
Marathon Times The following histogram of marathon times includes data for men and women and also for both an Olympic marathon and an amateur marathon. Greater values indicate slower runners. (Sources: www.forestcityroadraces.com and www.runnersworld.com)
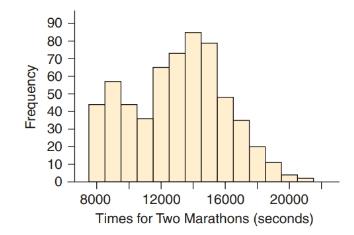
a. Describe the shape of the distribution.
b. What are two different possible reasons for the two
c. Knowing that there are usually fewer women who run marathons than men and that more people ran in the amateur marathon than in the Olympic marathon, look at the size of the mounds and try to decide which of the reasons stated in part b is likely to cause this. Explain.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
INTRODUCTORY STATISTICS (LOOSELEAF)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach (3rd Edition)
- Wind Mountain is an archaeological study area located in southwestern New Mexico. Potsherds are broken pieces of prehistoric Native American clay vessels. One type of painted ceramic vessel is called Mimbres classic black-on-white. At three different sites the number of such sherds was counted in local dwelling excavations. Test given. Site I Site II Site III 63 19 60 43 34 21 23 49 51 48 11 15 16 46 26 20 31 Find .arrow_forwardRothamsted Experimental Station (England) has studied wheat production since 1852. Each year many small plots of equal size but different soil/fertilizer conditions are planted with wheat. At the end of the growing season, the yield (in pounds) of the wheat on the plot is measured. Suppose for a random sample of years, one plot gave the following annual wheat production (in pounds): 4.46 4.21 4.40 4.81 2.81 2.90 4.93 3.54 4.16 4.48 3.26 4.74 4.97 4.02 4.91 2.59 Use a calculator to verify that the sample variance for this plot is . Another random sample of years for a second plot gave the following annual wheat production (in pounds): 3.89 3.81 3.95 4.07 4.01 3.73 4.02 3.78 3.72 3.96 3.62 3.76 4.02 3.73 3.94 4.03 Use a calculator to verify that the sample variance for this plot is . Suppose that we test the claim using that the population variance of annual wheat production for the first plot is larger…arrow_forwardIt is thought that prehistoric Native Americans did not take their best tools, pottery, and household items when they visited higher elevations for their summer camps. It is hypothesized that archaeological sites tend to lose their cultural identity and specific cultural affiliation as the elevation of the site increases. Let x be the elevation (in thousands of feet) for an archaeological site in the southwestern United States. Let y be the percentage of unidentified artifacts (no specific cultural affiliation) at a given elevation. Suppose that the following data were obtained for a collection of archaeological sites in New Mexico: x 5.50 6.00 6.75 7.00 7.75 y 37 38 92 70 99 Find the equation of the least squares line . Round a and b to three decimal places.arrow_forward
- A fitness trainer wants to estimate the effect of fitness activities on muscle mass for different weight categories of club members. They choose the most popular fitness classes at the gym: yoga, circuit training, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Suppose that the weights of club members are separated into three levels: under 155 pounds, 155 – 200 pounds, and over 200 pounds. Draw a flow chart showing the design of this experiment.arrow_forwardThe systolic blood pressure of individuals is thought to be related to both age and weight. Let the systolic blood pressure, age, and weight be represented by the variables x1, x2, and x3, respectively. Suppose that Minitab was used to generate the following descriptive statistics, correlations, and regression analysis for a random sample of 15 individuals. Descriptive Statistics Variable N Mean Median TrMean StDev SE Mean x 1 15 154.14 154.34 154.14 3.842 0.992000 x 2 15 59.69 60.19 59.69 1.462 0.377487 x 3 15 205.55 204.75 205.55 4.558 1.176871 Variable Minimum Maximum Q1 Q3 x 1 125 178 141.803 167.244 x 2 41 80 47.754 78.415 x 3 126 240 140.395 224.008 Correlations (Pearson) x 1 x 2 x 2 0.892 x 3 