
(a)
Interpretation:
Location of the element magnesium in terms of s area, p area, d area, or f area has to be specified.
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
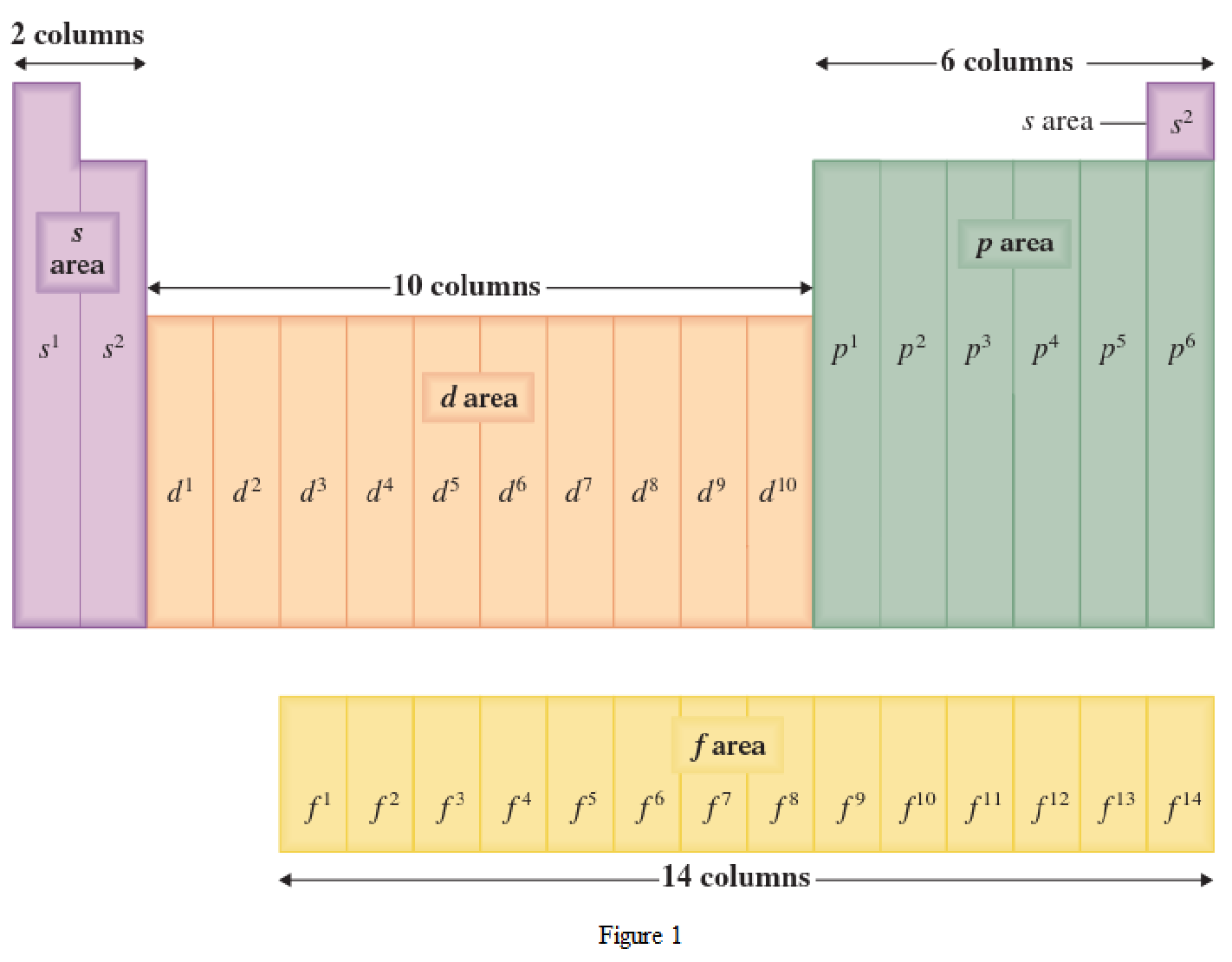
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
(b)
Interpretation:
Location of the element copper in terms of s area, p area, d area, or f area has to be specified.
