
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(a)
Answer to Problem 3.144EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is ethylthioethane and common name is diethyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
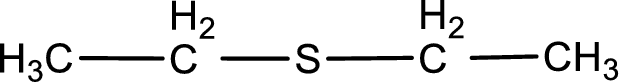
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a two carbon chain. Hence, the base name is ethane.
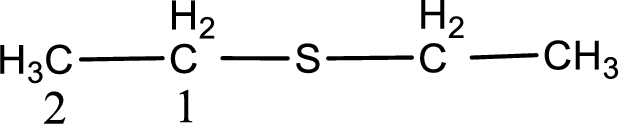
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be ethylthio as it contains two carbon atoms.
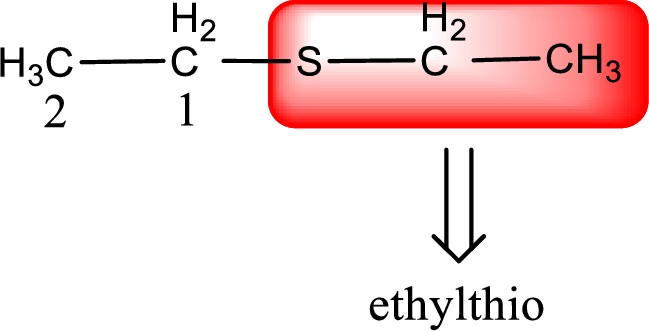
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as ethylthioethane.
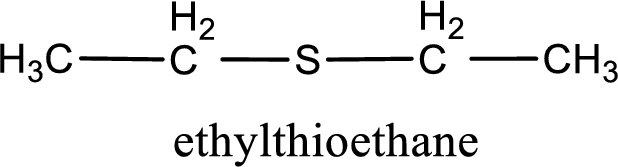
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is ethylthioethane.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, two ethyl groups are present. Therefore, prefix di- is added to the alkyl group followed by the word sulfide. Common name for the given thioether is diethyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3.144EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 2-ethylthiopropane and common name is ethyl isopropyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
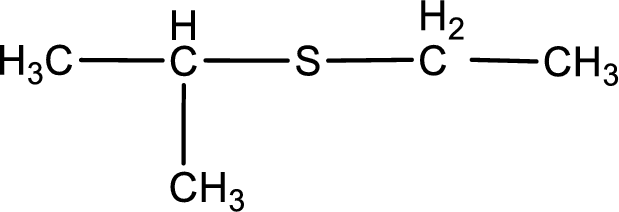
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a three carbon chain. Hence, the base name is propane.
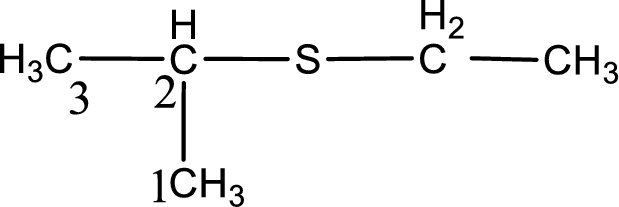
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be ethylthio as it contains two carbon atoms. The point of attachment in the propane for ethylthio group is in the second carbon atom.
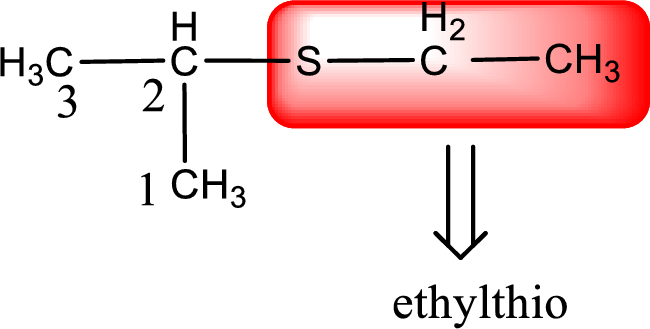
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as 2-ethylthiopropane.