0.839 0.567 Regression Analysis The regression equation is x 1 = 0.883 + 1.257x2 + 0.871x3 Predictor Coef StDev T P Constant 0.883 0.635 1.39 0.095 x 2 1.257 0.635 1.98 0.036 x 3 0.871 0.419 2.08 0.030 S = 0.428 R-sq = 92.7 %…arrow_forwardAccording to health professionals, a person’s weight is expected to increase with age. To examine that statement, a nutritionist collected data from 11 random females from different age categories between the ages of 21 and 43. In the following table, x is the age of a person and y is the weight in pounds. x, age 21 24 27 29 31 33 35 38 40 42 43 y, weight in lb 121.4 122.3 130.3 131.7 133.3 134.6 136.7 138.4 140.3 142.0 145.1 Select the correct graph of the least-squares line on a scatter diagram.arrow_forward
- Let x be a random variable that represents the percentage of successful free throws a professional basketball player makes in a season. Let y be a random variable that represents the percentage of successful field goals a professional basketball player makes in a season. A random sample of n = 6 professional basketball players gave the following information. x 82 69 73 84 74 64 y 42 48 46 46 46 42 Verify that ∑x =446, ∑y =270, ∑x2 =33,442, ∑y2 =12,180, ∑xy =20,070, and r = 0, and find the critical value for a test using a 5% level of significance claiming that ρis not equal than zero. Round your answer to three decimal places.arrow_forwardLet x be a random variable that represents the percentage of successful free throws a professional basketball player makes in a season. Let y be a random variable that represents the percentage of successful field goals a professional basketball player makes in a season. A random sample of n = 6 professional basketball players gave the following information. x 75 72 75 81 74 81 y 46 39 42 47 49 50 Verify that Se ࣈ 3.591,a ࣈ –10.145, bࣈ0.729, and , and find the predicted percentage of successful field goals for a player with x= 88%successful free throws. Round your answer to the nearest tenth of a percentarrow_forwardAn editor wants to analyze if there is a significant difference in the ratings of books in four different genres. Random samples of book ratings were collected for four different genres. The editor recorded ratings in a 0 to 10 scale in the following table. Fiction Novel Biography Science&Technology 8.5 8.4 6.2 9.1 5.3 5.3 5.5 4.3 7.7 4.2 7.0 9.7 5.1 9.8 9.3 5.2 6.9 8.6 6.7 7.9 4.8 7.1 6.9 8.4 Shall we reject or not reject the claim that there are no differences among the population means of book ratings for the different genres? Use.arrow_forward
- Peggy conducted a study to identify the randomness of rainy days in fall. For 15 days, she recorded whether it rained that day or not. They denoted a rainy day with the letter R, a day without rain with the letter N. R N N R R N N R R N N R R R R Test the sequence for randomness. Use .arrow_forwardConsider the grades for the math and history exams for 10 students on a scale from 0 to 12 in the following table. Student Math History 1 4 8 2 5 9 3 7 9 4 12 10 5 10 8 6 8 5 7 9 6 8 9 6 9 11 9 10 7 10 Compute the Spearman correlation coefficient. Round your answer to three decimal places.arrow_forwardTo compare two elementary schools regarding teaching of reading skills, 12 sets of identical twins were used. In each case, one child was selected at random and sent to school A, and his or her twin was sent to school B. Near the end of fifth grade, an achievement test was given to each child. The results follow: Twin Pair 1 2 3 4 5 6 School A 169 157 115 99 119 113 School B 123 157 112 99 121 122 Twin Pair 7 8 9 10 11 12 School A 120 121 124 145 138 117 School B 153 90 124 140 142 102 Suppose a sign test for matched pairs with a 1% level of significance is used to test the hypothesis that the schools have the same effectiveness in teaching reading skills against the alternate hypothesis that the schools have different levels of effectiveness in teaching reading skills. Let p denote portion of positive signs when the scores of school B are subtracted from the corresponding scores of school…arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning