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, then the elements with similar chemical properties occur at regular intervals or periodic intervals. The elements are arranged in a periodic table in which the arrangement was based on the atomic number of the elements and the elements that have similar chemical properties are positioned in vertical columns.
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
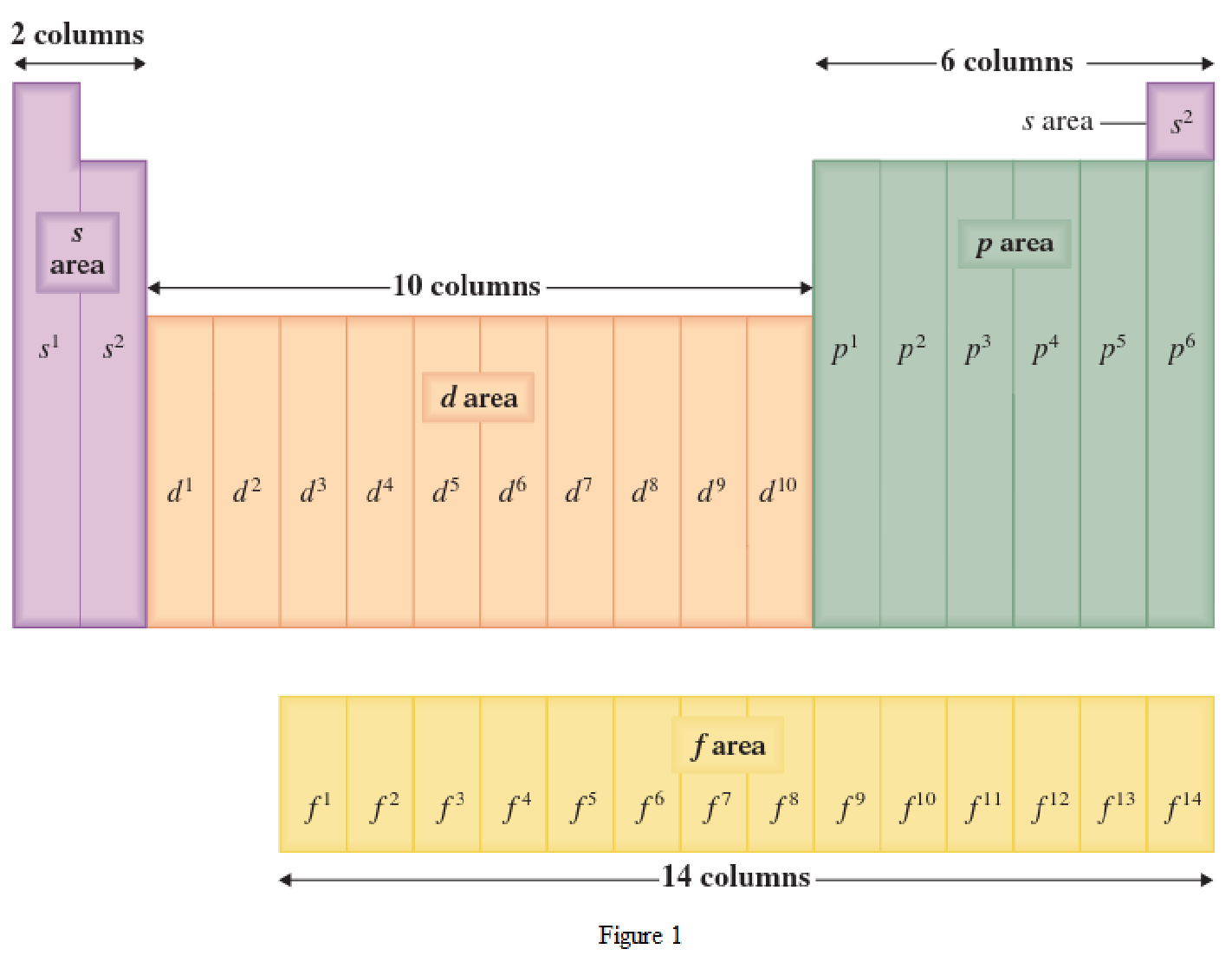
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
(c)
Interpretation:
Location of the element bromine in terms of s area, p area, d area, or f area has to be specified.
