
(a)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming thioalcohols that contain single thiol group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains thiol group also. The chain name is obtained by adding the suffix “-thiol”. If the compound contains an unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to
alkane . - • The numbering has to be given so that the thiol group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the thiol group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
IUPAC rules for naming thioalcohols that contain more than one thiol group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of thiol groups that is present.
(a)
Answer to Problem 3.139EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 1-pentanethiol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is
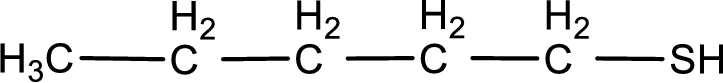
First step is to identify the longest continuous carbon chain. In the given structure, it is found that the longest carbon chain is five carbon chain. Hence, the parent alkane is pentane.
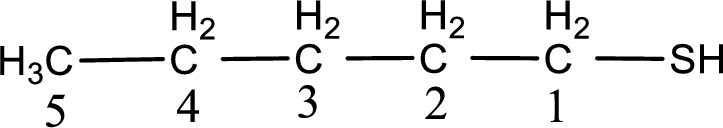
The suffix -thiol is added to the parent alkane name. This gives the name as pentanethiol.
Next step is to number the carbon atoms so that the thiol
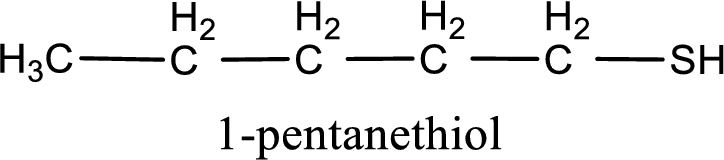
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3.139EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 1-pentanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is
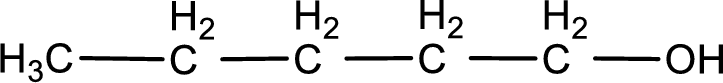
The longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group is found to be five carbon chain. Therefore, the parent alkane is pentane. As a hydroxyl group is present the name of the alcohol can be given as pentanol.
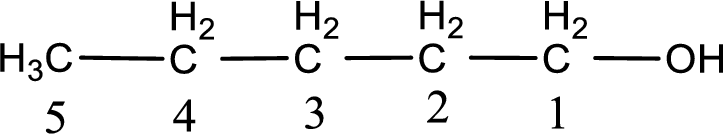
The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. In this case, the hydroxyl group is present in the first carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name can be given as 1-pentanol.
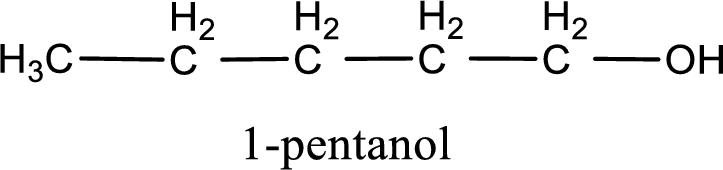
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming thioalcohols that contain single thiol group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains thiol group also. The chain name is obtained by adding the suffix “-thiol”. If the compound contains an unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the thiol group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the thiol group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
IUPAC rules for naming thioalcohols that contain more than one thiol group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of thiol groups that is present.
(c)
Answer to Problem 3.139EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 3-methyl-2-butanethiol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
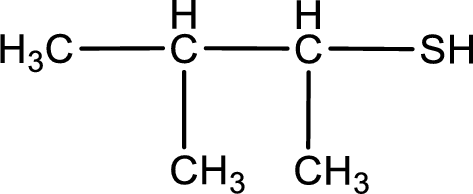
First step is to identify the longest continuous carbon chain. In the given structure, it is found that the longest carbon chain is four carbon chain. Hence, the parent alkane is butane.
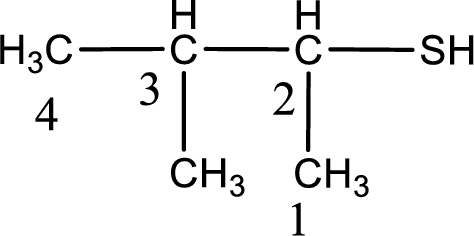
The suffix -thiol is added to the parent alkane name. This gives the name as butanethiol.
Next step is to number the carbon atoms so that the thiol functional group gets the least numbering. In this case, it is in second carbon atom. Methyl group is present as substituent in the third carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is 3-methyl-2-butanethiol.
