
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming ether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in ether.
- ✓ The suffix –yl has to be changed to –oxy in order to obtain the alkoxy group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethoxy, methyl becomes as methoxy etc.
- ✓ Alkoxy name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkoxy group is attached) followed by the base name.
(a)
Answer to Problem 3.104EP
IUPAC name of the given compound is 1,3-dimethoxypropane.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given compound is shown below,
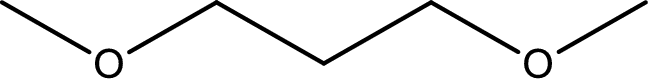
First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a three carbon chain. Hence, the base name is propane.
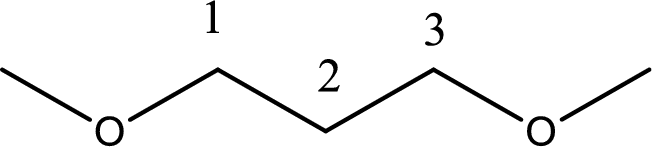
Next step is to identify the alkoxy group. In the given compound, the alkoxy group is found to be two methoxy groups.
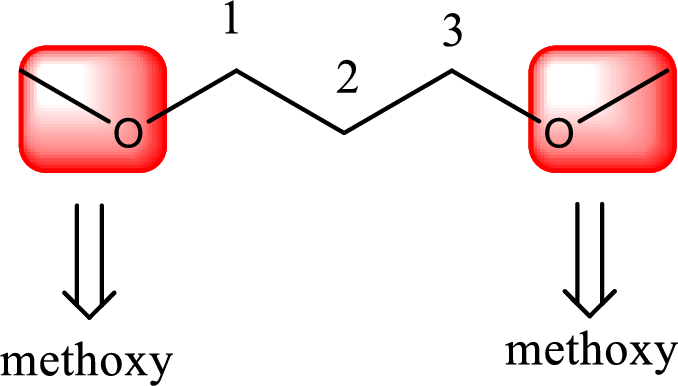
Alkoxy name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkoxy group is attached. In this case as two methoxy groups are present prefix di- is added before methoxy. This gives the IUPAC name as 1,3-dimethoxypropane.
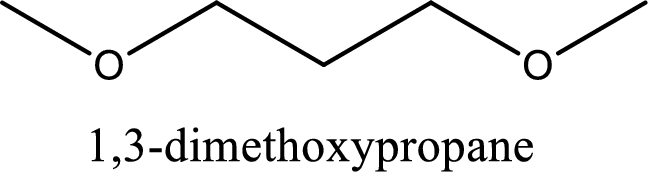
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in
alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane. - • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3.104EP
IUPAC name of the given compound is 1-butanol.
Explanation of Solution
Given structure is,
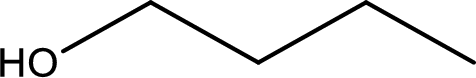
The longest continuous carbon chain with the hydroxyl group is found to be four carbon chain. Therefore, the parent alkane is butane. As a hydroxyl group is present the name of the alcohol can be given as butanol.
The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering. In this case, the hydroxyl group is present in the first carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name can be given as 1-butanol.
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
Any organic molecule can be named by using certain rules given by IUPAC (International Union for Pure and applied chemistry). IUPAC name consists of three parts in major namely Prefix suffix and root word.
Prefix represents the substituent present in the molecule and its position in the root name.
Suffix denotes the presence of functional group if any in the molecule. It can be an alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acid, alcohol etc.
Root word represents the longest continuous carbon skeleton of the organic molecule.
IUPAC rules for naming ether:
- ✓ The base name is found from the longest carbon chain present in ether.
- ✓ The suffix –yl has to be changed to –oxy in order to obtain the alkoxy group name. For example, ethyl becomes as ethoxy, methyl becomes as methoxy etc.
- ✓ Alkoxy name has to be placed first with the number (carbon atom to which the alkoxy group is attached) followed by the base name.
(c)
Answer to Problem 3.104EP
IUPAC name of the given compound is 1-ethoxypropane.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given compound is shown below,

First step is to identify the longest carbon chain. In this case it is a three carbon chain. Hence, the base name is propane.