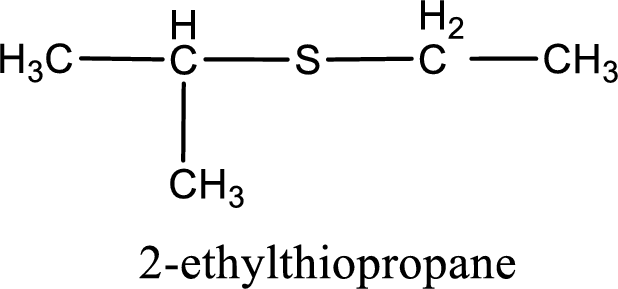
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is 2-ethylthiopropane.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, an ethyl and an isopropyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is ethyl isopropyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(c)
Answer to Problem 3.144EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is methylthiocyclopentane and common name is cyclopentyl methyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
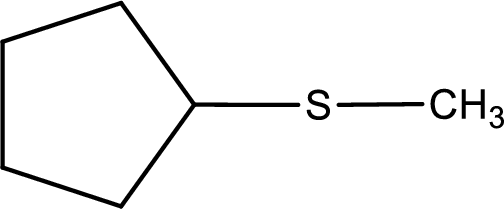
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a five carbon cyclic chain that is saturated. Hence, the base name is cyclopentane.
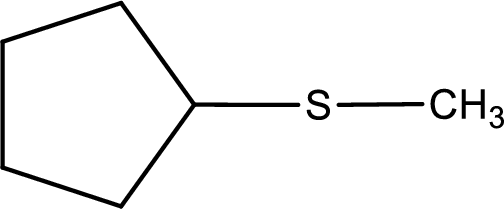
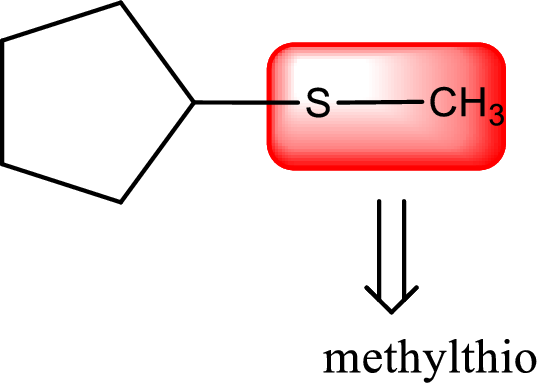
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be methylthio as it contains only one carbon atom.
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as methylthiocyclopentane.
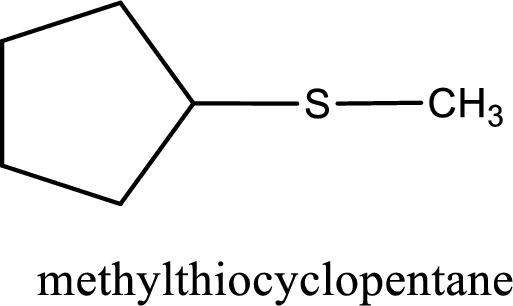
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is methylthiocyclopentane.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, a methyl and a cyclopentyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is cyclopentyl methyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming thioether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in thioether.
- ✓ The suffix –thio has to be added in order to obtain the alkylthio group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethylthio, methyl becomes as methylthio etc.
- ✓ Alkylthio name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkykthio group is attached) followed by the base name.
Rules for assigning common names to thioether:
For obtaining common name for thioether, two rules are applicable, one for symmetrical ethers and one for unsymmetrical ethers.
- ✓ For unsymmetrical thioethers, the two hydrocarbon groups that is attached to the oxygen atom is arranged in an alphabetical order and the word sulfide is added. The words are separated by a space. These names have three words with space between them.
- ✓ For symmetrical ethers, prefix di- is used. Then the word sulfide is added with a space between the two words. These names have two words with space between them.
(d)
Answer to Problem 3.144EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 3-(ethylthio)-1-propene and common name is allyl ethyl sulfide.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
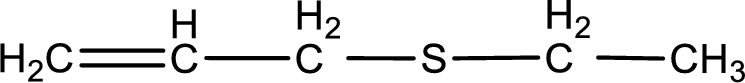
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a three carbon chain with a double bond. Hence, the base name is propene.
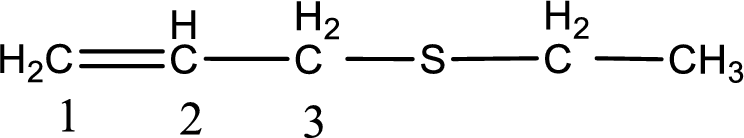
Next step is to identify the alkylthio group. In the given thioether, the alkylthio group is found to be ethylthio as it contains two carbon atoms.
