard: Butanol Standards of Alcohols: Methanol, Ethanol, Isopropyl, n-Propanol, Butanol Recorded Retention Times: 0.645, 0.692, 0.737, 0.853, 0.977 Formula: [ (Aanalyte / Canalyte) / (AIS / CIS) ]arrow_forwardplease draw it for me and tell me where i need to modify the structurearrow_forwardPlease help determine the standard curve for my Kinase Activity in Excel Spreadsheet. Link: https://mnscu-my.sharepoint.com/personal/vi2163ss_go_minnstate_edu/_layouts/15/Doc.aspx?sourcedoc=%7B958f5aee-aabd-45d7-9f7e-380002892ee0%7D&action=default&slrid=9b178ea1-b025-8000-6e3f-1cbfb0aaef90&originalPath=aHR0cHM6Ly9tbnNjdS1teS5zaGFyZXBvaW50LmNvbS86eDovZy9wZXJzb25hbC92aTIxNjNzc19nb19taW5uc3RhdGVfZWR1L0VlNWFqNVc5cXRkRm4zNDRBQUtKTHVBQldtcEtWSUdNVmtJMkoxQzl3dmtPVlE_cnRpbWU9eEE2X291ZHIzVWc&CID=e2126631-9922-4cc5-b5d3-54c7007a756f&_SRM=0:G:93 Determine the amount of VRK1 is present 1. Average the data and calculate the mean absorbance for each concentration/dilution (Please over look for Corrections) 2. Blank Correction à Subtract 0 ug/mL blank absorbance from all readings (Please over look for Corrections) 3. Plot the Standard Curve (Please over look for Corrections) 4. Convert VRK1 concentration from ug/mL to g/L 5. Use the molar mass of VRK1 to convert to M and uM…arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