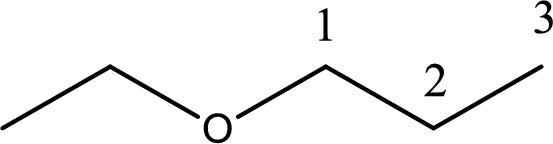
Next step is to identify the alkoxy group. In the given compound, the alkoxy group is found to be ethoxy as it contains two carbon atoms.
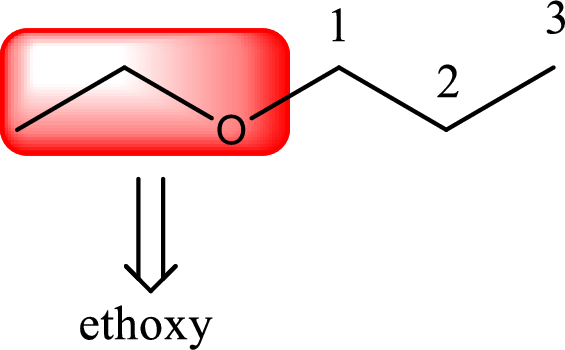
Alkoxy name is placed before the base name with the appropriate number that gives information about to which carbon atom the alkoxy group is attached. This gives the IUPAC name as 1-ethoxypropane.
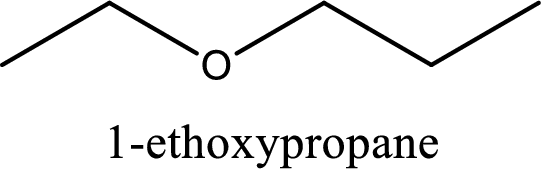
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain single hydroxyl group:
- • Longest carbon chain has to be identified that contains hydroxyl group also. The chain name is obtained by replacing the letter “-e” in alkane with “-ol”. If the compound contains a unsaturated bond, then the respective name has to be changed with regard to alkane.
- • The numbering has to be given so that the hydroxyl group gets the least numbering.
- • Name and location of any other substituent present in the chain has to be identified.
- • If in a ring the hydroxyl group is present, then that carbon is numbered 1 and the numbering then proceeds counterclockwise or clockwise in a way that substituents present if any gets the least numbering.
- • Hydroxyl group as a substituent in a molecule is named as hydroxy group rather than hydroxyl group.
- • If the compound contains bulky groups on same side of the double bond, then it is a cis isomer and if the bulkyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond, then it is a trans isomer.
- • In case of cycloalkane compounds, if the substitutions are present on same side of the ring of carbon atoms, it is a cis isomer. If the substitutions are present above and below the ring, then it is a trans isomer.
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols that contain more than one hydroxyl group:
- • The same rules said above is followed but the prefix di-, tri-, tetra etc is added corresponding to the number of hydroxyl groups that is present.
(d)
Answer to Problem 3.104EP
IUPAC name of the given compound is 2-methoxyphenol.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given compound is shown below,
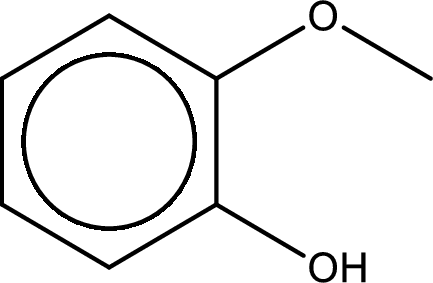
The given compound has two functional group namely, hydroxyl group and a alkoxy group. Alcohol has got more preference over ether. Therefore, the IUPAC name is given by using the parent as alcohol. In this case the parent alcohol is found to be phenol. The substituent that is present in the phenol is a methoxy group in the second carbon atom. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound can be written as 2-methoxyphenol.
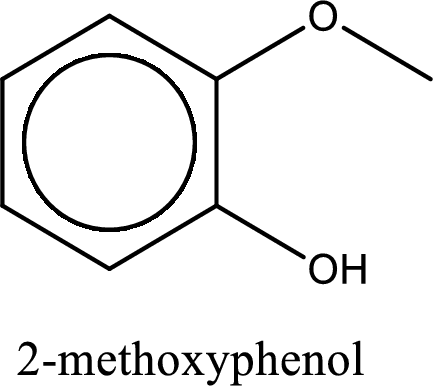
IUPAC name for the given compound is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Please helparrow_forward(a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forward
- Help me solve this problem.arrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forwardCHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning


