
(a)
Interpretation: The given compounds in each group are to be ranked in the order of increasing boiling point.
Concept introduction: Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
Intermolecular forces are also known as non-covalent interactions. The interactions present between molecules are known as intermolecular forces. A
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are
Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
The increasing order of intermolecular force strength is as follows:
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
The boiling point increases with an increase in the surface area.
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is
The increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is
(b)
Interpretation: The given compounds in each group are to be ranked in the order of increasing boiling point.
Concept introduction: Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
Intermolecular forces are also known as non-covalent interactions. The interactions present between molecules are known as intermolecular forces. A functional group present in a molecule decides the type of interaction.
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are
Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
In
The increasing order of intermolecular force strength is as follows:
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is
The increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is
(c)
Interpretation: The given compounds in each group are to be ranked in the order of increasing boiling point.
Concept introduction: Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
Intermolecular forces are also known as non-covalent interactions. The interactions present between molecules are known as intermolecular forces. A functional group present in a molecule decides the type of interaction.
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are
Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
In
The increasing order of intermolecular force strength is as follows:
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
The boiling point increases with an increase in the surface area. Branched chain alkanes have low boiling point than straight chain alkanes because in branched chain alkanes, surface area is less.
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is
The increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is
(d)
Interpretation: The given compounds in each group are to be ranked in the order of increasing boiling point.
Concept introduction: Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
Intermolecular forces are also known as non-covalent interactions. The interactions present between molecules are known as intermolecular forces. A functional group present in a molecule decides the type of interaction.
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The increasing order of intermolecular force strength for the given compounds is shown below.
![]()
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are,
![]()
Figure 1
Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
The compounds containing hydroxyl groups show hydrogen bonding.
The increasing order of intermolecular force strength is as follows:
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
The boiling point increases with an increase in the surface area. Branched chain
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is,
![]()
Figure 2
The increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is shown in Figure 2.
(e)
Interpretation: The given compounds in each group are to be ranked in the order of increasing boiling point.
Concept introduction: Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
Intermolecular forces are also known as non-covalent interactions. The interactions present between molecules are known as intermolecular forces. A functional group present in a molecule decides the type of interaction.
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The increasing order of intermolecular force strength for the given compounds is shown below.
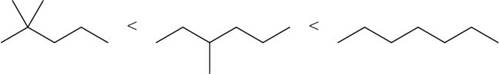
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are,
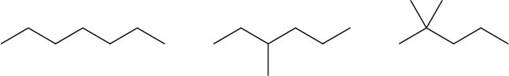
Figure 3
Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
The increasing order of intermolecular force strength is as follows:
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
The boiling point increases with an increase in the surface area. Branched chain alkanes have low boiling point than straight chain alkanes because in branched chain alkanes, surface area is less.
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is,

Figure 4
The increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is rightfully stated.
(f)
Interpretation: The given compounds in each group are to be ranked in the order of increasing boiling point.
Concept introduction: Boiling point depends upon the intermolecular forces. Greater is the intermolecular forces, greater will be the boiling point.
Intermolecular forces are also known as non-covalent interactions. The interactions present between molecules are known as intermolecular forces. A functional group present in a molecule decides the type of interaction. The increasing order of intermolecular force strength is as follows:
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point is as follows:
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The increasing order of intermolecular force strength for the given compounds is shown below.
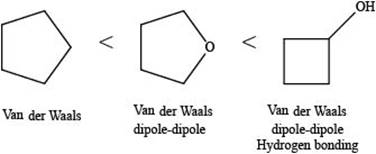
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are,
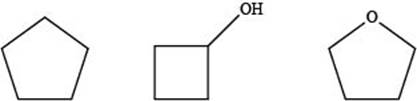
Figure 5
A hydrogen bond is a strong electrostatic attraction which takes place when hydrogen atom is bonded to an electronegative atom (
Dipole-dipole interactions are the forces present between two polar molecules.
Van der Waals forces are the weak forces that are present between non-polar compounds or molecules.
The increasing order of intermolecular force strength is as follows:
The interaction present in cyclopentane is Van der Waals forces because it is a non-polar compound.
The interactions present in cyclobutanolare Van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, and dipole-dipole interactions.
Due to electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen, ethers are polar molecule. Thus, the interaction present in polar molecules is Dipole-dipole interaction. The interactions present in tetrahydrofuran are Van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions.
Therefore, the increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is,
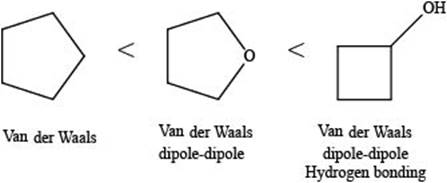
Figure 6
The increasing order of boiling point for the given compounds is rightfully stated.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- help 20arrow_forwardProvide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning