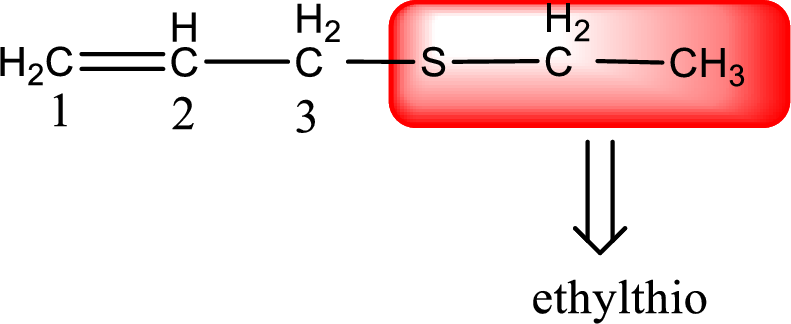
Alkylthio name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkylthio group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as 3-(ethylthio)-1-propene.
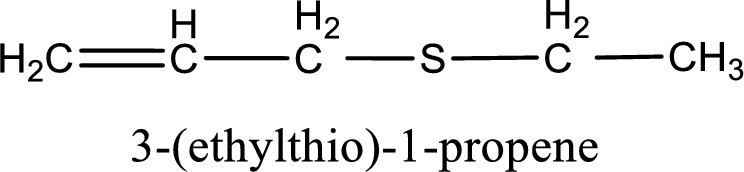
The IUPAC name of the given thioether is 3-(ethylthio)-1-propene.
To obtain common name the two hydrocarbon groups that are attached to the sulfur atom is named first. In the given structure, an ethyl and an allyl group is present. Arranging them in the alphabetical order and adding the word sulfide after them gives the common name for the given thioether. Common name for the given thioether is allyl ethyl sulfide.
IUPAC name and common name for the given thioether is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Can anyone help me solve this step by step. Thank you in advaarrow_forwardPlease draw the mechanism for this Friedel-crafts acylation reaction using arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the Fischer projection of D-fructose. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Skip Part Check AP 14 tv SC F1 F2 80 F3 a F4 ! 2 # 3 CF F5 75 Ax MacBook Air 894 $ 5olo % Λ 6 > W F6 K F7 &arrow_forward
- Consider this step in a radical reaction: Y What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ionization propagation initialization passivation none of the abovearrow_forward22.16 The following groups are ortho-para directors. (a) -C=CH₂ H (d) -Br (b) -NH2 (c) -OCHS Draw a contributing structure for the resonance-stabilized cation formed during elec- trophilic aromatic substitution that shows the role of each group in stabilizing the intermediate by further delocalizing its positive charge. 22.17 Predict the major product or products from treatment of each compound with Cl₁/FeCl₂- OH (b) NO2 CHO 22.18 How do you account for the fact that phenyl acetate is less reactive toward electro- philic aromatic substitution than anisole? Phenyl acetate Anisole CH (d)arrow_forwardShow how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forward
- Help me solve this problem. Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.7 Predict the monoalkylated products of the following reactions with benzene. (a) AlCl3 Ya (b) AlCl3 (c) H3PO4 (d) 22.8 Think-Pair-Share AICI3 The reaction below is a common electrophilic aromatic substitution. SO3 H₂SO4 SO₂H (a) Draw the reaction mechanism for this reaction using HSO,+ as the electrophile. (b) Sketch the reaction coordinate diagram, where the product is lower in energy than the starting reactant. (c) Which step in the reaction mechanism is highest in energy? Explain. (d) Which of the following reaction conditions could be used in an electrophilic aro- matic substitution with benzene to provide substituted phenyl derivatives? (i) AICI3 HNO3 H₂SO4 K2Cr2O7 (iii) H₂SO4 (iv) H₂PO₁arrow_forwardIs an acid-base reaction the only type of reaction that would cause leavening products to rise?arrow_forward
- Help me understand this! Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.22 For each compound, indicate which group on the ring is more strongly activating and then draw a structural formula of the major product formed by nitration of the compound. Br CHO (a) CH3 (b) (c) CHO CH3 SO₂H (d) ☑ OCHS NO₂ (e) (f) CO₂H NHCOCH3 NHCOCH, (h) CHS 22.23 The following molecules each contain two aromatic rings. (b) 000-100- H3C (a) (c) Which ring in each undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution more readily? Draw the major product formed on nitration.arrow_forwardV Consider this step in a radical reaction: Br: ? What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ⚫ionization termination initialization neutralization none of the abc Explanation Check 80 Ο F3 F1 F2 2 F4 01 % do5 $ 94 #3 X 5 C MacBook Air 25 F5 F6 66 ©2025 ˇ F7 29 & 7 8arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





