
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780134641621
Author: Dean R. Appling, Spencer J. Anthony-Cahill, Christopher K. Mathews
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 8P
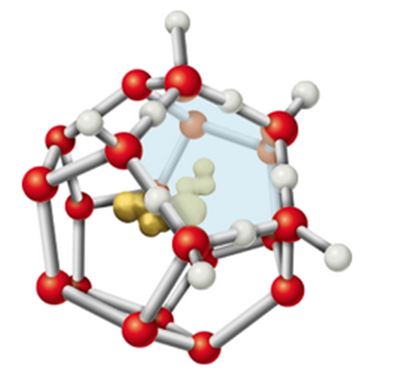
When a hydrophobic substance like a hydrocarbon is dissolved in water, a clathrate cage of ordered water molecules is formed about it (see Figure 2.14). If we consider only the effects on water, what do you expect the sign of

Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
9) Below, there is a representation of an SDS-PAGE gel. Assuming the samples in the
MW standard have masses of: 66 kDa, 45 kDa, 36 kDa, 29 kDa, 24 kDa, 20.1 kDa, and
14.2 kDa,
a) Figure 4: indicate where each of the measurements were taken and label as in II.6.
figure 2 above.
b) As in II.7. Table 1 above create Table 2 using the data below. Determine the r.f.
values for the MW standards, plot the relative mobility versus the log of the mass
for the standards, and use the best fit straight line to determine the molecular
weights of the proteins in the whey, peak 1, and peak 2 lanes. (5 pts—this will be
scaled up appropriately if your gel did not develop properly)
dye
MW
Whey
Peak 1 Peak 2
what are the different classes and some examples of neuroprotectants that can be used to treat, prevent, or combat neurotoxicity/a neurotoxicant...for example, antioxidants, nutraceuticals, etc.,..?
Imagine that aldolase can react with the seven carbon molecule Sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate (below). Use the mechanism to predict the two products generated.
Please draw out the stereochemistry in a fischer projection.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1PCh. 3 - Given the following reactions and their...Ch. 3 - The decomposition of crystalline N2O5...Ch. 3 - The oxidation of glucose to CO2 and water is a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 5PCh. 3 - In another key reaction in glycolysis,...Ch. 3 - Assume that some protein molecule, in its folded...Ch. 3 - When a hydrophobic substance like a hydrocarbon is...Ch. 3 - It is observed that as temperature is increased,...Ch. 3 - Suppose a reaction has Ho and So values...
Ch. 3 - Prob. 11PCh. 3 - Prob. 12PCh. 3 - Prob. 13PCh. 3 - Undergoing moderate activity, an average person...Ch. 3 - The major difference between a protein molecule in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 16PCh. 3 - Prob. 17PCh. 3 - Consider the degradation of glucose to pyruvate by...Ch. 3 - a. Consider the malate dehydrogenase reaction,...Ch. 3 - Bovine ribonuclease folds with Ho = -280 kJmol-1...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a potent inhibitor of aldolase. It is known to ONLY inhibit theenzyme when it is complexed with substrate. Treatment of the enzyme alone has no effect.What is the mechanism for this inhibition? Please draw out the mechanism and show how it inhibits this.arrow_forwardShow the fate of the proton on the 4-Oxygen molecule of F-1,6-BP. Please include a drawing showing the electron flow that occurs.arrow_forward1. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following aldol condensation? O NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forward
- An organic chemist ordered the wrong item. She wanted to obtain 1-hydroxy-2-butanone, butinstead ordered 2-hydroxybutyraldehyde. As a good biochemist, show how the organic chemistcould use biological catalysis to make her desired compound. Please show the mechanism by drawing.arrow_forwardShow the fate of the hydrogen on carbon-2 of glucose. Please draw out the structure using curve arrows to show electron flow.arrow_forward3. Which one of the compounds below is the major product formed by the reaction sequence shown here? CH3 + CH3NO2 NaOH H2, Ni ? nitromethane acetophenone OH OH HO HN- u x x x x Ph A HO -NH2 HO H Ph Ph Ph N- H B Ph NH2 D Earrow_forward
- 4. Only ONE of the five compounds below can be prepared by an aldol condensation in which a single carbonyl compound is treated with base. Which one is it? To solve this problem, reverse the aldol condensation that formed each of these molecules to find out what two molecules came together to make the products. The one in which the two molecules are identical is the answer. Ph Ph ཚིག གནས ག ནཱ ཀ ན ཀནཱ A Ph H B Ph Ph H D Ph. Ph Ph E Harrow_forward5. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? First, equimolar amounts of cyclopentanone and LDA are mixed at -78°C. Then propionaldehyde (propanal) is added. Addition of aqueous acid completes the process. LDA, -78°C. 1. 2. H₂O* H A B H 0 D H H Earrow_forward2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? NaOH, H₂O heat A B C D Earrow_forward
- CH3CH2CHO + propanal PhCH2CHO 2-phenylacetaldehyde mixture of four products NaOH 10. In the crossed aldol reaction of propanal and 2-phenylacetaldehyde shown above, a mixture of four products will be formed. Which ONE of the compounds below will NOT be formed in this crossed aldol reaction? OH Ph A H OH OH Ph H B OH OH H H H Ph Ph C Ph D Earrow_forwardAn organic chemist ordered the wrong item. She wanted to obtain 1-hydroxy-2-butanone, butinstead ordered 2-hydroxybutyraldehyde. As a good biochemist, show how the organic chemistcould use biological catalysis to make her desired compound.arrow_forwardPredict the products of aldolase catalyzing the reaction with acetone and (S)-3-hydroxybutyraldehyde.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning


Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

The Cell Membrane; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AsffT7XIXbA;License: Standard youtube license