
Concept explainers
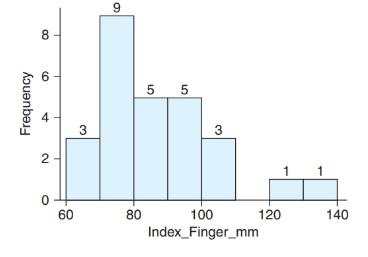
a. Use the histogram to approximate the mean ring finger length for the sample.
b. Approximate the mean by completing the work that is started below. Note that the left-hand side of each bin is being used in this approximation:
c. Explain why the method used in part (b) is an approximation of the mean rather than the actual mean.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
INTRODUCTORY STATISTICS (LOOSELEAF)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
Introductory Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECONOMICS
College Algebra Essentials (5th Edition)
- Suppose that the chance that an elementary student eats hot lunch is 30 percent. What’s the chance that, among 20 randomly selected students, between 6 and 8 students eat hot lunch (inclusive)?arrow_forwardBob’s commuting times to work are varied. He makes it to work on time 80 percent of the time. On 12 randomly selected trips to work, what’s the chance that Bob makes it on time at least 10 times?arrow_forwardYour chance of winning a small prize in a scratch-off ticket is 10 percent. You buy five tickets. What’s the chance you will win at least one prize?arrow_forward
- Suppose that 60 percent of families own a pet. You randomly sample four families. What is the chance that two or three of them own a pet?arrow_forwardIf 40 percent of university students purchase their textbooks online, in a random sample of five students, what’s the chance that exactly one of them purchased their textbooks online?arrow_forwardA stoplight is green 40 percent of the time. If you stop at this light eight random times, what is the chance that it’s green exactly five times?arrow_forward
- If 10 percent of the parts made by a certain company are defective and have to be remade, what is the chance that a random sample of four parts has one that is defective?arrow_forwardQuestion 4 Fourteen individuals were given a complex puzzle to complete. The times in seconds was recorded for their first and second attempts and the results provided below: 1 2 3 first attempt 172 255 second attempt 70 4 5 114 248 218 194 270 267 66 6 7 230 219 341 174 8 10 9 210 261 347 218 200 281 199 308 268 243 236 300 11 12 13 14 140 302 a. Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean time taken by each individual to complete the (i) first attempt and (ii) second attempt. [la] b. Test the hypothesis that the difference between the two mean times for both is 100 seconds. Use the 5% level of significance. c. Subsequently, it was learnt that the times for the second attempt were incorrecly recorded and that each of the values is 50 seconds too large. What, if any, difference does this make to the results of the test done in part (b)? Show all steps for the hypothesis testarrow_forwardQuestion 3 3200 students were asked about the importance of study groups in successfully completing their courses. They were asked to provide their current majors as well as their opinion. The results are given below: Major Opinion Psychology Sociology Economics Statistics Accounting Total Agree 144 183 201 271 251 1050 Disagree 230 233 254 227 218 1162 Impartial 201 181 196 234 176 988 Total 575 597 651 732 645 3200 a. State both the null and alternative hypotheses. b. Provide the decision rule for making this decision. Use an alpha level of 5%. c. Show all of the work necessary to calculate the appropriate statistic. | d. What conclusion are you allowed to draw? c. Would your conclusion change at the 10% level of significance? f. Confirm test results in part (c) using JASP. Note: All JASP input files and output tables should be providedarrow_forward
- Question 1 A tech company has acknowledged the importance of having records of all meetings conducted. The meetings are very fast paced and requires equipment that is able to capture the information in the shortest possible time. There are two options, using a typewriter or a word processor. Fifteen administrative assistants are selected and the amount of typing time in hours was recorded. The results are given below: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 typewriter 8.0 6.5 5.0 6.7 7.8 8.5 7.2 5.7 9.2 5.7 6.5 word processor 7.2 5.7 8.3 7.5 9.2 7.2 6.5 7.0 6.9 34 7.0 6.9 8.8 6.7 8.8 9.4 8.6 5.5 7.2 8.4 a. Test the hypothesis that the mean typing time in hours for typewriters is less than 7.0. Use the 1% level of significance. b. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the difference in mean typing time in hours, where a difference is equal to the typing time in hours of word processors minus typing time in hours of typewriter. c. Using the 5% significance level, determine whether there is…arrow_forwardIllustrate 2/7×4/5 using a rectangular region. Explain your work. arrow_forwardWrite three other different proportions equivalent to the following using the same values as in the given proportion 3 foot over 1 yard equals X feet over 5 yardsarrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill