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, then the elements with similar chemical properties occur at regular intervals or periodic intervals. The elements are arranged in a periodic table in which the arrangement was based on the atomic number of the elements and the elements that have similar chemical properties are positioned in vertical columns.
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
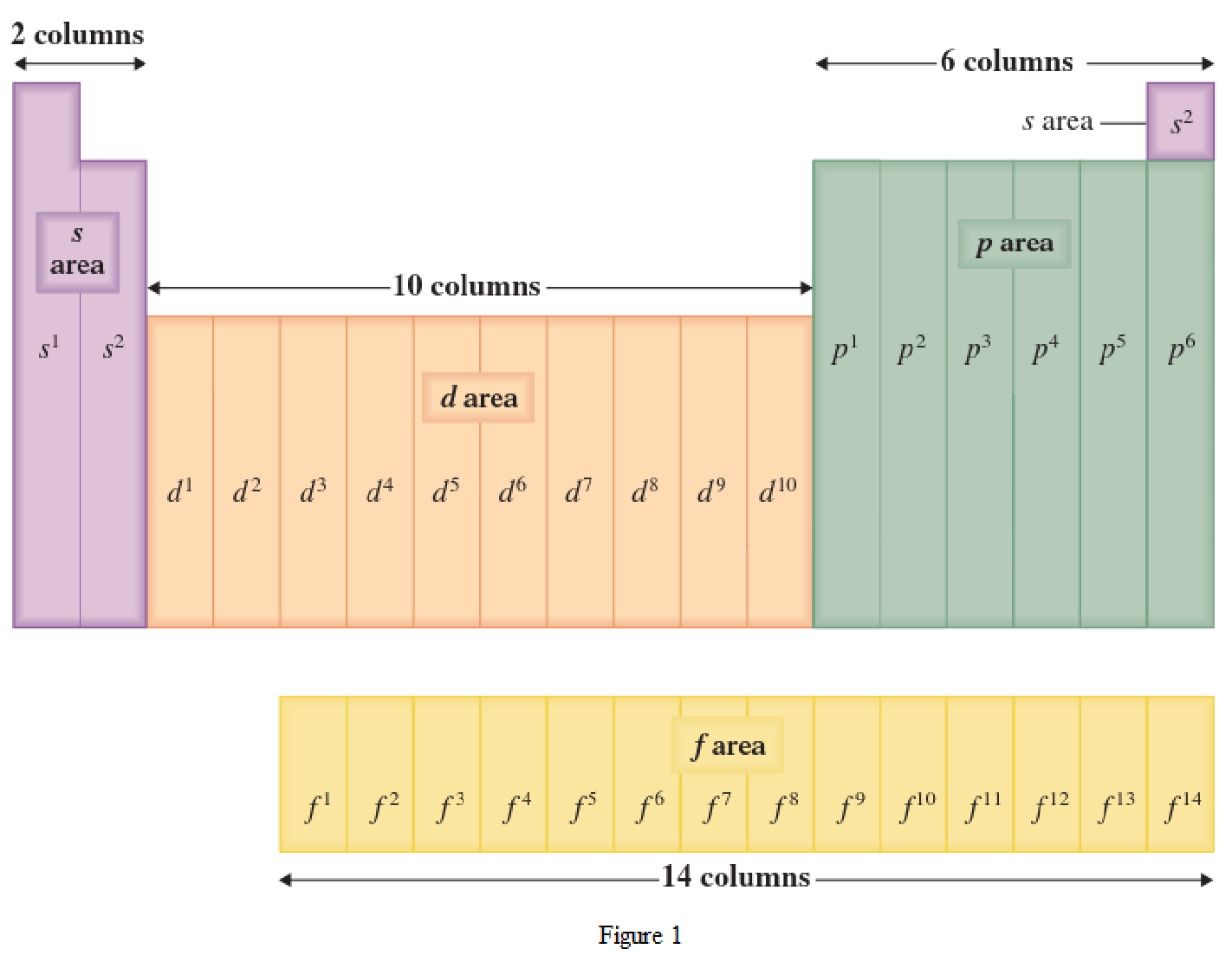
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
(d)
Interpretation:
Location of the element iron in terms of s area, p area, d area, or f area has to be specified.