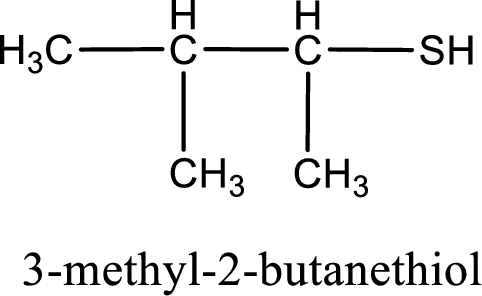
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(d)
Answer to Problem 3.139EP
IUPAC name for the given compound is 3-methyl-2-butanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure of compound is shown below,
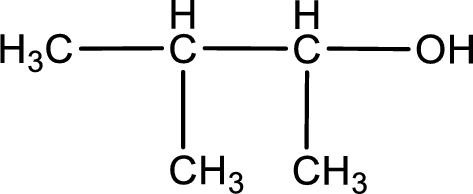
First step is to identify the longest continuous carbon chain. In the given structure, it is found that the longest carbon chain is four carbon chain. Hence, the parent alkane is butane.
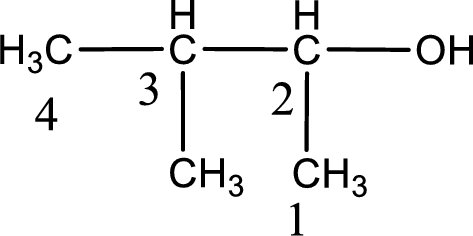
The suffix -ol is added to the parent alkane name by replacing the suffix “–e”. This gives the name as butanol.
Next step is to number the carbon atoms so that the hydroxyl functional group gets the least numbering. In this case, it is in second carbon atom. Methyl group is present as substituent in the third carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is 3-methyl-2-butanol.
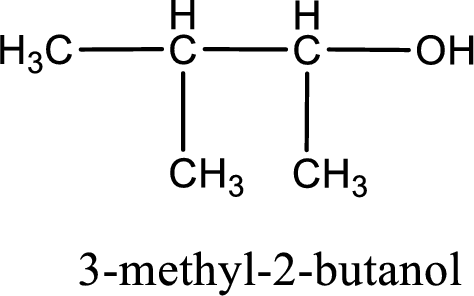
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Relative Abundance 20- Problems 501 (b) The infrared spectrum has a medium-intensity peak at about 1650 cm. There is also a C-H out-of-plane bending peak near 880 cm. 100- 80- 56 41 69 M(84) LL 15 20 25 30 35 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 m/zarrow_forwardPolyethylene furanoate is a polymer made from plant-based sources; it is used for packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forwardPhenol is the starting material for the synthesis of 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorophenol, known al-ternatively as pentachlorophenol, or more simply as penta. At one time, penta was widely used as a wood preservative for decks, siding, and outdoor wood furniture. Draw the structural formula for pentachlorophenol and describe its synthesis from phenol.arrow_forward
- 12 Mass Spectrometry (d) This unknown contains oxygen, but it does not show any significant infrared absorption peaks above 3000 cm . 59 100- BO 40 Relative Abundance M(102) - 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 5 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 mizarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H HO H HO H HO H H -OH CH2OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : Darrow_forward: Draw the structure of valylasparagine, a dipeptide made from valine and asparagine, as it would appear at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. P Darrow_forward
- Draw the Haworth projection of α-L-mannose. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS Data resource. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ཊི Х Darrow_forwardDraw the structure of serine at pH 6.8. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : d كarrow_forwardTake a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH H H H OH OH OH CH2OH H H H H OH H H OH H OH Is this a reducing sugar? yes α β ロ→ロ no ☑ yes Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. O no 0+0 If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. ☐arrow_forward
- Answer the questions in the table below about this molecule: H₂N-CH₂ -C—NH–CH–C—NH–CH—COO- CH3 CH CH3 What kind of molecule is this? 0= CH2 C If you said the molecule is a peptide, write a description of it using 3-letter codes separated ☐ by dashes. polysaccharide peptide amino acid phospolipid none of the above Хarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: CH₂OH C=O HO H H -OH H OH CH₂OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ Х S '☐arrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution 22.30 Predict all possible products formed from the following nucleophilic substitution reactions. (a) (b) 9 1. NaOH 2. HCI, H₂O CI NH₁(!) +NaNH, -33°C 1. NaOH 2. HCl, H₂Oarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning



