
Concept explainers
Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
(a) The reaction of aluminum and iron(III) oxide to form iron and aluminum oxide (known as the thermite reaction).
(b) The reaction of carbon and water at high temperature to form a mixture of gaseous CO and H2 (known as water gas and once used as a fuel).
(c) The reaction of liquid silicon tetrachloride and magnesium forming silicon and magnesium chloride. This is one step in the preparation of ultrapure silicon used in the semiconductor industry
(a)
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equation for given reaction should be written.
Concept introduction:
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms can be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, therefore, the number of atoms present in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms present in the products.
Answer to Problem 1PS
Aluminium and iron(III) oxide reacts together and produces liquid iron and aluminum oxide which is highly exothermic reaction. The balanced equation is given below.
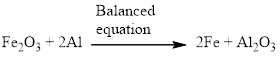
Explanation of Solution
Aluminium and iron(III) oxide reacts together and produces liquid iron and aluminum oxide which is highly exothermic reaction. The unbalanced equation is given below using correct molecular formula, the given reaction aluminium reduces the oxide of iron.

Balance the aluminum atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients.
There is one aluminium in the left side and two aluminium in the right side. Therefore according to the aluminium atom the balanced equation is given below.

Next, balance the iron atom in the equation, there are two iron atom in the left side and one iron atom in right side. For the balancing the iron atom, two molecules of iron is added to the right side. Therefore according to the iron atom the balanced equation is given below.

Now the equation is balanced, therefore the balanced equation is given below,
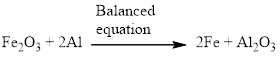
(b)
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equation for given reaction should be written.
Concept introduction:
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms can be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, therefore, the number of atoms present in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms present in the products.
Answer to Problem 1PS
The balanced equation is given below (b)

Explanation of Solution
Carbon monoxide reacts with water vapor which forms the carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen is called as water gas. This reaction is called as water-gas shift reaction (WGSR).
The unbalanced equation is given below using correct molecular formula, the given reaction Carbon monoxide reacts with water vapor which forms the carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and therefore the balanced equation is given below,

(c)
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equation for given reaction should be written.
Concept introduction:
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms can be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, therefore, the number of atoms present in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms present in the products.
Answer to Problem 1PS
Silicon tetrachloride and magnesium reacts together and produces silicon and magnesium chloride. The balanced equation is given below (c)
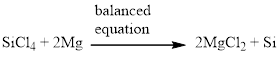
Explanation of Solution
Silicon tetrachloride and magnesium reacts together and produces silicon and magnesium chloride. The unbalanced equation is given below using correct molecular formula,
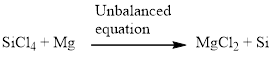
Balance the magnesium atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients.
There is one magnesium atom in the left side and one magnesium in the right side. Therefore according to the magnesium there is no change in the equation. The balanced equation is given below.
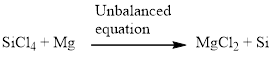
Next, balance the silicon atom in the equation, there is one silicon atom in the left side and one silicon atom in right side. Therefore according to the silicon atom the balanced equation is given below.
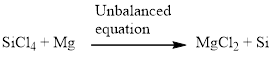
Next, balance the chlorine atom in the equation, there is four chlorine atom in the left side and two chlorine atom in the right side. Therefore 2 molecules of magnesium chloride is added to the right side of the reaction. When changing the magnesium chloride the number of magnesium is also changed therefore two molecules of magnesium is added to the left side of the reaction.
Now the equation is balanced, therefore the balanced equation is given below,
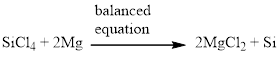
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- please help with synthesisarrow_forward10. Stereochemistry. Assign R/S stereochemistry for the chiral center indicated on the following compound. In order to recieve full credit, you MUST SHOW YOUR WORK! H₂N CI OH CI カー 11. () Stereochemistry. Draw all possible stereoisomers of the following compound. Assign R/S configurations for all stereoisomers and indicate the relationship between each as enantiomer, diastereomer, or meso. NH2 H HNH, -18arrow_forwardb) 8. Indicate whether the following carbocation rearrangements are likely to occur Please explain your rational using 10 words or less not likely to occur • The double bond is still in the Same position + Likely to oc occur WHY? -3 H3C Brave Chair Conformers. Draw the chair conformer of the following substituted cyclohexane. Peform a RING FLIP and indicate the most stable conformation and briefly explain why using 20 words or less. CI 2 -cobs ?? MUST INDICATE H -2 -2 Br EQ Cl OR AT Br H& most stable WHY? - 4arrow_forward
- CH 12 Conformational Analysis. Draw all 6 conformers (one above each letter) of the compound below looking down the indicated bond. Write the letter of the conformer with the HIGHEST and LOWEST in energies on the lines provided. NOTE: Conformer A MUST be the specific conformer of the structure as drawn below -4 NOT HOH OH 3 Conformer A: Br OH A Samo Br H 04 Br H H3 CH₂ H anti stagere Br CH clipsed H Brott H IV H MISSING 2 -2 B C D E F X 6 Conformer with HIGHEST ENERGY: 13. (1 structure LOWEST ENERGY: Nomenclature. a) Give the systematic (IUPAC) name structure. b) Draw the corresponding to this name. HINT: Do not forget to indicate stereochemistry when applicable. a) ८८ 2 "Br {t༐B,gt)-bemn€-nehpརི་ཚ༐lnoa Parent name (noname) 4 Bromo Sub = 2-methylethyl-4 Bromo nonane b) (3R,4S)-3-chloro-4-ethyl-2,7-dimethyloctane # -2 -2arrow_forwardin the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forward
- Molecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forwardIndicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