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, then the elements with similar chemical properties occur at regular intervals or periodic intervals. The elements are arranged in a periodic table in which the arrangement was based on the atomic number of the elements and the elements that have similar chemical properties are positioned in vertical columns.
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
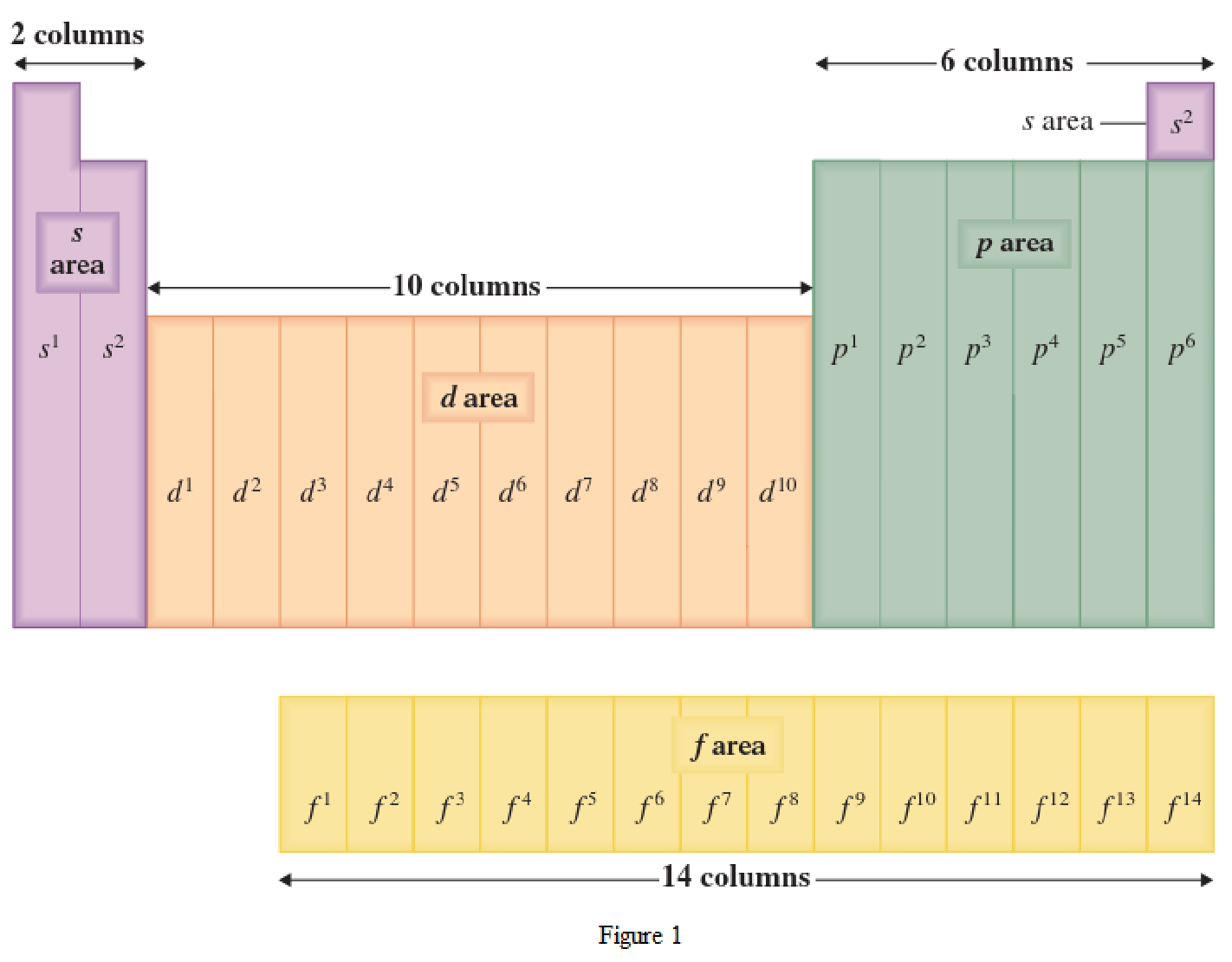
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





